Difference between revisions of "MIKE Flood to TUFLOW"
Ellis Symons (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (87 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=Introduction= | =Introduction= | ||
| − | This page provides guidance on a generalised method to convert a MIKE FLOOD model to a TUFLOW model format. MIKE | + | This page provides guidance on a generalised method to convert a MIKE FLOOD model to a TUFLOW model format. MIKE FLOOD is the top level program that couples MIKE21 (the MIKE 2D engine and program) with MIKE11 (the MIKE 1D engine and program). These programs are referenced when converting the relevant setup to TUFLOW format. These steps could therefore also be used for converting stand-alone MIKE21 or MIKE11 models to TUFLOW format.<br><br>If you have any suggestions to be included in these pages, please email <font color="blue"><u>support@tuflow.com</u></font>. |
==Requirements== | ==Requirements== | ||
| Line 9: | Line 7: | ||
* xsGenerator.exe (for MIKE11 conversion) | * xsGenerator.exe (for MIKE11 conversion) | ||
| − | MIKE Zero is required to extract data from the MIKE FLOOD model | + | MIKE Zero is required to extract data from the MIKE FLOOD model. The xsGenerator utility is freely available from the <u>[https://www.tuflow.com TUFLOW website]</u>. |
=Creating a TUFLOW Geometry Control File from MIKE21= | =Creating a TUFLOW Geometry Control File from MIKE21= | ||
| Line 34: | Line 32: | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
| − | Unlike TUFLOW, the grid cell size of the model in MIKE is determined directly by the input grid file. For more discussion on grid cell size and the differences in how MIKE and TUFLOW handle the underlying terrain please see the | + | Unlike TUFLOW, the grid cell size of the model in MIKE is determined directly by the input grid file. For more discussion on grid cell size and the differences in how MIKE and TUFLOW handle the underlying terrain please see the [[#Discussion|Discussion Section]] at the bottom of the page.<br><br>''Note: After grid conversion, it is important to perform checks that the ascii grid has been converted properly. This is best done in your preferred GIS package. '' |
| + | |||
| + | ===TUFLOW Commands=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The converted terrain grid can be read into the TGC using the following commands:<br><br><font color='green'><tt>! Set model terrain</tt></font><br><font color='blue'><tt>Set Zpts</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>''<Default Global Elevation Value>''</tt><br><font color='blue'><tt>Read Grid Zpts</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>..\model\grid\''<converted terrain file>''.asc</tt><br><br> | ||
==Converting Manning's== | ==Converting Manning's== | ||
| Line 46: | Line 48: | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
| − | More information on reading in manning’s grids into TUFLOW is provided in | + | More information on reading in manning’s grids into TUFLOW is provided in the <u>[https://docs.tuflow.com/classic-hpc/manual/latest/ TUFLOW Manual]</u>. |
| + | |||
| + | ===TUFLOW Commands=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The converted manning's grid can be read into the TGC using the following commands:<br><br><font color='green'><tt>! Set model roughness</tt></font><br><font color='blue'><tt>Set CnM</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>''<Default Manning's Value>''</tt><br><font color='blue'><tt>Read Grid CnM</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>..\model\grid\''<converted manning's file>''.asc</tt><br><br>If the manning's values are values of M, not n, then the following command needs to be specified in the TCF:<br><br><font color='green'><tt>! Set bed resistance type</tt></font><br><font color='blue'><tt>Bed Resistance Values</tt></font><font color='red'><tt> == </tt></font><tt>MANNINGS M</tt><br><br> | ||
==Model Domain== | ==Model Domain== | ||
| − | The model domain can be manually set by viewing the terrain and manning’s data in your preferred GIS program, or set using the Read Grid Location command.<br><br><font color='green'><tt>! Set model domain</tt></font><br><font color='blue'><tt>Read Grid Location</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> ..\model\grid\example_grid.asc<br> | + | The model domain can be manually set by viewing the terrain and manning’s data in your preferred GIS program, or set using the <b>Read Grid Location</b> command.<br><br><font color='green'><tt>! Set model domain</tt></font><br><font color='blue'><tt>Read Grid Location</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>..\model\grid\example_grid.asc</tt><br><br>Because the grid rotation is taken from the origin (lower left corner) of the domain, the resulting domain extent can end up unsuitable, as demonstrated by the image below (using a rotation of just 20 degrees). The <b>Read Grid Location</b> command is therefore best suited if there is no grid rotation. Other origin and orientation command methods are recommended when grid rotation is needed (e.g. <font color='blue'><tt>Read GIS Location</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>..\model\grs\2d_loc_001.shp</tt>).<br><br><b>LEFT: Rotation about Grid origin. RIGHT: Rotation about manually set Origin</b><br>[[File: Domain-rotation-atorigin-comparison.PNG|750px]] |
Grid rotation in the MIKE model can be determined using the following steps: | Grid rotation in the MIKE model can be determined using the following steps: | ||
| Line 60: | Line 66: | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
| − | <br>More information on setting the model domain extent and rotation in TUFLOW is provided in | + | ===TUFLOW Commands=== |
| + | |||
| + | The Domain in TUFLOW can now be set up in the TGC. Below is an example of how the Domain could be created, however there are several methods that could be used. The domain should always be checked by viewing the <b>dom_check</b> file. Be careful when translating a rotation from MIKE to TUFLOW, as they process the origin slightly differently.<br><br><font color='green'><tt>! Set model domain</tt></font><br><font color='blue'><tt>Origin</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>''<X>'', ''<Y>''</tt><br><font color='blue'><tt>Orientation Angle</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>''<angle_in_degrees_relative_to_east>''</tt><br><font color='blue'><tt>Grid Size (X, Y)</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>'' <X_length>'', ''<Y_length>''</tt> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br>More information on setting the model domain extent and rotation in TUFLOW is provided in the <u>[https://docs.tuflow.com/classic-hpc/manual/latest/ TUFLOW Manual]</u>. | ||
==TUFLOW Code Layer== | ==TUFLOW Code Layer== | ||
| − | The user can manually set the TUFLOW code layer by viewing the terrain data through their preferred GIS program. MIKE also uses a process of defining active cells by specifying a ‘Land’ elevation value. A ‘Land’ elevation value is defined in the .dsf2 grid file that specifies a value at which elevations equal to or greater than this value are considered ‘Land’ and will not be subject to possible wetting and drying. This value could be used as a guidance for producing a TUFLOW code layer. The 'Land' value can be found in <b>Custom Blocks</b>, the same location as grid rotation. Following the same steps as above in determining rotation the 'Land' value can be determined, this time looking at the fourth element value<br>[[File: MikeZero-Edit-CustomBlocks.PNG|350px|]] | + | The user can manually set the TUFLOW code layer by viewing the terrain data through their preferred GIS program. MIKE also uses a process of defining active cells by specifying a ‘Land’ elevation value. A ‘Land’ elevation value is defined in the .dsf2 grid file that specifies a value at which elevations equal to or greater than this value are considered ‘Land’ and will not be subject to possible wetting and drying. This value could be used as a guidance for producing a TUFLOW code layer. The 'Land' value can be found in <b>Custom Blocks</b>, the same location as grid rotation. Following the same steps as above in determining rotation, the 'Land' value can be determined, this time looking at the fourth element value.<br>[[File: MikeZero-Edit-CustomBlocks.PNG|350px|]] |
| − | ''Note: | + | ''Note: It is important to inspect the terrain data before use. Elevations in the .dfs2 grid may have been manually modified such that the area outside the flood extent has a constant ‘Land’ elevation.'' |
| + | |||
| + | ===TUFLOW Commands=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The following commands can be added to the TGC to read in a digitised Code layer:<br><br><font color='green'><tt>! Set model active cells</tt></font><br><font color='blue'><tt>Set Code</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>0</tt><br><font color='blue'><tt>Read GIS Code</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>..\model\gis\''<<nowiki>Code Layer</nowiki>>''.shp</tt><br><br> | ||
=Creating a TUFLOW Boundary Control File from MIKE21 and MIKE Flood= | =Creating a TUFLOW Boundary Control File from MIKE21 and MIKE Flood= | ||
| Line 88: | Line 102: | ||
<li> In excel convert these (j,k) coordinates to an absolute reference (X, Y) | <li> In excel convert these (j,k) coordinates to an absolute reference (X, Y) | ||
<ol> | <ol> | ||
| − | <li> | + | <li> From the converted terrain ascii grid ([[#Converting_Terrain|Section 2.1]] - Converting Terrain), copy <b>Cellsize</b>, <b>xllcorner</b>, and <b>yllcorner</b> values from the grid header into Excel |
<li> Copy your (j, k) values into Excel | <li> Copy your (j, k) values into Excel | ||
<li> Use the following formulas to convert your (j, k) values to (X, Y) | <li> Use the following formulas to convert your (j, k) values to (X, Y) | ||
| Line 96: | Line 110: | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
| + | ''Note: Grid rotation should also be considered when locating the X, Y coordinates, and the above method may need to be modified slightly to account for it. [[#Model_Domain|Section 2.3]] provides detail on determining the grid rotation angle.'' | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
| Line 104: | Line 119: | ||
* Viewing <b>Item</b> which corresponds to the boundary name<br>[[File: MIKE21-HP-Boundary-Names.PNG|750px|]] | * Viewing <b>Item</b> which corresponds to the boundary name<br>[[File: MIKE21-HP-Boundary-Names.PNG|750px|]] | ||
| − | The Upstream boundary can be digitised in TUFLOW as a 2d_bc (type | + | The Upstream boundary can be digitised in TUFLOW as a 2d_bc (type ‘QT’), or as a 2d_SA polygon. For more discussion on selecting an appropriate upstream boundary type, please see the [[#Discussion|Discussion Section]] at the bottom of the page. |
| + | |||
| + | ''Note: TUFLOW does not require pre-wetting of the upstream boundary. Terrain modifications and initial water level conditions are not required to be converted across to TUFLOW for these cases.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===TUFLOW Commands=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The boundaries can now be input into the TBC using the following commands: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <font color='green'><tt>! Set model boundaries</tt></font><br> | ||
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>Read GIS BC</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>..\model\gis\''<BC Boundary>''.shp</tt> <font color='green'><tt>! Upstream and / or Downstream Boundary</tt></font> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''or for SA polygons'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>Read GIS SA</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>..\model\gis\''<SA Boundary>''.shp</tt> <font color='green'><tt>! Upstream Boundary</tt></font><br><br> | ||
==Source Boundaries== | ==Source Boundaries== | ||
| Line 110: | Line 138: | ||
The location of source boundaries can be found in the MIKE21 control file (.m21) in the <b>Basic Parameters</b> >> <b>Source and Sink</b> tab. The location of the boundaries are specified as a point object using the local (j, k) coordinate system. These are required to be converted to absolute coordinates so an identical boundary location can be digitised in TUFLOW. The conversion process can be undertaken using identical steps as performed with converting upstream and downstream boundaries. | The location of source boundaries can be found in the MIKE21 control file (.m21) in the <b>Basic Parameters</b> >> <b>Source and Sink</b> tab. The location of the boundaries are specified as a point object using the local (j, k) coordinate system. These are required to be converted to absolute coordinates so an identical boundary location can be digitised in TUFLOW. The conversion process can be undertaken using identical steps as performed with converting upstream and downstream boundaries. | ||
| − | It is recommended that the source boundary point from MIKE be converted to a 2d_SA polygon in TUFLOW. The 2d_SA polygon should be enlarged to encompass a larger region such that it is able to apply flow to more than one cell. This is considered to give a more stable and accurate representation of flow distribution to the model. More information on how 2d_SA polygons distributes flow can be found in | + | It is recommended that the source boundary point from MIKE be converted to a 2d_SA polygon in TUFLOW. The 2d_SA polygon should be enlarged to encompass a larger region such that it is able to apply flow to more than one cell. This is considered to give a more stable and accurate representation of flow distribution to the model. More information on how 2d_SA polygons distributes flow can be found in the <u>[https://docs.tuflow.com/classic-hpc/manual/latest/ TUFLOW Manual]</u>. |
The name of the boundary can be found from <B>Hydrodynamic Parameters</b> >> <b>Source and Sink</b> tab.<br>[[File: MIKE21-HP-Source-Names.PNG|750px|]] | The name of the boundary can be found from <B>Hydrodynamic Parameters</b> >> <b>Source and Sink</b> tab.<br>[[File: MIKE21-HP-Source-Names.PNG|750px|]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===TUFLOW Command=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Source boundaries can now be input into the TBC using the following command: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <font color='green'><tt>! Set internal source boundaries</tt></font><br> | ||
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>Read GIS SA</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>..\model\gis\''<SA Boundary>''.shp</tt><br><br> | ||
==1D/2D Linking Boundaries== | ==1D/2D Linking Boundaries== | ||
| − | The location of the 1D / 2D boundaries can be found in the MIKE Flood control file (.couple) under the <b>Link Definitions</b> tab. The (X, Y) coordinates specify the vertices of a polyline that can be digitised in TUFLOW using either ‘SX’ or ‘HX’ connections.<br>[[File: MIKEFlood-Linkages.PNG|750px|]] | + | The location of the 1D / 2D boundaries can be found in the MIKE Flood control file (.couple) under the <b>Link Definitions</b> tab. The (X, Y) coordinates specify the vertices of a polyline that can be digitised in TUFLOW using either ‘SX’ or ‘HX’ connections. Link Type <b>Standard</b> is similar to 'SX' connections, <b>Lateral</b> to 'HX' connections and <b>River/Urban</b> is for connections from Mike Urban package.<br>[[File: MIKEFlood-Linkages.PNG|750px|]] |
| + | |||
| + | More information on 1D/2D linking in TUFLOW can be found in the <u>[https://docs.tuflow.com/classic-hpc/manual/latest/ TUFLOW Manual]</u>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===TUFLOW Command=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The 1D / 2D linking boundaries can now be input into the TBC using the following command: | ||
| − | + | <font color='green'><tt>! Set 1D/2D linking boundaries</tt></font><br> | |
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>Read GIS BC</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>..\model\gis\''<1D/2D boundary>''.shp</tt><br><br> | ||
| − | =Creating a Boundary | + | =Creating a Boundary Condition Database from MIKE= |
| − | A Boundary | + | A Boundary Condition Database (bc_dbase) consists of the values (time series or constant value) and the linking boundary names. The boundary names, constant values, and data source for time series, can be obtained from the steps outlined in: |
| − | * | + | * [[#Creating_a_TUFLOW_Boundary_Control_File_from_MIKE21_and_MIKE_Flood|Section 3]] - Creating a TUFLOW Boundary Condition File from MIKE21 and MIKE Flood |
| − | * | + | * [[#1D_Boundaries|Section 5.2]] – 1D Boundaries |
| + | The bc_dbase should be created in a comma delimited .csv file like the example shown below.<br>[[File: MIKE-bcdbase example.PNG]] | ||
==Converting DSF0 time series== | ==Converting DSF0 time series== | ||
| Line 136: | Line 179: | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
| − | The time series will need to be formatted so that the time column units are in hours. This can be done in MS Excel or equivalent. More information on setting up inflow boundaries | + | The time series will need to be formatted so that the time column units are in hours. This can be done in MS Excel or equivalent. More information on setting up inflow boundaries can be found in the <u>[https://docs.tuflow.com/classic-hpc/manual/latest/ TUFLOW Manual]</u>. |
=Creating an Estry Control File from MIKE11= | =Creating an Estry Control File from MIKE11= | ||
| Line 148: | Line 191: | ||
==1D Network Conversion (xsGenerator.exe Utility)== | ==1D Network Conversion (xsGenerator.exe Utility)== | ||
| − | To make the conversion of the MIKE11 1D network easier, the xsGenerator utility has been built to automate the bulk of the conversion. The xsGenerator.exe utility is freely available to download from the <u>[https://www.tuflow.com | + | To make the conversion of the MIKE11 1D network easier, the xsGenerator utility has been built to automate the bulk of the conversion. The xsGenerator.exe utility is freely available to download from the <u>[https://www.tuflow.com TUFLOW website]</u>. |
To undertake the automation, a number of files will be required as inputs: | To undertake the automation, a number of files will be required as inputs: | ||
* Projection.mif (or Header.mif) | * Projection.mif (or Header.mif) | ||
* The MIKE11 .nwk11 | * The MIKE11 .nwk11 | ||
| − | * The MIKE11 . | + | * The MIKE11 .hd11 |
* The MIKE11 exported <Cross_sections>.txt | * The MIKE11 exported <Cross_sections>.txt | ||
At this time, the utility is only able to output to .mif and this would need to be converted to .shp if required. | At this time, the utility is only able to output to .mif and this would need to be converted to .shp if required. | ||
| − | Cross | + | Cross sections from MIKE11 can be exported by following the steps below: |
<ol> | <ol> | ||
<li> Open MIKE Zero | <li> Open MIKE Zero | ||
| Line 169: | Line 212: | ||
After the conversion is complete it is important to check the output. Some key areas to check are: | After the conversion is complete it is important to check the output. Some key areas to check are: | ||
* The 1d_nwk.mif file appears to have created channels at reasonable locations | * The 1d_nwk.mif file appears to have created channels at reasonable locations | ||
| − | * The 1d_nwk.mif ‘Type’ attribute is correct (currently the utility will assign all channels to type ‘S’ (see below for checking for culverts in MIKE11) | + | * The 1d_nwk.mif ‘Type’ attribute is correct (currently the utility will assign all channels to type ‘S’ (see below for checking for culverts in MIKE11)) |
* The 1d_xs.mif file appears to be at reasonable locations (if the cross sections in MIKE11 didn’t have X,Y coordinates, then the equivalent 1d_xs cross sections can look strange) | * The 1d_xs.mif file appears to be at reasonable locations (if the cross sections in MIKE11 didn’t have X,Y coordinates, then the equivalent 1d_xs cross sections can look strange) | ||
** TUFLOW also does not require cross sections at embedded 1D/2D culverts, therefore cross sections at these locations can be deleted | ** TUFLOW also does not require cross sections at embedded 1D/2D culverts, therefore cross sections at these locations can be deleted | ||
| Line 180: | Line 223: | ||
<li> This will display the network spatially<br>[[File: MIKE11-nwk11-map.PNG]] | <li> This will display the network spatially<br>[[File: MIKE11-nwk11-map.PNG]] | ||
<li> To view the details, select <b>View</b> >> <b>Tabular View…</b> | <li> To view the details, select <b>View</b> >> <b>Tabular View…</b> | ||
| − | <li> From this screen you view information on <b>Structures</b> that you can use to populate attributes in the 1d_nwk TUFLOW layer<br>[[File: MIKE11-nwk11-tablular.PNG|750px]] | + | <li> From this screen you view information on <b>Structures</b> that you can use to populate attributes for any structures in the 1d_nwk TUFLOW layer<br>[[File: MIKE11-nwk11-tablular.PNG|750px]] |
</ol> | </ol> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===TUFLOW Commands=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The 1D network can now be read into the ECF using the following commands: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <font color='green'><tt>! Set model 1D network</tt></font><br> | ||
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>Read GIS Network</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>..\model\gis\''<1D Network>''.shp</tt><br> | ||
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>Read GIS Table Links</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>..\model\xs\''<1D Cross Sections>''.shp</tt> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Water Level Lines can also be used to view the 1D results in the 2D mapping. For more explanation on Water Level Lines, please see the <u>[https://docs.tuflow.com/classic-hpc/manual/latest/ TUFLOW Manual]</u>. The command to read in Water Level Lines is as follows: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <font color='green'><tt>! Read 1D Water Level Lines</tt></font><br> | ||
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>Read GIS WLL</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>..\model\gis\''<1D Water Level Lines>''.shp</tt><br><br> | ||
==1D Boundaries== | ==1D Boundaries== | ||
| Line 191: | Line 247: | ||
<li> This will display all 1D boundaries<br>[[File: MIKE11-bnd11.PNG]] | <li> This will display all 1D boundaries<br>[[File: MIKE11-bnd11.PNG]] | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
| − | Identifying the boundary types and values is as simple as reading the Boundary Type, TS Type, and File/Value. The only thing to be careful of is that 1D/2D linking boundaries are usually specified as Water Level and won’t need to be transferred across (1D/2D linking conversion has already been discussed in [[ | + | Identifying the boundary types and values is as simple as reading the Boundary Type, TS Type, and File/Value. The only thing to be careful of is that 1D/2D linking boundaries are usually specified as Water Level and won’t need to be transferred across (1D/2D linking conversion has already been discussed in [[#1D.2F2D_Linking_Boundaries|Section 3.3]] - 1D/2D Linking Boundaries). |
| + | |||
| + | ===TUFLOW Command=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The 1D boundaries can now be read into the ECF file using the following command: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <font color='green'><tt>! Set model 1D boundaries</tt></font><br> | ||
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>Read GIS BC</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>..\model\gis\''<1D Boundary>''.shp</tt><br><br> | ||
==1D Run Settings== | ==1D Run Settings== | ||
| − | The 1D run settings can be obtained from the .sim11 file. However it is recommended that appropriate run settings for TUFLOW be applied and direct | + | The 1D run settings can be obtained from the .sim11 file. However it is recommended that appropriate run settings for TUFLOW be applied and direct copy from MIKE is not necessary. |
| + | |||
| + | ===TUFLOW Commands=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The following commands can now written into the ECF to specify the Run Settings: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <font color='green'><tt>! Set 1D Run Settings</tt></font><br> | ||
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>Timestep</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>''<1D Timestep Interval in Seconds>''</tt><br> | ||
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>Output Interval (s)</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>''<1D Output Interval in Seconds>''</tt><br><br> | ||
=Creating a TUFLOW Control File from MIKE21= | =Creating a TUFLOW Control File from MIKE21= | ||
| − | == | + | The primary run setting to extract from the MIKE21 model is the duration of the simulation. This can be done by following the steps below: |
| + | <ol> | ||
| + | <li> Open MIKE Zero | ||
| + | <li> Open the .m21 file through <b>Open</b> (or drag and drop) | ||
| + | <li> Select the tab <b>Basic Parameters</b> >> <b>Simulation Period</b> | ||
| + | <li> You can obtain the start and end dates from this tab which need to be converted to hours for TUFLOW (in the screenshot below, the simulation duration is 3 hours)<br>[[File: MIKE21-Simulation-Period.PNG]] | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
| + | The 2D timestep should be set to an appropriate TUFLOW interval and not be copied directly from the MIKE21 model. It also up to the user to consider output types and time series Plot Output (PO) locations. More information on appropriate timestep intervals and map output types can be found in the <u>[https://docs.tuflow.com/classic-hpc/manual/latest/ TUFLOW Manual]</u>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===TUFLOW Commands=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The following commands can be written into the TCF. There are numerous commands and options that can be written into the TCF, however these are an example of the basic commands and parameters required to run a TUFLOW model. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <font color='green'><tt>! Set GIS format and Projection</tt></font><br> | ||
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>GIS Format</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>''<GIS File Format e.g. SHP or MIF>''</tt><br> | ||
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>SHP Projection</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>..\model\gis\''<Projection File>''.prj</tt><font color='green'><tt> ! If using SHP format</tt></font><br> | ||
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>MI Projection</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>..\model\gis\''<Projection File>''.mif</tt><font color='green'><tt> ! If using MI format</tt></font><br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <font color='green'><tt>! Set Model Control Files</tt></font><br> | ||
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>Geometry Control File</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>..\model\''<Converted TGC File>''.tgc</tt><br> | ||
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>BC Control File</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>..\model\''<Converted TBC File>''.tbc</tt><br> | ||
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>BC Database</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>..\bc_dbase\''<Converted bc_dbase File>''.csv</tt><br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <font color='green'><tt>! Set Simulation Controls</tt></font><br> | ||
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>Start Time</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>''<Model Start Time in hours>''</tt><br> | ||
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>End Time</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>''<Model End Time in hours>''</tt><br> | ||
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>Timestep</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>''<Model Timestep in seconds>''</tt><br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <font color='green'><tt>! Set Output Controls</tt></font><br> | ||
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>Log Folder</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>''<Log Folder location>''</tt><br> | ||
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>Output Folder</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>..\Results\''<Output Folder location>''</tt><br> | ||
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>Write Check Files</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>..\Check\''<Check Folder location>''\</tt><br> | ||
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>Map Output Data Types</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>''<Map Output Data Types e.g. d h V>''</tt><br> | ||
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>Start Map Output</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>''<Start Map Output Time in hours>''</tt><br> | ||
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>Map Output Interval</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>''<Map Output Interval in seconds>''</tt><br> | ||
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>Map Output Format</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>''<Map Output Format Types e.g. ASC XMDF>''</tt><br> | ||
| + | <font color='blue'><tt>Maximums and Minimums Only For Grids</tt></font> <font color='red'><tt>==</tt></font> <tt>ON</tt> <font color='green'><tt>! Writes maximums only for grid type output formats e.g. asc types</tt></font><br> | ||
| − | |||
| − | = | + | {{Tips Navigation |
| + | |uplink=[[Main_Page| Back to Main Page]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 10:17, 23 September 2024
Introduction
This page provides guidance on a generalised method to convert a MIKE FLOOD model to a TUFLOW model format. MIKE FLOOD is the top level program that couples MIKE21 (the MIKE 2D engine and program) with MIKE11 (the MIKE 1D engine and program). These programs are referenced when converting the relevant setup to TUFLOW format. These steps could therefore also be used for converting stand-alone MIKE21 or MIKE11 models to TUFLOW format.
If you have any suggestions to be included in these pages, please email support@tuflow.com.
Requirements
The following programs are required in the conversion process:
- MIKE Zero
- xsGenerator.exe (for MIKE11 conversion)
MIKE Zero is required to extract data from the MIKE FLOOD model. The xsGenerator utility is freely available from the TUFLOW website.
Creating a TUFLOW Geometry Control File from MIKE21
This section discusses how to extract geometry data from a MIKE21 model to populate the TUFLOW Geometry Control file (TGC). The TGC file defines the:
- Terrain elevation
- Manning's values
- Model domain
- Active cells
The MIKE21 (.m21) control file can be used to determine the specific geometry input files for the MIKE21 model. You can view the MIKE21 control file using MIKE Zero.
Converting Terrain
Like TUFLOW, MIKE uses a grid file to define the underlying terrain. MIKE uses its own grid format (.dsf2) as well as a local coordinate system. For these reasons, it needs to be converted into a format that TUFLOW can read as well as an absolute coordinate system.
The terrain .dfs2 grid can be converted through the MIKE Zero toolbox. This can be done through the following steps:
- Open the MIKE Zero program
- From the MIKE Zero shell select File >> New >> File
- On the MIKE Zero button select MIKE Zero Toolbox (.mzt). Click OK.
- Under the GIS dropdown, double click MIKE2GRD
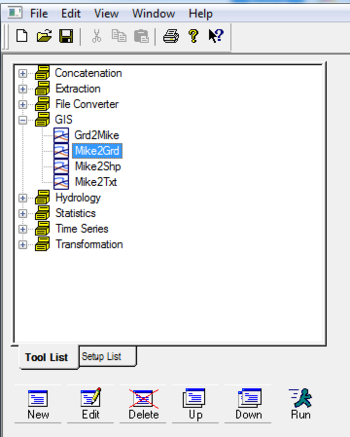
- Work through the steps being careful to specify an appropriate projection
- Before clicking Finish, ensure you have clicked Execute to run the conversion

- This should produce an ascii file that can be directly read by TUFLOW
Unlike TUFLOW, the grid cell size of the model in MIKE is determined directly by the input grid file. For more discussion on grid cell size and the differences in how MIKE and TUFLOW handle the underlying terrain please see the Discussion Section at the bottom of the page.
Note: After grid conversion, it is important to perform checks that the ascii grid has been converted properly. This is best done in your preferred GIS package.
TUFLOW Commands
The converted terrain grid can be read into the TGC using the following commands:
! Set model terrain
Set Zpts == <Default Global Elevation Value>
Read Grid Zpts == ..\model\grid\<converted terrain file>.asc
Converting Manning's
Follow the same steps as converting terrain to convert the manning’s grid using the Mike Zero Toolbox. It is important to identify the manning’s value type (M or n) so that it can be correctly read into TUFLOW. This can be done by viewing the .dfs2 grid in Mike Zero following the steps below:
- Open the MIKE Zero program
- Open the .dfs2 file through Open (or drag and drop)
- From the toolbar select Edit >> Items…
- The value should be listed in Type
More information on reading in manning’s grids into TUFLOW is provided in the TUFLOW Manual.
TUFLOW Commands
The converted manning's grid can be read into the TGC using the following commands:
! Set model roughness
Set CnM == <Default Manning's Value>
Read Grid CnM == ..\model\grid\<converted manning's file>.asc
If the manning's values are values of M, not n, then the following command needs to be specified in the TCF:
! Set bed resistance type
Bed Resistance Values == MANNINGS M
Model Domain
The model domain can be manually set by viewing the terrain and manning’s data in your preferred GIS program, or set using the Read Grid Location command.
! Set model domain
Read Grid Location == ..\model\grid\example_grid.asc
Because the grid rotation is taken from the origin (lower left corner) of the domain, the resulting domain extent can end up unsuitable, as demonstrated by the image below (using a rotation of just 20 degrees). The Read Grid Location command is therefore best suited if there is no grid rotation. Other origin and orientation command methods are recommended when grid rotation is needed (e.g. Read GIS Location == ..\model\grs\2d_loc_001.shp).
LEFT: Rotation about Grid origin. RIGHT: Rotation about manually set Origin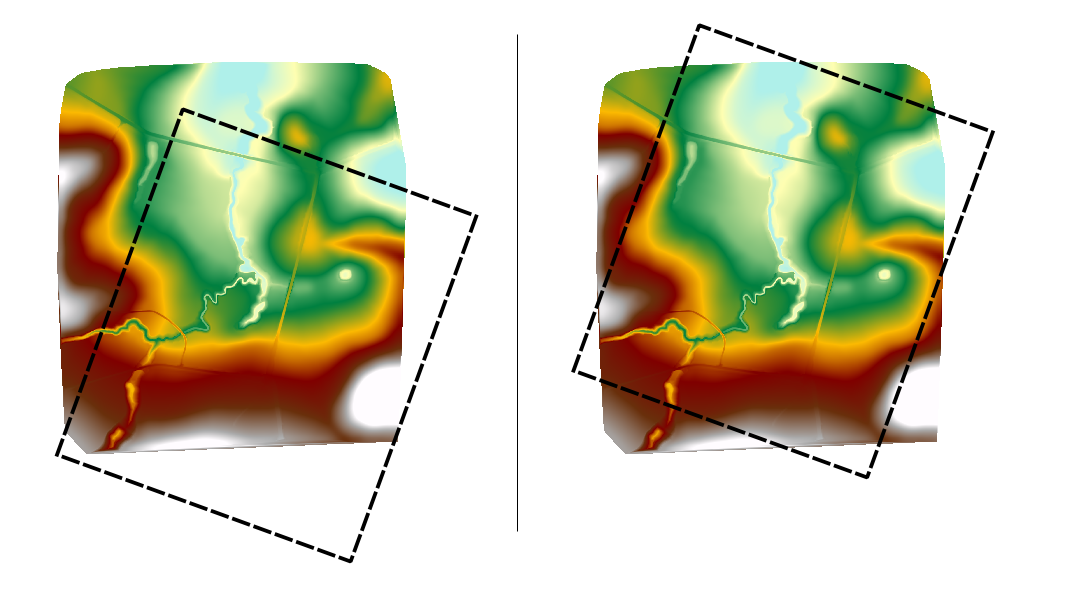
Grid rotation in the MIKE model can be determined using the following steps:
- Open the MIKE Zero program
- Open the .dfs2 elevation grid through Open (or drag and drop)
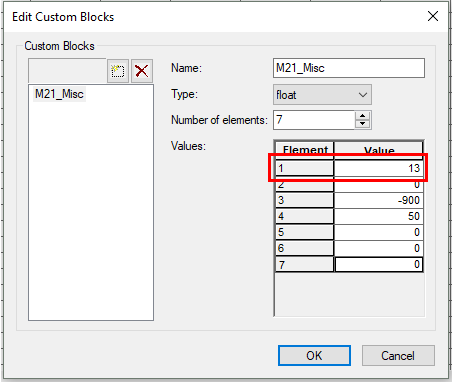
- From the toolbar select Edit >> Custom Blocks…
- The first element value is the rotation value (orientation at origin relative to true north)
TUFLOW Commands
The Domain in TUFLOW can now be set up in the TGC. Below is an example of how the Domain could be created, however there are several methods that could be used. The domain should always be checked by viewing the dom_check file. Be careful when translating a rotation from MIKE to TUFLOW, as they process the origin slightly differently.
! Set model domain
Origin == <X>, <Y>
Orientation Angle == <angle_in_degrees_relative_to_east>
Grid Size (X, Y) == <X_length>, <Y_length>
More information on setting the model domain extent and rotation in TUFLOW is provided in the TUFLOW Manual.
TUFLOW Code Layer
The user can manually set the TUFLOW code layer by viewing the terrain data through their preferred GIS program. MIKE also uses a process of defining active cells by specifying a ‘Land’ elevation value. A ‘Land’ elevation value is defined in the .dsf2 grid file that specifies a value at which elevations equal to or greater than this value are considered ‘Land’ and will not be subject to possible wetting and drying. This value could be used as a guidance for producing a TUFLOW code layer. The 'Land' value can be found in Custom Blocks, the same location as grid rotation. Following the same steps as above in determining rotation, the 'Land' value can be determined, this time looking at the fourth element value.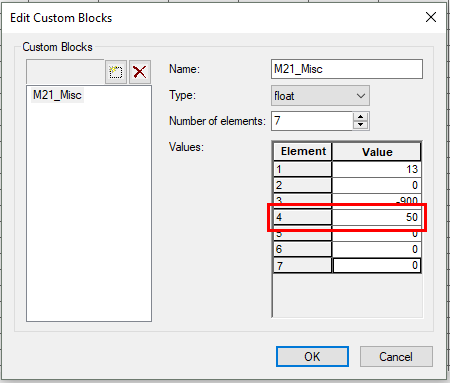
Note: It is important to inspect the terrain data before use. Elevations in the .dfs2 grid may have been manually modified such that the area outside the flood extent has a constant ‘Land’ elevation.
TUFLOW Commands
The following commands can be added to the TGC to read in a digitised Code layer:
! Set model active cells
Set Code == 0
Read GIS Code == ..\model\gis\<Code Layer>.shp
Creating a TUFLOW Boundary Control File from MIKE21 and MIKE Flood
This section discusses how to extract data from a MIKE model to populate the TUFLOW Boundary Control file (TBC). The TBC file defines the:
- Downstream boundary
- Inflow locations
- 1D/2D linking
Upstream and Downstream Boundaries
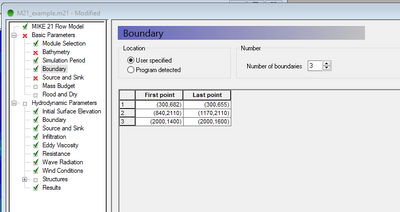
The location of upstream and downstream boundaries can be found in the MIKE21 control file (.m21) in the Basic Parameters >> Boundary tab. The location of the boundaries are specified as a line object using the start and end vertices in the local (j, k) coordinate system. These are required to be converted to absolute coordinates so an identical boundary location can be digitised in TUFLOW. This can be done in MS Excel using the following steps:
- Identify boundary locations
- In excel convert these (j,k) coordinates to an absolute reference (X, Y)
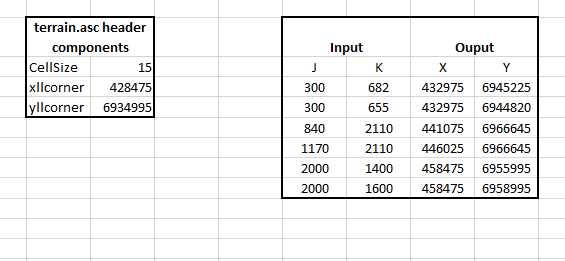
- From the converted terrain ascii grid (Section 2.1 - Converting Terrain), copy Cellsize, xllcorner, and yllcorner values from the grid header into Excel
- Copy your (j, k) values into Excel
- Use the following formulas to convert your (j, k) values to (X, Y)
Note: Grid rotation should also be considered when locating the X, Y coordinates, and the above method may need to be modified slightly to account for it. Section 2.3 provides detail on determining the grid rotation angle.
The type of the boundary is defined in the Hydrodynamic Parameters >> Boundary tab. This tab specifies whether the boundary is ‘Flux’ (QT), ‘Level’ (HT), or ‘Rating Curve’ (HQ), as well as whether the data is a time series (type 0 data file) or constant.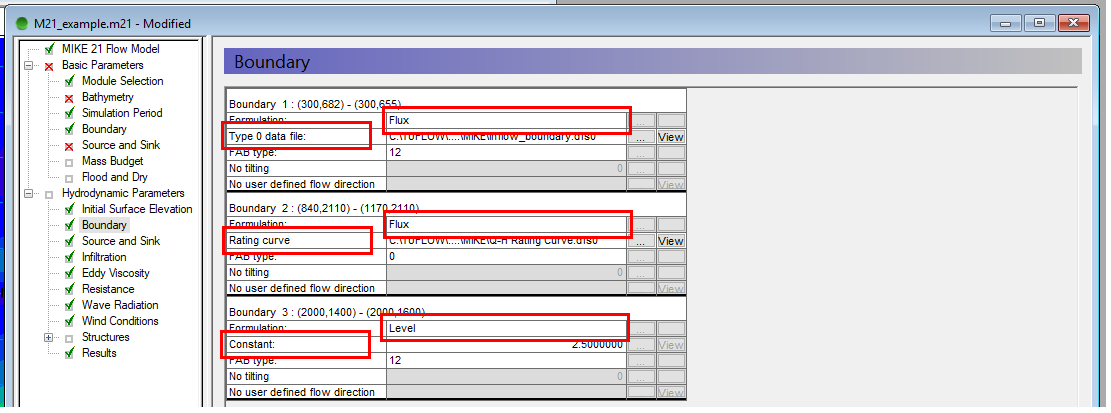
The name of the boundary can be found following the below steps:
The Upstream boundary can be digitised in TUFLOW as a 2d_bc (type ‘QT’), or as a 2d_SA polygon. For more discussion on selecting an appropriate upstream boundary type, please see the Discussion Section at the bottom of the page.
Note: TUFLOW does not require pre-wetting of the upstream boundary. Terrain modifications and initial water level conditions are not required to be converted across to TUFLOW for these cases.
TUFLOW Commands
The boundaries can now be input into the TBC using the following commands:
! Set model boundaries
Read GIS BC == ..\model\gis\<BC Boundary>.shp ! Upstream and / or Downstream Boundary
or for SA polygons
Read GIS SA == ..\model\gis\<SA Boundary>.shp ! Upstream Boundary
Source Boundaries
The location of source boundaries can be found in the MIKE21 control file (.m21) in the Basic Parameters >> Source and Sink tab. The location of the boundaries are specified as a point object using the local (j, k) coordinate system. These are required to be converted to absolute coordinates so an identical boundary location can be digitised in TUFLOW. The conversion process can be undertaken using identical steps as performed with converting upstream and downstream boundaries.
It is recommended that the source boundary point from MIKE be converted to a 2d_SA polygon in TUFLOW. The 2d_SA polygon should be enlarged to encompass a larger region such that it is able to apply flow to more than one cell. This is considered to give a more stable and accurate representation of flow distribution to the model. More information on how 2d_SA polygons distributes flow can be found in the TUFLOW Manual.
The name of the boundary can be found from Hydrodynamic Parameters >> Source and Sink tab.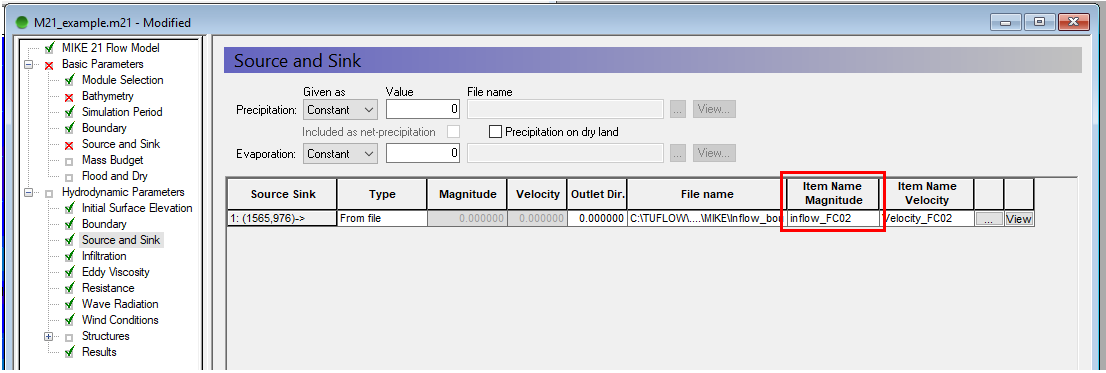
TUFLOW Command
The Source boundaries can now be input into the TBC using the following command:
! Set internal source boundaries
Read GIS SA == ..\model\gis\<SA Boundary>.shp
1D/2D Linking Boundaries
The location of the 1D / 2D boundaries can be found in the MIKE Flood control file (.couple) under the Link Definitions tab. The (X, Y) coordinates specify the vertices of a polyline that can be digitised in TUFLOW using either ‘SX’ or ‘HX’ connections. Link Type Standard is similar to 'SX' connections, Lateral to 'HX' connections and River/Urban is for connections from Mike Urban package.
More information on 1D/2D linking in TUFLOW can be found in the TUFLOW Manual.
TUFLOW Command
The 1D / 2D linking boundaries can now be input into the TBC using the following command:
! Set 1D/2D linking boundaries
Read GIS BC == ..\model\gis\<1D/2D boundary>.shp
Creating a Boundary Condition Database from MIKE
A Boundary Condition Database (bc_dbase) consists of the values (time series or constant value) and the linking boundary names. The boundary names, constant values, and data source for time series, can be obtained from the steps outlined in:
- Section 3 - Creating a TUFLOW Boundary Condition File from MIKE21 and MIKE Flood
- Section 5.2 – 1D Boundaries
The bc_dbase should be created in a comma delimited .csv file like the example shown below.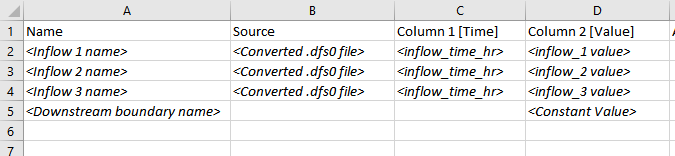
Converting DSF0 time series
Time series values need to be extracted from MIKE time series files (.dfs0). This can be done following the steps below:
- Open the MIKE Zero program
- Open the .dfs0 file through Open (or drag and drop)
- Select File >> Export to ASCII…
- This will export the time series data to a text based format
The time series will need to be formatted so that the time column units are in hours. This can be done in MS Excel or equivalent. More information on setting up inflow boundaries can be found in the TUFLOW Manual.
Creating an Estry Control File from MIKE11
This section discusses how to extract data from a MIKE11 model to create an Estry Control File (ECF). An ECF file defines the:
- 1D network – Channels, structures
- 1D cross sections
- 1D boundaries
- 1D run settings
1D Network Conversion (xsGenerator.exe Utility)
To make the conversion of the MIKE11 1D network easier, the xsGenerator utility has been built to automate the bulk of the conversion. The xsGenerator.exe utility is freely available to download from the TUFLOW website.
To undertake the automation, a number of files will be required as inputs:
- Projection.mif (or Header.mif)
- The MIKE11 .nwk11
- The MIKE11 .hd11
- The MIKE11 exported <Cross_sections>.txt
At this time, the utility is only able to output to .mif and this would need to be converted to .shp if required.
Cross sections from MIKE11 can be exported by following the steps below:
- Open MIKE Zero
- Open the .xns11 through Open (or drag and drop)
- Select File >> Export All Sections >> Export Raw Data…
- Save the cross sections out as a .txt file
The final step is to convert the network data into TUFLOW format. This can be done by creating a batch file to run the utility. Below is an example of the arguments used to convert the MIKE11 network. Documentation on the utility can be found on the xsGenerator wiki page
xsGenerator.exe -N -m11 Projection.mif XS_example.txt HD_example.hd11 M11_example.nwk11.
After the conversion is complete it is important to check the output. Some key areas to check are:
- The 1d_nwk.mif file appears to have created channels at reasonable locations
- The 1d_nwk.mif ‘Type’ attribute is correct (currently the utility will assign all channels to type ‘S’ (see below for checking for culverts in MIKE11))
- The 1d_xs.mif file appears to be at reasonable locations (if the cross sections in MIKE11 didn’t have X,Y coordinates, then the equivalent 1d_xs cross sections can look strange)
- TUFLOW also does not require cross sections at embedded 1D/2D culverts, therefore cross sections at these locations can be deleted
- The created cross section .csv files are reasonable (geometry and manning’s values)
The following steps describe how to inspect channel locations and types in MIKE11 for the purpose of checking the utility output:
- Open MIKE Zero
- Open the .nwk11 file through Open (or drag and drop)
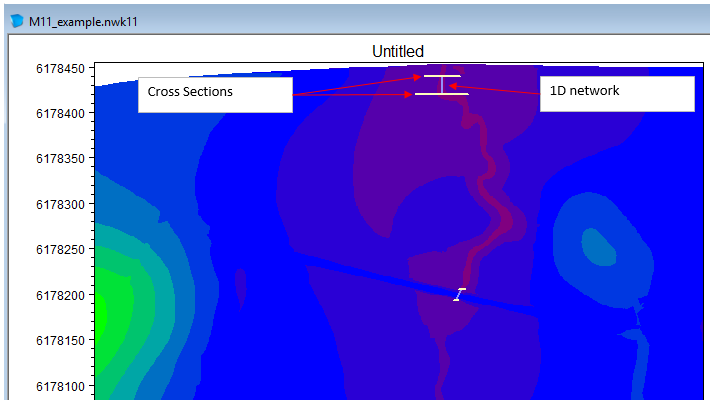
- This will display the network spatially
- To view the details, select View >> Tabular View…
- From this screen you view information on Structures that you can use to populate attributes for any structures in the 1d_nwk TUFLOW layer
TUFLOW Commands
The 1D network can now be read into the ECF using the following commands:
! Set model 1D network
Read GIS Network == ..\model\gis\<1D Network>.shp
Read GIS Table Links == ..\model\xs\<1D Cross Sections>.shp
Water Level Lines can also be used to view the 1D results in the 2D mapping. For more explanation on Water Level Lines, please see the TUFLOW Manual. The command to read in Water Level Lines is as follows:
! Read 1D Water Level Lines
Read GIS WLL == ..\model\gis\<1D Water Level Lines>.shp
1D Boundaries
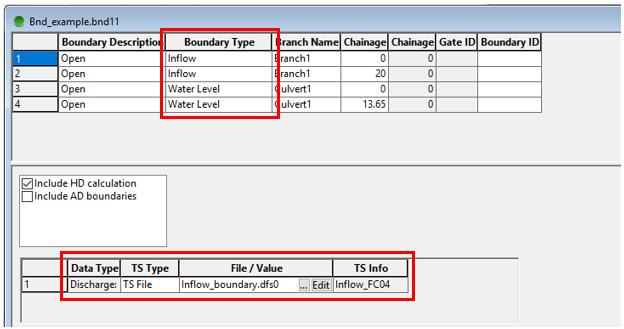
The following steps will help identify the types of 1D boundaries and the attributes used in MIKE11 for transfer to TUFLOW:
- Open MIKE Zero
- Open the .bnd11 file through Open (or drag and drop)
- This will display all 1D boundaries
Identifying the boundary types and values is as simple as reading the Boundary Type, TS Type, and File/Value. The only thing to be careful of is that 1D/2D linking boundaries are usually specified as Water Level and won’t need to be transferred across (1D/2D linking conversion has already been discussed in Section 3.3 - 1D/2D Linking Boundaries).
TUFLOW Command
The 1D boundaries can now be read into the ECF file using the following command:
! Set model 1D boundaries
Read GIS BC == ..\model\gis\<1D Boundary>.shp
1D Run Settings
The 1D run settings can be obtained from the .sim11 file. However it is recommended that appropriate run settings for TUFLOW be applied and direct copy from MIKE is not necessary.
TUFLOW Commands
The following commands can now written into the ECF to specify the Run Settings:
! Set 1D Run Settings
Timestep == <1D Timestep Interval in Seconds>
Output Interval (s) == <1D Output Interval in Seconds>
Creating a TUFLOW Control File from MIKE21
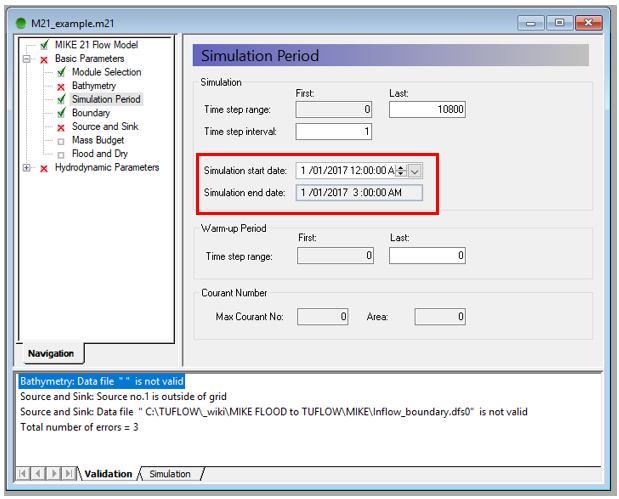
The primary run setting to extract from the MIKE21 model is the duration of the simulation. This can be done by following the steps below:
- Open MIKE Zero
- Open the .m21 file through Open (or drag and drop)
- Select the tab Basic Parameters >> Simulation Period
- You can obtain the start and end dates from this tab which need to be converted to hours for TUFLOW (in the screenshot below, the simulation duration is 3 hours)
The 2D timestep should be set to an appropriate TUFLOW interval and not be copied directly from the MIKE21 model. It also up to the user to consider output types and time series Plot Output (PO) locations. More information on appropriate timestep intervals and map output types can be found in the TUFLOW Manual.
TUFLOW Commands
The following commands can be written into the TCF. There are numerous commands and options that can be written into the TCF, however these are an example of the basic commands and parameters required to run a TUFLOW model.
! Set GIS format and Projection
GIS Format == <GIS File Format e.g. SHP or MIF>
SHP Projection == ..\model\gis\<Projection File>.prj ! If using SHP format
MI Projection == ..\model\gis\<Projection File>.mif ! If using MI format
! Set Model Control Files
Geometry Control File == ..\model\<Converted TGC File>.tgc
BC Control File == ..\model\<Converted TBC File>.tbc
BC Database == ..\bc_dbase\<Converted bc_dbase File>.csv
! Set Simulation Controls
Start Time == <Model Start Time in hours>
End Time == <Model End Time in hours>
Timestep == <Model Timestep in seconds>
! Set Output Controls
Log Folder == <Log Folder location>
Output Folder == ..\Results\<Output Folder location>
Write Check Files == ..\Check\<Check Folder location>\
Map Output Data Types == <Map Output Data Types e.g. d h V>
Start Map Output == <Start Map Output Time in hours>
Map Output Interval == <Map Output Interval in seconds>
Map Output Format == <Map Output Format Types e.g. ASC XMDF>
Maximums and Minimums Only For Grids == ON ! Writes maximums only for grid type output formats e.g. asc types
| Up |
|---|