FM Tute M01 QGIS 1D2D Banks: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Content deleted Content added
Andrew.Sims (talk | contribs) Created page with "=Method= <li>Import in an empty 2d_bc_empty.shp layer from within the TUFLOW\model\gis\empty folder and save as 2d_bc_FMT_M01_HX_001.gis</li> <li>Open the 1D_2D_HX_Links.shp G..." |
Tuflowduncan (talk | contribs) |
||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| ⚫ | |||
=Introduction= |
|||
In this section we will define the bank elevations of the watercourse. These are the elevations of the 1D/2D boundary cells that link the 1D Flood Modeller watercourse to the 2D TUFLOW floodplain.<br> |
|||
Note that it is these cell elevations that determine whether water spills from the 1D Flood Modeller domain into the 2D TUFLOW domain. The bank elevations of the Flood Modeller 1D cross-sections do not control the spill. |
|||
=Method= |
=Method= |
||
<li>Import in an empty |
<li>Import in an empty <b>2d_bc_empty_P.shp</b> layer from within the FMT_tutorial\FMT_M01\TUFLOW\model\gis\empty folder.</li> |
||
<li>Save the layer as <b>2d_bc_FMT_M01_HX_001_P.shp</b> in the FMT_tutorial\FMT_M01\TUFLOW\model\gis folder. </li> |
|||
<li>Open the |
<li>Open the <b>1D_2D_Points_P.shp</b> GIS layer from Module_Data\Module_01\gis folder. Select all objects from within this layer, copy and paste into <b>2d_bc_FMT_M01_HX_001_P.SHP </b>. </li> |
||
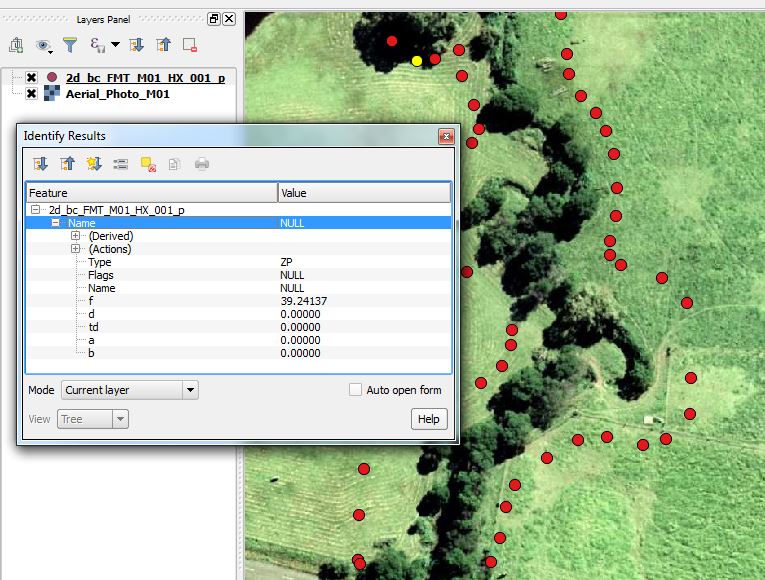
<li>Interrogate one of the lines running along the banks of the watercourse. These lines are the 1D/2D boundary links and have been assigned a type ‘HX’.</li> |
|||
<li>Interrogate one of the |
<li>Interrogate one of the digitised points and inspect the attributes. The ‘type’ attribute is ‘ZP’ to denote that it is a z-point which will define the elevation on the banks. The ‘f’ attribute is the elevation of the bank link in mAOD. </li> |
||
<li>Now add the layer <b>2d_bc_FMT_M01_HX_001_L.SHP</b> from the '''FMT_tutorial\FMT_M01\TUFLOW\model\gis''' folder created in the previous step. Note that all the 'ZP' points created in the layer <b>2d_bc_FMT_M01_HX_001_P.SHP</b> are snapped to vertices of the layer <b>2d_bc_FMT_M01_HX_001_L.SHP</b>. This is because these two layers work together to define the bank locations and crest elevations. The layer <b>2d_bc_FMT_M01_HX_001_L.SHP</b> defines the location and the layer <b>2d_bc_FMT_HX_001_P.SHP</b> defines the elevations. |
|||
In the figure below, the water level is calculated in Flood Modeller at the nodes FC01.16, FC01.15 and FC01.14. These water levels are linearly interpolated along the lengths of the HX line on both left and right banks of the watercourse. When the water level exceeds the ZC elevation of the boundary cell, water is able to flow on the the TUFLOW 2D floodplain. <br> |
|||
<br> |
<br> |
||
<li>Note that where there are junctions within the Flood Modeller 1D model (i.e. at structures), both the upstream and downstream nodes are connected to TUFLOW. The HX lines are broken between the nodes. This is a requirement of a linked Flood Modeller – TUFLOW model. </li> |
|||
In the figure below, the HX lines are broken between FC01.35 and FC01.34 as a culvert is located between these nodes. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
[[File:FMT_1D2D_Banks.JPG|600px]] |
|||
<li>The CN and HX lines between nodes FC02.06 and FC02.01d along the tributary have not been digitised. Digitise these lines to connect the nodes to the 2D domain. The figure below shows how the nodes are connected at the confluence. Note that all Flood Modeller nodes at the junction are present within the 1d_x1D_nodes layer, and are connected to the 2D domain. The HX lines are broken around the junction. </li> |
|||
<br> |
|||
<li>Save the file.</li> |
|||
<li>Once all the CN and HX lines have been digitised along the tributary, save the file and import into TUFLOW.</li> |
|||
<div style="background-color: #D6E9E0; margin: 20px; text-align: center; |
|||
{| class="wikitable" |
|||
border: 5px solid #1ABDC9"> |
|||
! style="background-color:#005581; color:white;"| The digitised direction of the HX and CN lines is not important. The CN lines however should be digitised approximately perpendicular to the direction of flow. Two CN lines are digitised for each node and connected to the HX boundary lines along the left and right banks. The HX boundary lines should be digitised along the top of each bank such that the width between the lines approximately correlates to the width of the 1D channel. |
|||
<p style="font-weight: bold; color: #E20177">Key Tip!</p> |
|||
|} |
|||
<p> The bank (1D/2D boundary) elevations may also be defined using a 2d_zsh layer or other 3D breakline layer. The advantage of using a 2d_bc layer is it ensures the boundary cell elevations are raised and not that of adjacent cells. </p> |
|||
</div> |
|||
Please return to the [[Flood_Modeller_Tutorial_Module01#Deactivate_2D_cells|Flood Modeller Tutorial Model]]. |
|||
</ol> |
|||
Please return to the Flood Modeller Tutorial Model module 1 page [[Flood_Modeller_Tutorial_Module01#Define_Bank_Elevations|here]]. |
|||
Latest revision as of 23:24, 7 December 2018
- Import in an empty 2d_bc_empty_P.shp layer from within the FMT_tutorial\FMT_M01\TUFLOW\model\gis\empty folder.
- Save the layer as 2d_bc_FMT_M01_HX_001_P.shp in the FMT_tutorial\FMT_M01\TUFLOW\model\gis folder.
- Open the 1D_2D_Points_P.shp GIS layer from Module_Data\Module_01\gis folder. Select all objects from within this layer, copy and paste into 2d_bc_FMT_M01_HX_001_P.SHP .
- Interrogate one of the digitised points and inspect the attributes. The ‘type’ attribute is ‘ZP’ to denote that it is a z-point which will define the elevation on the banks. The ‘f’ attribute is the elevation of the bank link in mAOD.
- Now add the layer 2d_bc_FMT_M01_HX_001_L.SHP from the FMT_tutorial\FMT_M01\TUFLOW\model\gis folder created in the previous step. Note that all the 'ZP' points created in the layer 2d_bc_FMT_M01_HX_001_P.SHP are snapped to vertices of the layer 2d_bc_FMT_M01_HX_001_L.SHP. This is because these two layers work together to define the bank locations and crest elevations. The layer 2d_bc_FMT_M01_HX_001_L.SHP defines the location and the layer 2d_bc_FMT_HX_001_P.SHP defines the elevations.
- Save the file.
Introduction
In this section we will define the bank elevations of the watercourse. These are the elevations of the 1D/2D boundary cells that link the 1D Flood Modeller watercourse to the 2D TUFLOW floodplain.
Note that it is these cell elevations that determine whether water spills from the 1D Flood Modeller domain into the 2D TUFLOW domain. The bank elevations of the Flood Modeller 1D cross-sections do not control the spill.
Method
Key Tip!
The bank (1D/2D boundary) elevations may also be defined using a 2d_zsh layer or other 3D breakline layer. The advantage of using a 2d_bc layer is it ensures the boundary cell elevations are raised and not that of adjacent cells.
Please return to the Flood Modeller Tutorial Model.