Talk:QGIS Tips: Difference between revisions
| (11 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
How to Update a Column (Equivalent of MapInfo Update Column) |
== How to Update a Column (Equivalent of MapInfo Update Column) == |
||
[[QGIS_Update_Column_Values | This user contributed tip can now be found here.]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
[[QGIS_Extract_CrossSections | This user contributed tip can now be found here]] |
|||
To quickly enter the "f" (multiplication factor applied to the boundary values) attribute for all CN type boundaries |
|||
== Plot grid elevation profiles== |
|||
[[QGIS_Profile_Tool | This user contributed tip can now be found here.]] |
|||
== Alternate method for generating grid from points == |
|||
1. Open Attribute Table |
|||
Tested on QGIS 1.8.<br> |
|||
2. Select all CN attributes, this can be achieved if you sort by type so that all CN attributes are grouped,alternatively, for more complex situations, use the Advanced Search tool in the bottom right. This allows you to select using an SQL Query |
|||
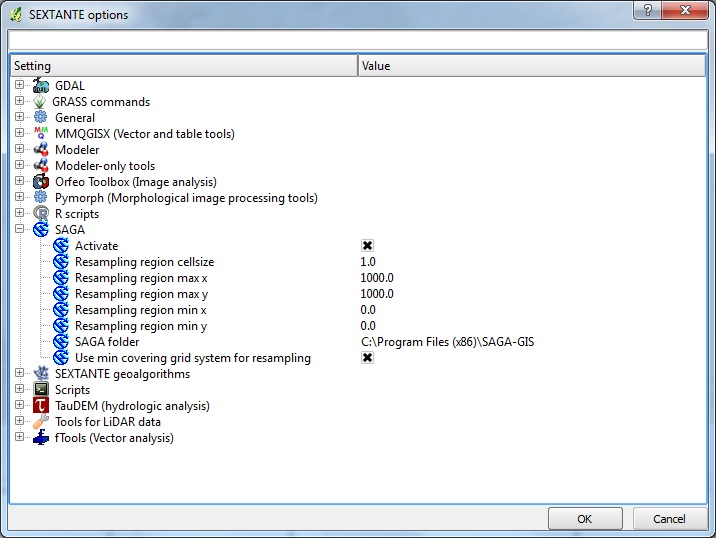
Install the Sextante plugin, this is a useful tool that incorporates the modules from many other open source GIS packages into Quantum. You will also need to install Saga and set the path of the Saga executable in the Sextante options and configuration menu (under analysis in QGIS). |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
3. From the attribute table, open the field calculator (you need to be editing to open the field calculator) |
|||
The Saga modules should now all be available in the Sextante Toolbox.<br> |
|||
4. Ensure that "Only update selected features" is turned on, and set the "Update existing field" to "f" |
|||
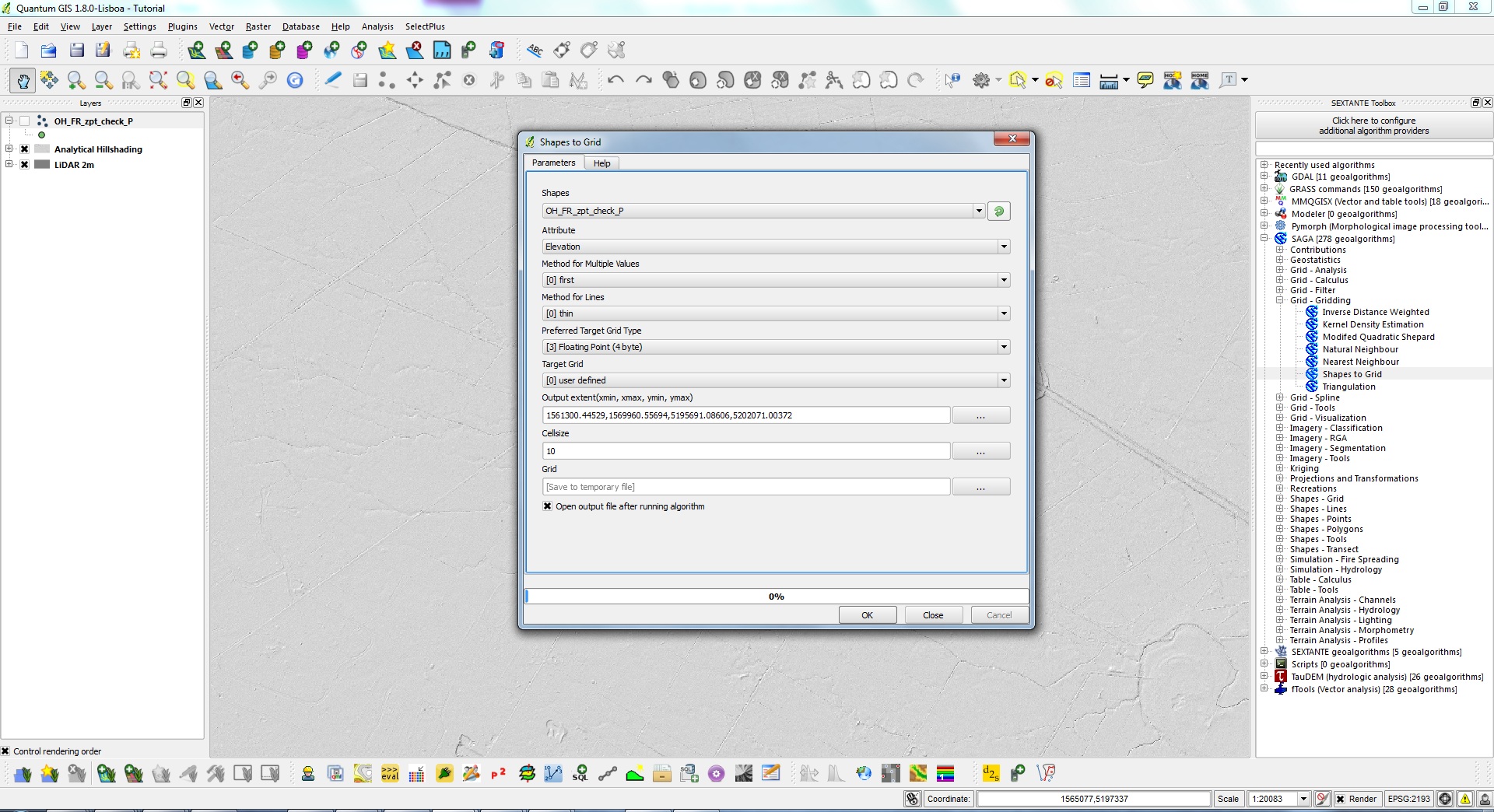
Load the Zpt file, in the Sextante toolbox select the ''Saga >>> Grid - Gridding >>> Shapes to Grid'' module. Fill out the appropriate options,<br> |
|||
*'''attribute''' should be set as elevation, |
|||
*'''target grid''' is user defined, |
|||
*'''output extent''' you must click the three dots on the right hand side and select your point file, this will ensure that your grid has the same extent as point file, |
|||
*'''cellsize''' I set the cell size to the same size as the grid used in Tuflow. |
|||
For more advanced options check out the other gridding modules that Saga (and Grass) offer. If you need to interpolate between points, there are multiple options availableoptions such as Tin, Kriging, Spline etc |
|||
5. Type "1" into the "Field calculator expression" box and hit "OK". Note, if you want to insert a string such as 'S' you need to enter it with the inverted comma. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
[[File:QGIS_Points_to_Grid.jpg]] |
|||
Done! |
|||
You can also use the field calculator for more advanced tasks, for example when naming the Source attribute for XS, the expression |
|||
'XSName'||rownum*50-50||'.csv' **NOTE** Do not copy and paste the expression to the left into QGiS - it has to be typed within the QGIS interfac. Do not type the "||" character either, at the time of writing this operator has to be selected from the available operators in the field calculator. |
|||
will generate in the source column: |
|||
XSName0.csv |
|||
XSName50.csv ...etc |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
== Quickly identify top of levees/embankments as Zln == |
|||
To use QGIS to extract cross sections from your DEM: |
|||
The aim of this tip is to show you how you can get the maximum elvations for you levee/embankment. |
|||
1. Draw your cross sections using the Tuflow 1d_xs file, be sure to fill in the source column. |
|||
Install the Sextante plugin for QGIS - See "Alternative method for generating grid from points ". <br> |
|||
2. Install the QGIS plug-in "profile from line" (note you may also need to install shapely - see [http://osgeo-org.1560.n6.nabble.com/plugin-profile-from-line-td4133320.html]). |
|||
Draw a line along the top of your levee/embankment. <br> |
|||
3. Run the plugin, it is pretty self explanatory, select your cross sections and dem, choose a suitable sampling interval. |
|||
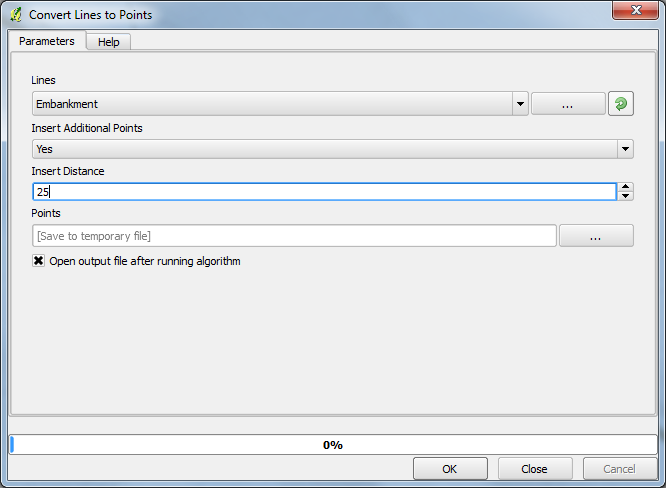
Select the ''Saga >>> Shapes - Points >>> Convert Lines to Points'' module, fill in as required... <br> |
|||
The '''Insert Distance''' option specifies the maximum distance between lines Save a copy of the shape file so you have two point files that are the same. |
|||
4. Upon running the plugin, QGIGS will add a new points file to the workspace, save this as a .csv. This file will contain the source of every cross section as well as the corresponding chainages and elevations. |
|||
[[File:QGiS_LinesToPoints.png]] |
|||
5. To split this data into individual .csv files in a format that tuflow can read in, download [[File:XSExtractor.xls]] |
|||
6. Follow the instructions in the spreadsheet, after exporting to individual worksheets use the Tuflow "Export Entire Workbook to csv" to obtain all the cross sections in a tuflow format. |
|||
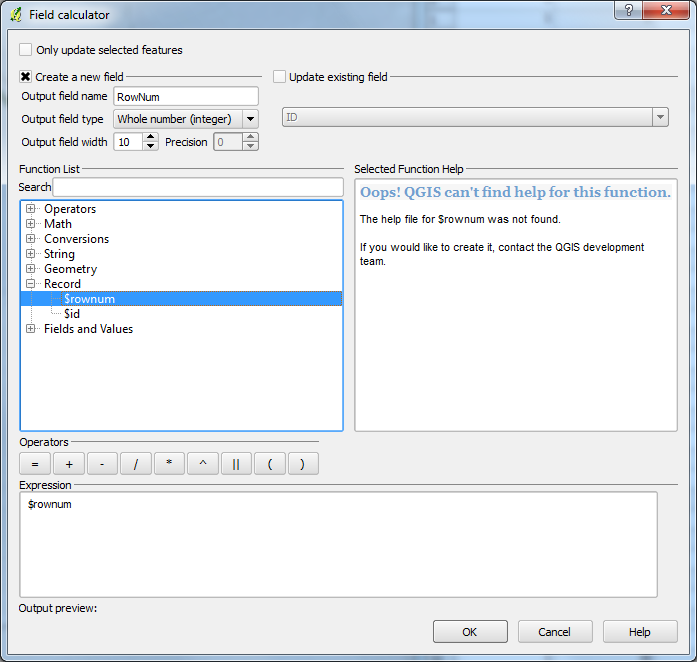
Using the field calculator, create a new column (I have called it rownum) and assign a rownum to each attribute. Save the shape file and then create a duplicate shape file using the save as. With the duplicate shape file, do the same as above but add 1 to the the rownum, i.e $rownum + 1 as the expression instead of $rownum |
|||
Done! |
|||
== Display Elevation Profiles == |
|||
To display elevation profiles in QGiS you need to install the Terrain Profile Plugin. (QgiS 1.80) |
|||
[[File:QGiS_FieldCalc.png]] |
|||
Simply select a raster that you wish to display (you can add more later) and then draw your line. Finish with a double click. Any intermediate clicks will display on your elevation profile as a vertical black line. |
|||
Below is a comparison of the 2m grid and the 10m check grid. |
|||
Merge these two shapefiles, I use the ''Saga >>> Shapes - Tools >>> Merge Shapes Layers'' module <br> |
|||
[[QGiS Elevation Profile.jpg]] |
|||
Then convert these points back to a line ''Saga >>> Shapes - Lines >>> Convert Points to Lines'' module. You will want to order and seperate by the column with the rownums <br> |
|||
The point of the above is to break your lines into segments. <b> |
|||
To be continued.. |
|||
Latest revision as of 13:13, 1 August 2013
How to Update a Column (Equivalent of MapInfo Update Column)
This user contributed tip can now be found here.
Extract Cross-Sections/Elevations from 2-D Domain to .csv format
This user contributed tip can now be found here
Plot grid elevation profiles
This user contributed tip can now be found here.
Alternate method for generating grid from points
Tested on QGIS 1.8.
Install the Sextante plugin, this is a useful tool that incorporates the modules from many other open source GIS packages into Quantum. You will also need to install Saga and set the path of the Saga executable in the Sextante options and configuration menu (under analysis in QGIS).
The Saga modules should now all be available in the Sextante Toolbox.
Load the Zpt file, in the Sextante toolbox select the Saga >>> Grid - Gridding >>> Shapes to Grid module. Fill out the appropriate options,
- attribute should be set as elevation,
- target grid is user defined,
- output extent you must click the three dots on the right hand side and select your point file, this will ensure that your grid has the same extent as point file,
- cellsize I set the cell size to the same size as the grid used in Tuflow.
For more advanced options check out the other gridding modules that Saga (and Grass) offer. If you need to interpolate between points, there are multiple options availableoptions such as Tin, Kriging, Spline etc
Quickly identify top of levees/embankments as Zln
The aim of this tip is to show you how you can get the maximum elvations for you levee/embankment.
Install the Sextante plugin for QGIS - See "Alternative method for generating grid from points ".
Draw a line along the top of your levee/embankment.
Select the Saga >>> Shapes - Points >>> Convert Lines to Points module, fill in as required...
The Insert Distance option specifies the maximum distance between lines Save a copy of the shape file so you have two point files that are the same.
Using the field calculator, create a new column (I have called it rownum) and assign a rownum to each attribute. Save the shape file and then create a duplicate shape file using the save as. With the duplicate shape file, do the same as above but add 1 to the the rownum, i.e $rownum + 1 as the expression instead of $rownum
Merge these two shapefiles, I use the Saga >>> Shapes - Tools >>> Merge Shapes Layers module
Then convert these points back to a line Saga >>> Shapes - Lines >>> Convert Points to Lines module. You will want to order and seperate by the column with the rownums
The point of the above is to break your lines into segments.
To be continued..