MIKE Flood to TUFLOW: Difference between revisions
Ellis Symons (talk | contribs) |
Ellis Symons (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
<ol> |
<ol> |
||
<li> X = xllcorner + j * cellsize |
<li> X = xllcorner + j * cellsize |
||
<li> Y = yllcorner + k * cellsize<br> |
<li> Y = yllcorner + k * cellsize<br>[[File: MIKE-JK-XY_conv.PNG|350px|]] |
||
</ol> |
</ol> |
||
</ol> |
</ol> |
||
</ol> |
</ol> |
||
The type of the boundary is defined in the <b>Hydrodynamic Parameters</b> >> <b>Boundary</b> tab. This tab specifies the whether the boundary is ‘Flux’ (QT), ‘Level’ (HT), or ‘Rating Curve’ (HQ), as well as whether the data is a time series (type 0 data file) or constant. |
|||
The name of the boundary can be found following the below steps: |
|||
* Clicking the <b>‘…’</b> button to browse |
|||
* Viewing <b>Item</b> which corresponds to the boundary name |
|||
The Upstream boundary can be digitised in TUFLOW as a 2d_bc (type ‘HT’), or as a 2d_SA polygon. For more discussion on selecting an appropriate upstream boundary type, please see the discussion at the bottom of the page. |
|||
==Source Boundaries== |
|||
The location of source boundaries can be found in the MIKE21 control file (.m21) in the <b>Basic Parameters</b> >> <b>Source and Sink</b>. The location of the boundaries are specified as a point object using the local (j, k) coordinate system. These are required to be converted to absolute coordinates so an identical boundary location can be digitised in TUFLOW. The conversion process can be undertaken using identical steps as performed with converting upstream and downstream boundaries. |
|||
It is recommended that the source boundary point from MIKE be converted to a 2d_SA polygon in TUFLOW. The 2d_SA polygon should be enlarged to encompass a larger region such that it is able to apply flow to more than one cell. This is considered to give a more stable and accurate representation of flow distribution to the model. More information on how 2d_SA polygons distributes flow can be found in Section 7.4.2 of the <u>[https://www.tuflow.com/Download/TUFLOW/Releases/2016-03/TUFLOW%20Manual.2016-03.pdf TUFLOW Manual]</u>. |
|||
==Inflow Boundaries== |
==Inflow Boundaries== |
||
Revision as of 20:58, 12 October 2017
This page is currently under construction
Introduction
This page provides guidance on a generalised method to convert a MIKE FLOOD model to a TUFLOW model format. MIKE Flood is the top level program that couples MIKE21 (the MIKE 2D engine and program) with MIKE11 (the MIKE 1D engine and program). These programs are referenced when converting the relevant setup to TUFLOW format. These steps could therefore also be used for converting stand-alone MIKE21 or MIKE11 models to TUFLOW format.
If you have any suggestions to be included in these pages, please email support@tuflow.com.
Requirements
The following programs are required in the conversion process:
- MIKE Zero
- xsGenerator.exe (for MIKE11 conversion)
MIKE Zero is required to extract data from the MIKE FLOOD model. The tools required are freely available using the Demo version of Mike Zero.
For MIKE11 conversion, the xsGenerator utility has been made to automate some of the steps. The xsGenerator utility is freely available from the TUFLOW website.
Creating a TUFLOW Geometry Control File from MIKE21
This section discusses how to extract geometry data from a MIKE21 model to populate the TUFLOW Geometry Control file (TGC). The TGC file defines the:
- Terrain elevation
- Manning's values
- Model domain
- Active cells
The MIKE21 (.m21) control file can be used to determine the specific geometry input files for the MIKE21 model. You can view the MIKE21 control file using MIKE Zero.
Converting Terrain
Like TUFLOW, MIKE uses a grid file to define the underlying terrain. MIKE uses its own grid format (.dsf2) as well as a local coordinate system. For these reasons, it needs to be converted into a format that TUFLOW can read as well as an absolute coordinate system.
The terrain .dfs2 grid can be converted through the MIKE Zero toolbox. This can be done through the following steps:
- Open the MIKE Zero program
- From the MIKE Zero shell select File >> New >> File
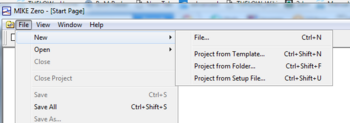
- On the MIKE Zero button select MIKE Zero Toolbox (.mzt). Click OK.
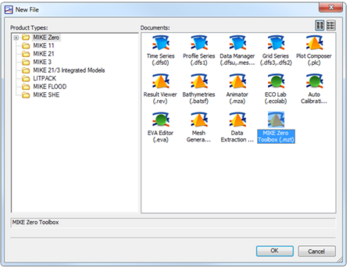
- Under the GIS dropdown, double click MIKE2GRD
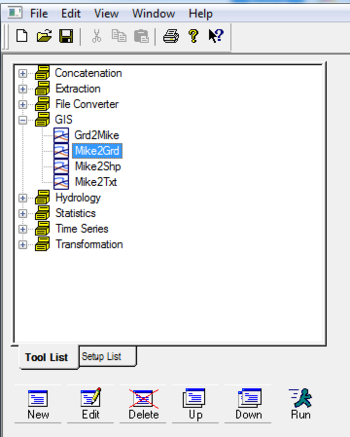
- Work through the steps being careful to specify an appropriate projection
- Before clicking Finish, ensure you have clicked Execute to run the conversion

- This should produce an ascii file that can be directly read by TUFLOW
Unlike TUFLOW, the grid cell size of the model in MIKE is determined directly by the input grid file. For more discussion on grid cell size and the differences in how MIKE and TUFLOW handle the underlying terrain please see the discussion section at the bottom of the page.
Note: After grid conversion, it is important to perform checks that the ascii grid has converted properly. This is best done in your preferred GIS package.
Converting Manning's
Follow the same steps as converting terrain to convert the manning’s grid using the Mike Zero Toolbox. It is important to identify the manning’s value type (M or n) so that it can be correctly read into TUFLOW. This can be done by viewing the .dfs2 grid in Mike Zero following the steps below:
- Open the MIKE Zero program
- Open the .dfs2 file through Open (or drag and drop)
- From the toolbar select Edit >> Items…
- The value should be listed in Type
More information on reading in manning’s grids into TUFLOW is provided in Section 6.9 of the TUFLOW Manual.
Model Domain
The model domain can be manually set by viewing the terrain and manning’s data in your preferred GIS program, or set using the Read Grid Location command.
! Set model domain
Read Grid Location == ..\model\grid\example_grid.asc
More information on setting the model domain is provided in Section 6.5 of the TUFLOW Manual.
TUFLOW Code Layer
The user can manually set the TUFLOW code layer by viewing the terrain data through their preferred GIS program or, it should be noted, that MIKE uses a process of defining active cells by defining a ‘Land’ elevation value. A ‘Land’ elevation value is specified in the .dsf2 grid file that specifies a value at which elevations equal to or greater than this value are considered ‘Land’ and will not be subject to possible wetting and drying. This value could be used as a guidance for producing a TUFLOW code layer. The steps in identifying this value are as follows:
- Open the MIKE Zero program
- Open the .dfs2 elevation grid through Open (or drag and drop)
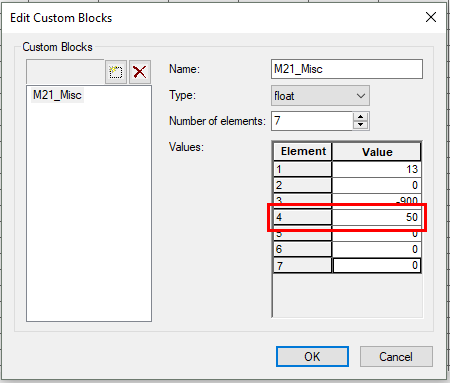
- From the toolbar select Edit >> Custom Blocks…
- The fourth element value is the ‘Land’ value elevation
Note: A downfall of this method in MIKE, is that elevations in the .dfs2 grid could have been manually modified such that the area outside the flood extent has a constant ‘Land’ elevation. Inspection of the terrain data before use is highly recommended.
Creating a TUFLOW Boundary Control File from MIKE21 and MIKE Flood
This section discusses how to extract data from a MIKE model to populate the TUFLOW Boundary Control file (TBC). The TBC file defines the:
- Downstream boundary
- Inflow locations
- 1D/2D linking
Upstream and Downstream Boundaries
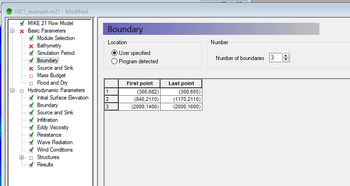
The location of upstream and downstream boundaries can be found in the MIKE21 control file (.m21) in the Basic Parameters >> Boundary tab. The location of the boundaries are specified as a line object using the start and end vertices in the local (j, k) coordinate system. These are required to be converted to absolute coordinates so an identical boundary location can be digitised in TUFLOW. This can be done in MS Excel using the following steps:
- Identify boundary locations
- In excel convert these (j,k) coordinates to an absolute reference (X, Y)
The type of the boundary is defined in the Hydrodynamic Parameters >> Boundary tab. This tab specifies the whether the boundary is ‘Flux’ (QT), ‘Level’ (HT), or ‘Rating Curve’ (HQ), as well as whether the data is a time series (type 0 data file) or constant.
The name of the boundary can be found following the below steps:
- Clicking the ‘…’ button to browse
- Viewing Item which corresponds to the boundary name
The Upstream boundary can be digitised in TUFLOW as a 2d_bc (type ‘HT’), or as a 2d_SA polygon. For more discussion on selecting an appropriate upstream boundary type, please see the discussion at the bottom of the page.
Source Boundaries
The location of source boundaries can be found in the MIKE21 control file (.m21) in the Basic Parameters >> Source and Sink. The location of the boundaries are specified as a point object using the local (j, k) coordinate system. These are required to be converted to absolute coordinates so an identical boundary location can be digitised in TUFLOW. The conversion process can be undertaken using identical steps as performed with converting upstream and downstream boundaries.
It is recommended that the source boundary point from MIKE be converted to a 2d_SA polygon in TUFLOW. The 2d_SA polygon should be enlarged to encompass a larger region such that it is able to apply flow to more than one cell. This is considered to give a more stable and accurate representation of flow distribution to the model. More information on how 2d_SA polygons distributes flow can be found in Section 7.4.2 of the TUFLOW Manual.