TUFLOW Benchmarking: Difference between revisions
Chris Huxley (talk | contribs) |
Chris Huxley (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
= University Thesis Studies = |
= University Thesis Studies = |
||
== Syme (1991) == |
== Syme (1991) == |
||
TUFLOW was first developed as a result of this PhD study. This thesis presents a discussion on the process of selecting TUFLOW's 1-D and 2-D schemes; and the details of: |
TUFLOW was first developed as a result of this PhD study. This thesis summarises the mathematical theory that underpins TUFLOW. It presents a discussion on the process of selecting TUFLOW's 1-D and 2-D schemes; and the details of: |
||
* the methodology used for coding the 2-D scheme; |
|||
* the wetting and drying method; the dynamic 2-D/1-D link; and |
|||
* the stabilisation of oblique water level boundaries. |
|||
[[File:Syme_1991.PNG|300px]] |
[[File:Syme_1991.PNG|300px]] |
||
Revision as of 07:26, 23 September 2015
Hardware Benchmark Testing
University Thesis Studies
Syme (1991)
TUFLOW was first developed as a result of this PhD study. This thesis summarises the mathematical theory that underpins TUFLOW. It presents a discussion on the process of selecting TUFLOW's 1-D and 2-D schemes; and the details of:
- the methodology used for coding the 2-D scheme;
- the wetting and drying method; the dynamic 2-D/1-D link; and
- the stabilisation of oblique water level boundaries.
Barton (2001)
This thesis study investigated the ability of 2D hydrodynamic models to adequately predict energy losses through an abrupt constriction. In particular, the investigation focuses on the impact that model spatial resolution has on the ability of the model to predict expansion and contraction losses due to the abrupt constriction.
Principal outcomes of the study were:
- An improved understanding of different numerical solution schemes;
- An improved understanding of the nature of contracting and expanding flow;
- The confirmation that the spatial resolution of 2D models does have an impact on the ability of these models to predict energy losses due to turbulent effects;
- An understanding of the importance of the eddy viscosity formulation technique on the predictive ability of 2D models;
- A preliminary assessment of the impact of varying the eddy viscosity formulation technique.
Huxley (2004)
This thesis validates TUFLOW against independent analytical calculations. The study used over 300 benchmark models to verify the accuracy of TUFLOW for a range of flow conditions (super critical, critical and subcritical). The specific test cases included:
- 1D culvert flow;
- 1D weir flow;
- 2D weir flow;
- 2D channel flow;
- 2D floodplain flow; and
- 2D channel/floodplain flow.
The TUFLOW results were found to be within a 2% accuracy of the analytical estimates in 97% of the benchmark models.
Caddis (2010)
Boyte (2014)
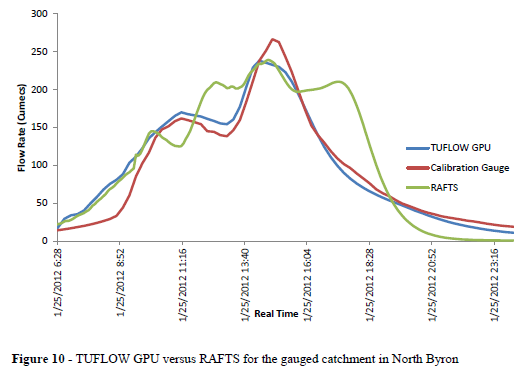
This thesis investigated incorporating hydrology into direct rainfall models, with consideration given to hydraulic resistance mechanisms at shallow flow. The direct rainfall methodology was implemented into a two dimensional shallow water model, TUFLOW GPU; which was compared against an industry standard hydrologic model, XP RAFTS.
The primary objectives were to determine whether TUFLOW GPU was a suitable software package to use in industry applications, whether the direct rainfall model was able to reproduce the hydrology of a real storm event in a gauged catchment more accurately than the hydrologic model; and to understand hydraulic resistance mechanisms at shallow flow and at different roughness scales. These objectives were met through numerical modelling with real data produced from experiments, stream gauges, or analytical solutions. Dressler’s sloping dam break analytical model was used to validate TUFLOW GPU, a gauged catchment in New South Wales was used to compare hydrology representation in the direct rainfall model and hydrologic model, and experimental data from an open channel at shallow flow was analysed to analyse hydraulic resistance mechanisms. Monte Carlo testing by simulating non uniformity in bed roughness was undertaken on an ungauged catchment in New South Wales to determine the practical impacts of secondary flows, which arose after analysis of the experimental data.
Independent Benchmark Testing
United Kingdom Environment Agency
The United Kingdom Environment Agency have documented independent testing of most 2D modeling packages. This is a good resource for comparing TUFLOW to other available software: