Tute M01 Materials QGIS Archive
Introduction
This page details the method for using QGIS to create the GIS based material types (land use areas). Once the GIS layers are setup (in this section), surface roughness or bed-resistance values (e.g. Manning's n) are assigned to each of these land use areas (in the main tutorial module, here).
The Module_Data\Module_01\QGIS\ folder already contains the materials files that we will use.
Method
- Open the aerial photo from the Module_Data\Aerial_Photos\QGIS\Aerial_Photo_M01.jpg
- Copy the 2d_mat_M01_002_R files from the Module_Data\Module_01\QGIS\ directory to TUFLOW\Model\gis\. There should be five (5) files, with the extensions dbf, prj, shp, .shx and .qml (this is a style layer).
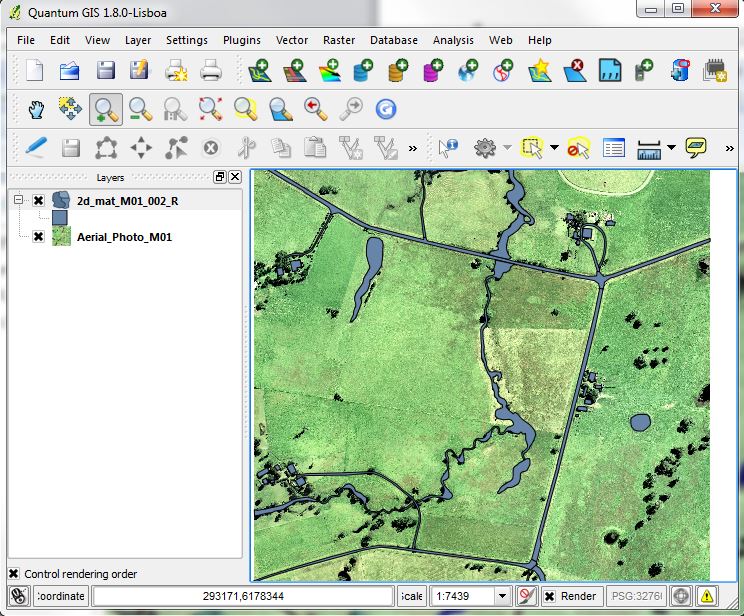
- Load the TUFLOW\Model\gis\2d_mat_M01_002_R.shp file. The map window should be displaying the aerial photography, with a series of polygons covering certain areas, as per the image below.
- Each of the regions contains an integer value that defines the land use type. To make this more obvious in QGIS, we can colour the regions based on the individual values. To do this:
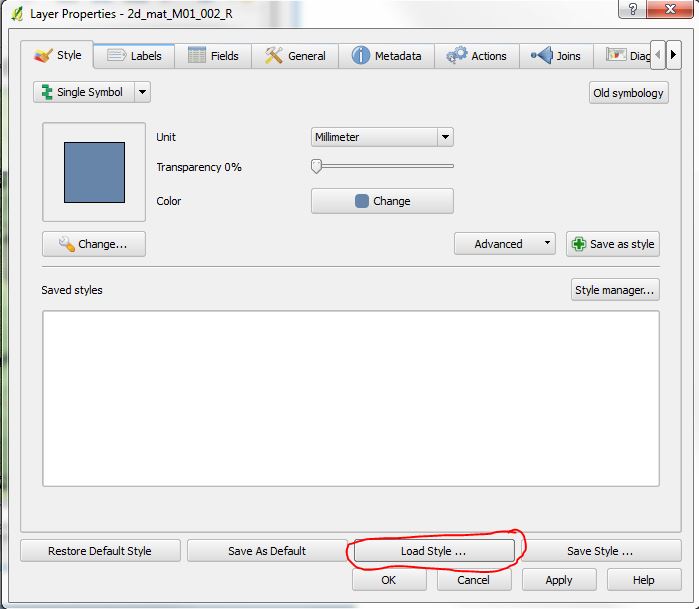
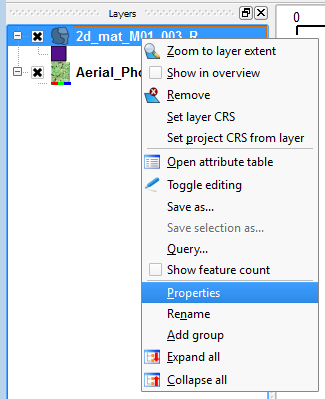
- Right click on the the layer 2d_mat_M01_002_R layer and select Properties (1st image below);
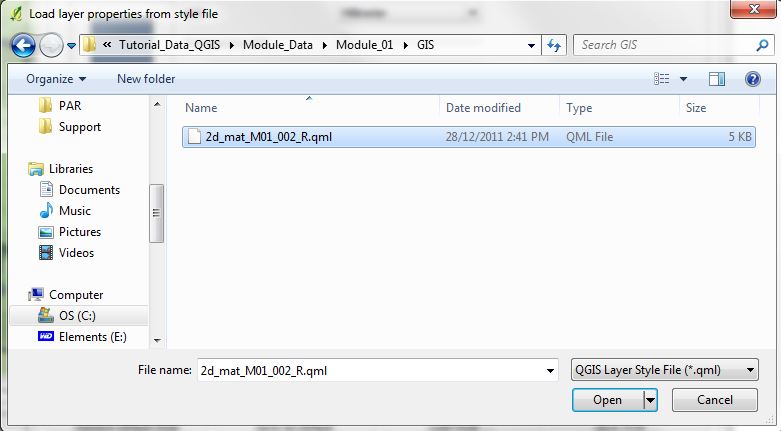
- In the layer properties dialogue, select Load Style (2nd image below);
- Select the 2d_mat_M01_002_R.qml (3rd image below); and
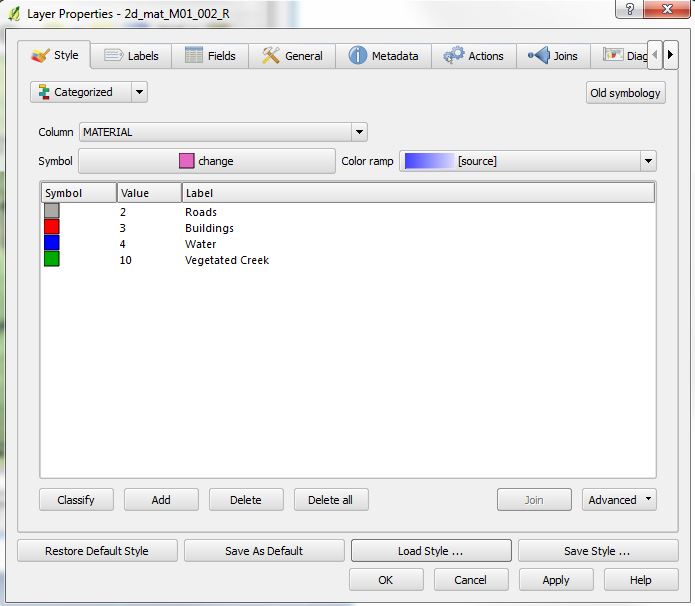
- The layer properties should now show four different symbols. In the value field is the integer ID as stored in the shapefile. In the label field is a description of the land-use type (4th image below).
- Select Apply.
Frame
Frame
Frame
Frame
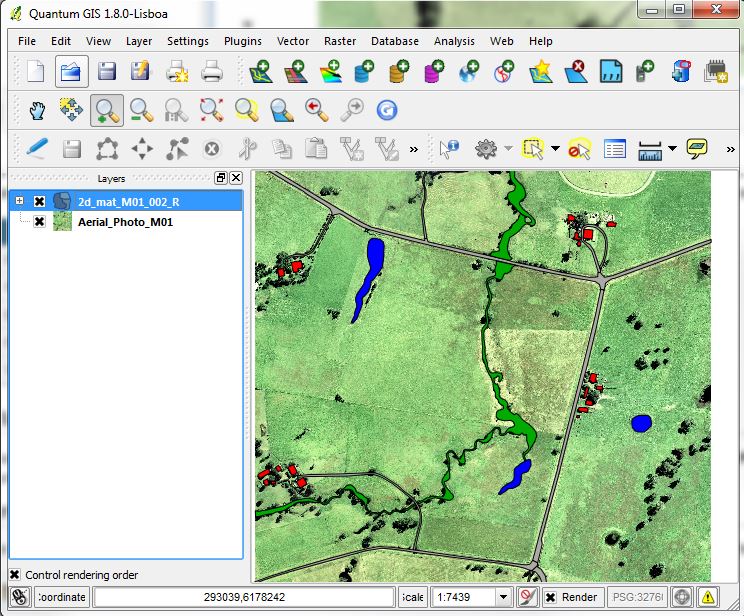
Once the styling has been applied, each of the regions should be shaded depending on the Material ID (integer). The map window should now appear as it does in the image below.
You may notice that the open pasture land-use that covers most of the study area has not been defined. This will be our default land use type, to save time we only need to define the areas where the land use differs from the default.
NOTE: The material attribute associated with each polygon is an integer number specific to a type of land-use. In the next step we link the material ID (integer) to a roughness coefficient. A table is provided below for reference.
Material ID Land Use Manning's n 1 Pasture 0.06 2 Roads 0.022 3 Buildings 3.0 4 Ponds and other water 0.03 10 Vegetated Creek 0.03
Alternate Method If you would like to create your own material inputs rather than using the supplied dataset.
- Load the empty (template) file named 2d_mat_empty_R.shp from TUFLOW\Model\gis\empty\ and save this in the TUFLOW\model\gis\ folder as as 2d_mat_M01_002_R.shp, make this layer editable (toggle editing) and digitise the material polygons ensuring to assign a Material ID to each polygon using the land use types in the table above.
TUFLOW Geometry Control (TGC) File Updates
In order to read in the GIS layer created above. Enter the following text into the TGC file:
Set Mat == 1 ! Set every cell to a material ID of 1 (Pasture)
Read GIS Mat == gis\2d_mat_M01_002_R.shp
The Set Mat command sets all 2D cells to a Material ID of 1, which is used for pasture. The Read GIS Mat command updates any 2D cells that fall within the polygons in the 2d_mat layer with the Material attribute value of each polygon. As discussed for the cell code values in the previous section, the order of these Mat commands is important.
Conclusion
QGIS has been used to view or create a 2d_mat layer which defines the spatial extents of the land use categories. Material commands have been added to the TGC. Please return to Tutorial Module 1.