Difference between revisions of "RES to RES"
| (8 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
=Introduction= | =Introduction= | ||
This utility performs a variety of operations on the TUFLOW 2D outputs. Valid formats are .xmdf (as of utility version 2012-10-AC) and .dat files. This page is split into two section, utility operations (e.g. maximum, difference etc.) and general options. The general options can be used regardless of operation being performed. The table of contents can be used to jump to a desired operation. | This utility performs a variety of operations on the TUFLOW 2D outputs. Valid formats are .xmdf (as of utility version 2012-10-AC) and .dat files. This page is split into two section, utility operations (e.g. maximum, difference etc.) and general options. The general options can be used regardless of operation being performed. The table of contents can be used to jump to a desired operation. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 10: | ||
This can be used to extract the maximum from a number of input datasets. Any number of input files can be specified. If a maximum folder exists in an .xmdf file for the type specified, this dataset will be used, for dat files use -t99999 to use the maximum data in the .dat file.<br> | This can be used to extract the maximum from a number of input datasets. Any number of input files can be specified. If a maximum folder exists in an .xmdf file for the type specified, this dataset will be used, for dat files use -t99999 to use the maximum data in the .dat file.<br> | ||
<u>Examples</u><br> | <u>Examples</u><br> | ||
| − | <li><tt>res_to_res.exe -max -typeH results_1.xmdf results_2.xmdf results_3.xmdf</tt>< | + | <ol> |
| − | + | <li>Extracts the maximum water level from the three .xmdf files.<br> | |
| − | < | + | <tt>res_to_res.exe -max -typeH results_1.xmdf results_2.xmdf results_3.xmdf</tt> |
| − | When no maximums has been written directly, extracts the maximum water level of all available output times. Note this does not provide the true, tracked maximum over all timesteps. | + | <li>When maximums are tracked over all timesteps, extracts the maximum water level from the maximums output.<br> |
| + | <tt>res_to_res.exe -max -typeH results.xmdf</tt> | ||
| + | <li>When no maximums has been written directly, extracts the maximum water level of all available output times. Note this does not provide the true, tracked maximum over all timesteps.<br> | ||
| + | <tt>res_to_res.exe -max -typeH results.xmdf</tt> | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
==Min== | ==Min== | ||
| Line 21: | Line 24: | ||
This can be used to extract the minimums from a number of input datasets. Any number of input files can be specified. If a minimum folder exists in an .xmdf file for the type specified, this dataset will be used.<br> | This can be used to extract the minimums from a number of input datasets. Any number of input files can be specified. If a minimum folder exists in an .xmdf file for the type specified, this dataset will be used.<br> | ||
<u>Examples</u><br> | <u>Examples</u><br> | ||
| − | <li><tt>res_to_res.exe -min -typeH results_1.xmdf results_2.xmdf results_3.xmdf</tt>< | + | <ol> |
| − | Extracts the minimum water level from the three xmdf files. | + | <li>Extracts the minimum water level from the three xmdf files.<br> |
| − | < | + | <tt>res_to_res.exe -min -typeH results_1.xmdf results_2.xmdf results_3.xmdf</tt> |
| − | + | <li>Extracts the minimum water level from the three xmdf files with output name "Minimums.xmdf".<br> | |
| + | <tt>res_to_res.exe -min -typeH -out Minimums.xmdf results_1.xmdf results_2.xmdf results_3.xmdf</tt> | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
==Difference== | ==Difference== | ||
| Line 34: | Line 39: | ||
The -t option can be used to carry out the difference at a particular time (rather than all times). The most common time is to take the difference at the flood peak, ie. specify -t99999.<br> | The -t option can be used to carry out the difference at a particular time (rather than all times). The most common time is to take the difference at the flood peak, ie. specify -t99999.<br> | ||
<u>Examples</u><br> | <u>Examples</u><br> | ||
| − | < | + | <ol> |
| − | Extracts the difference in water level, the output is results_developed minus results_existing for all timesteps. | + | <li>Extracts the difference in water level, the output is results_developed minus results_existing for all timesteps.<br> |
| − | < | + | <tt>res_to_res.exe -dif -typeH results_developed.xmdf results_existing.xmdf</tt> |
| − | Extracts the difference in water level for the maximum water level and suppresses the wet/dry check described above. | + | <li>Extracts the difference in water level for the maximum water level and suppresses the wet/dry check described above.<br> |
| + | <tt>res_to_res.exe -dif -typeH -t99999 -nowetdry results_developed.xmdf results_existing.xmdf</tt> | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
==Duration== | ==Duration== | ||
| Line 44: | Line 51: | ||
Determines the duration in hours that the the results exceed the cut off value.<br> | Determines the duration in hours that the the results exceed the cut off value.<br> | ||
'''Note: ''' A preferable approach is to use the .tcf file command: <tt>Time Output Cutoff Depths == <cut off value or values></tt>. With this command specified TUFLOW tracks this on a timestep by timestep basis rather than post processing this at the map output interval.<br> | '''Note: ''' A preferable approach is to use the .tcf file command: <tt>Time Output Cutoff Depths == <cut off value or values></tt>. With this command specified TUFLOW tracks this on a timestep by timestep basis rather than post processing this at the map output interval.<br> | ||
| − | <u> | + | <u>Example</u><br> |
| − | <li><tt>res_to_res.exe -dur0.1 -typeD results.xmdf</tt></ | + | <ol> |
| − | + | <li>Extracts the duration in flooding above 0.1m deep.<br> | |
| + | <tt>res_to_res.exe -dur0.1 -typeD results.xmdf</tt> | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
==Keep== | ==Keep== | ||
| Line 53: | Line 62: | ||
Can be used to extract a single timestep from a results file. This is useful to extract the maximums to a separate file making it easier to transfer electronically. To keep a range of output times see the -range option below.<br> | Can be used to extract a single timestep from a results file. This is useful to extract the maximums to a separate file making it easier to transfer electronically. To keep a range of output times see the -range option below.<br> | ||
<u>Examples</u><br> | <u>Examples</u><br> | ||
| − | < | + | <ol> |
| − | Creates a new results file containing just the maximum from the water level results. | + | <li>Creates a new results file containing just the maximum from the water level results.<br> |
| − | < | + | <tt>res_to_res.exe -k99999 -typeH results.xmdf</tt> |
| − | Creates a new results file containing just velocity results for the 2.5 hour output. | + | <li>Creates a new results file containing just velocity results for the 2.5 hour output.<br> |
| + | <tt>res_to_res.exe -k2.5 -typeV results.xmdf</tt> | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
==Range== | ==Range== | ||
| Line 62: | Line 73: | ||
<u>Description</u><br> | <u>Description</u><br> | ||
Extracts all timestep between start time and end time (inclusive) into a separate results file.<br> | Extracts all timestep between start time and end time (inclusive) into a separate results file.<br> | ||
| − | <u> | + | <u>Example</u><br> |
| − | < | + | <ol> |
| − | Creates a new results file containing the depth outputs between 1.0 and 2.5 hours. Both 1 and 2.5 hour outputs are included. | + | <li>Creates a new results file containing the depth outputs between 1.0 and 2.5 hours. Both 1 and 2.5 hour outputs are included.<br> |
| + | <tt>res_to_res.exe -rangeA1 -rangeB2.5 -typeD results.xmdf</tt> | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
==Remove== | ==Remove== | ||
| Line 70: | Line 83: | ||
<u>Description</u><br> | <u>Description</u><br> | ||
Creates a new output file and removes the output time from this.<br> | Creates a new output file and removes the output time from this.<br> | ||
| − | <u> | + | <u>Example</u><br> |
| − | <li><tt>res_to_res.exe -r3 -typeD results.xmdf</tt></ | + | <ol> |
| − | + | <li>Creates a new output file which does not include the output at 3.<br> | |
| + | <tt>res_to_res.exe -r3 -typeD results.xmdf</tt> | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
==Trim Values== | ==Trim Values== | ||
| Line 78: | Line 93: | ||
<u>Description</u><br> | <u>Description</u><br> | ||
Creates a new output file which has any values above <value> set to <value>. If the input is a vector data, the vector magnitude is used to trim the value (direction is unchanged).<br> | Creates a new output file which has any values above <value> set to <value>. If the input is a vector data, the vector magnitude is used to trim the value (direction is unchanged).<br> | ||
| − | <u> | + | <u>Example</u><br> |
| − | < | + | <ol> |
| − | Creates a new output of velocity with any outputs greater than 5.0 set to 5.0. | + | <li>Creates a new output of velocity with any outputs greater than 5.0 set to 5.0.<br> |
| + | <tt>res_to_res.exe -trim5 -typeV results.xmdf</tt> | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
==Times== | ==Times== | ||
| Line 86: | Line 103: | ||
<u>Description</u><br> | <u>Description</u><br> | ||
Creates a text file which contains the output times in the .dat or xmdf file. If no output filename is specified with the -out option the output file will be called "times.txt". For xmdf files see also the -xnfo option below.<br> | Creates a text file which contains the output times in the .dat or xmdf file. If no output filename is specified with the -out option the output file will be called "times.txt". For xmdf files see also the -xnfo option below.<br> | ||
| − | <u> | + | <u>Example</u><br> |
| − | < | + | <ol> |
| − | Creates an an output file "times.txt" which contains all timesteps that are contained in the results file. | + | <li>Creates an an output file "times.txt" which contains all timesteps that are contained in the results file.<br> |
| + | <tt>res_to_res.exe -times -typeH results.xmdf</tt> | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
==XMDF Information== | ==XMDF Information== | ||
| Line 94: | Line 113: | ||
<u>Description</u><br> | <u>Description</u><br> | ||
Creates a text file which contains a list of the datasets contained within the .xmdf file. The number of output times and the output times are also exported to the text file.<br> | Creates a text file which contains a list of the datasets contained within the .xmdf file. The number of output times and the output times are also exported to the text file.<br> | ||
| − | <u> | + | <u>Example</u><br> |
| − | < | + | <ol> |
| − | Creates an an output file with the specified filename "xmdf_info.txt", which contains information about the contents of the xmdf file. | + | <li>Creates an an output file with the specified filename "xmdf_info.txt", which contains information about the contents of the xmdf file.<br> |
| + | <tt>res_to_res.exe -xnfo -out xmdf_info.txt results.xmdf</tt> | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
==Vector Angle== | ==Vector Angle== | ||
| Line 102: | Line 123: | ||
<u>Description</u><br> | <u>Description</u><br> | ||
Outputs the vector direction in degrees relative to north (North = 0°, East = 90°, South = 180°/-180°, West = -90°).<br> | Outputs the vector direction in degrees relative to north (North = 0°, East = 90°, South = 180°/-180°, West = -90°).<br> | ||
| − | <u> | + | <u>Example</u><br> |
| − | <li><tt>res_to_res.exe -va -typeV results.xmdf</tt></ | + | <ol> |
| − | + | <li>Outputs the velocity direction for all timesteps in the results file.<br> | |
| + | <tt>res_to_res.exe -va -typeV results.xmdf</tt> | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
==Concatenate== | ==Concatenate== | ||
| Line 110: | Line 133: | ||
<u>Description</u><br> | <u>Description</u><br> | ||
Concatenates (joins) two or more results files into one. Each results file must be from the same 1D/2D mesh.<br> | Concatenates (joins) two or more results files into one. Each results file must be from the same 1D/2D mesh.<br> | ||
| − | <u> | + | <u>Example</u><br> |
| − | <li><tt>res_to_res.exe -con -typeH results_1.xmdf results_2.xmdf results_3.xmdf</tt></ | + | <ol> |
| − | + | <li>Joins the water level results contained in the three files into a single file.<br> | |
| + | <tt>res_to_res.exe -con -typeH results_1.xmdf results_2.xmdf results_3.xmdf</tt> | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
==Convert== | ==Convert== | ||
| Line 119: | Line 144: | ||
Converts between .dat and .xmdf format results. Not to be confused with -con (concatenate option described above)!<br> | Converts between .dat and .xmdf format results. Not to be confused with -con (concatenate option described above)!<br> | ||
<u>Examples</u><br> | <u>Examples</u><br> | ||
| − | < | + | <ol> |
| − | Converts the maximum water level results in the xmdf file into .dat file format. | + | <li>Converts the maximum water level results in the xmdf file into .dat file format.<br> |
| − | < | + | <tt>res_to_res.exe -conv -typeH -t99999 results.xmdf</tt> |
| − | Converts all datasets and times in the .xmdf file into .dat file format. This will output a number of .dat files. | + | <li>Converts all datasets and times in the .xmdf file into .dat file format. This will output a number of .dat files.<br> |
| − | < | + | <tt>res_to_res.exe -conv results.xmdf</tt> |
| − | Converts all times in the .dat file into xmdf file format. | + | <li>Converts all times in the .dat file into xmdf file format.<br> |
| + | <tt>res_to_res.exe -conv results_h.dat</tt> | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
==Time of Increase== | ==Time of Increase== | ||
'''Input Switch: -toi<cutoff>'''<br> | '''Input Switch: -toi<cutoff>'''<br> | ||
Calculates the time taken for the results to increase by the cutoff. For example if a value of 0.2 is used for a depth grid, the output result contains the time required for the depth to increase by 0.2m. If there are depth values greater than 0.2 initially (due to initial water level conditions), the output is the time for the depth to increase by 0.2m. For dry areas it is the time for the depth to reach 0.2m.<br> | Calculates the time taken for the results to increase by the cutoff. For example if a value of 0.2 is used for a depth grid, the output result contains the time required for the depth to increase by 0.2m. If there are depth values greater than 0.2 initially (due to initial water level conditions), the output is the time for the depth to increase by 0.2m. For dry areas it is the time for the depth to reach 0.2m.<br> | ||
| − | <u> | + | <u>Example</u><br> |
| − | <li><tt>res_to_res.exe -toi0.2 -typeD results.xmdf</tt></ | + | <ol> |
| − | + | <li>Extracts the time taken for the depth to increase by 0.2m.<br> | |
| + | <tt>res_to_res.exe -toi0.2 -typeD results.xmdf</tt> | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
==Ensight (beta)== | ==Ensight (beta)== | ||
| Line 145: | Line 174: | ||
'''This conversion is in its beta stage of development. This utility can currently only process 2D results. 1D channel result are currently not supported.<br> | '''This conversion is in its beta stage of development. This utility can currently only process 2D results. 1D channel result are currently not supported.<br> | ||
Any feedback regarding this utility function is welcome and can be sent to support@tuflow.com.<br> | Any feedback regarding this utility function is welcome and can be sent to support@tuflow.com.<br> | ||
| − | <u> | + | <u>Example</u><br> |
| − | <li><tt>res_to_res.exe -ensight results.xmdf</tt></ | + | <ol> |
| − | + | <li>Converts all datasets in the xmdf file into Ensight format.<br> | |
| + | <tt>res_to_res.exe -ensight results.xmdf</tt> | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
=General Options= | =General Options= | ||
| Line 185: | Line 216: | ||
==XMDF Dataset Example== | ==XMDF Dataset Example== | ||
| + | Display the datasets available within an XMDF file in a DOS window by starting any operation. <br> | ||
| + | To keep the DOS window open write "pause" at the end of the processing batch file and ensure -b switch is not included. <br> | ||
| + | The list of available datasets will be displayed towards the start of the DOS window. <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <u>Examples</u><br> | ||
| + | <tt>res_to_res.exe -xnfo results.xmdf<br> | ||
| + | pause</tt><br><br> | ||
| + | Displays the following DOS window: <br> | ||
[[File: xmdf_dataset_example.png]]<br> | [[File: xmdf_dataset_example.png]]<br> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 191: | Line 230: | ||
|uplink=[[TUFLOW_Utilities | Back to TUFLOW Utilities]] | |uplink=[[TUFLOW_Utilities | Back to TUFLOW Utilities]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 15:50, 22 July 2024
Introduction
This utility performs a variety of operations on the TUFLOW 2D outputs. Valid formats are .xmdf (as of utility version 2012-10-AC) and .dat files. This page is split into two section, utility operations (e.g. maximum, difference etc.) and general options. The general options can be used regardless of operation being performed. The table of contents can be used to jump to a desired operation.
Operations
The section below contains a list of the operations that the utility can perform. One of these operations must be specified or the utility will generate an error.
Max
Input Switch: -max
Description
This can be used to extract the maximum from a number of input datasets. Any number of input files can be specified. If a maximum folder exists in an .xmdf file for the type specified, this dataset will be used, for dat files use -t99999 to use the maximum data in the .dat file.
Examples
- Extracts the maximum water level from the three .xmdf files.
res_to_res.exe -max -typeH results_1.xmdf results_2.xmdf results_3.xmdf - When maximums are tracked over all timesteps, extracts the maximum water level from the maximums output.
res_to_res.exe -max -typeH results.xmdf - When no maximums has been written directly, extracts the maximum water level of all available output times. Note this does not provide the true, tracked maximum over all timesteps.
res_to_res.exe -max -typeH results.xmdf
Min
Input Switch: -min
Description
This can be used to extract the minimums from a number of input datasets. Any number of input files can be specified. If a minimum folder exists in an .xmdf file for the type specified, this dataset will be used.
Examples
- Extracts the minimum water level from the three xmdf files.
res_to_res.exe -min -typeH results_1.xmdf results_2.xmdf results_3.xmdf - Extracts the minimum water level from the three xmdf files with output name "Minimums.xmdf".
res_to_res.exe -min -typeH -out Minimums.xmdf results_1.xmdf results_2.xmdf results_3.xmdf
Difference
Input Switch: -dif
Description
This can be used to compare two datasets. If a third file is specified, the third file is used as the output file. The output filename can also be specified with the -out option. The output is the first result minus the second result file.
A special wet/dry algorithm is used. If water level results are not specified (_h.dat or -typeH), the algorithm opens these files, as well as opens the .2dm file associated with the results files, and uses the water levels and ZH Zpt values (for 2D cells) and elevations at the WLL triangle corners to determine whether a node (corner of a mesh element) is wet or dry. This allows two special values to be output in the event that a node is dry in one results file and wet in the other or vice versa. A value of -99 is used to indicate that a node is dry in the first results file, but is flooded in the second results file, while +99 indicates that the node was wet in the first results file but is dry in the second results file. Specifying -nowetdry does not carry out a wet/dry check using the water level results.
The -t option can be used to carry out the difference at a particular time (rather than all times). The most common time is to take the difference at the flood peak, ie. specify -t99999.
Examples
- Extracts the difference in water level, the output is results_developed minus results_existing for all timesteps.
res_to_res.exe -dif -typeH results_developed.xmdf results_existing.xmdf - Extracts the difference in water level for the maximum water level and suppresses the wet/dry check described above.
res_to_res.exe -dif -typeH -t99999 -nowetdry results_developed.xmdf results_existing.xmdf
Duration
Input Switch: -dur<cut of value>
Description
Determines the duration in hours that the the results exceed the cut off value.
Note: A preferable approach is to use the .tcf file command: Time Output Cutoff Depths == <cut off value or values>. With this command specified TUFLOW tracks this on a timestep by timestep basis rather than post processing this at the map output interval.
Example
- Extracts the duration in flooding above 0.1m deep.
res_to_res.exe -dur0.1 -typeD results.xmdf
Keep
Input Switch: -k<output time>
Description
Can be used to extract a single timestep from a results file. This is useful to extract the maximums to a separate file making it easier to transfer electronically. To keep a range of output times see the -range option below.
Examples
- Creates a new results file containing just the maximum from the water level results.
res_to_res.exe -k99999 -typeH results.xmdf - Creates a new results file containing just velocity results for the 2.5 hour output.
res_to_res.exe -k2.5 -typeV results.xmdf
Range
Input Switch: -rangeA<start time> -rangeB<end time>
Description
Extracts all timestep between start time and end time (inclusive) into a separate results file.
Example
- Creates a new results file containing the depth outputs between 1.0 and 2.5 hours. Both 1 and 2.5 hour outputs are included.
res_to_res.exe -rangeA1 -rangeB2.5 -typeD results.xmdf
Remove
Input Switch: -r<output time>
Description
Creates a new output file and removes the output time from this.
Example
- Creates a new output file which does not include the output at 3.
res_to_res.exe -r3 -typeD results.xmdf
Trim Values
Input Switch: -trim<value>
Description
Creates a new output file which has any values above <value> set to <value>. If the input is a vector data, the vector magnitude is used to trim the value (direction is unchanged).
Example
- Creates a new output of velocity with any outputs greater than 5.0 set to 5.0.
res_to_res.exe -trim5 -typeV results.xmdf
Times
Input Switch: -times
Description
Creates a text file which contains the output times in the .dat or xmdf file. If no output filename is specified with the -out option the output file will be called "times.txt". For xmdf files see also the -xnfo option below.
Example
- Creates an an output file "times.txt" which contains all timesteps that are contained in the results file.
res_to_res.exe -times -typeH results.xmdf
XMDF Information
Input Switch: -xnfo
Description
Creates a text file which contains a list of the datasets contained within the .xmdf file. The number of output times and the output times are also exported to the text file.
Example
- Creates an an output file with the specified filename "xmdf_info.txt", which contains information about the contents of the xmdf file.
res_to_res.exe -xnfo -out xmdf_info.txt results.xmdf
Vector Angle
Input Switch: -va
Description
Outputs the vector direction in degrees relative to north (North = 0°, East = 90°, South = 180°/-180°, West = -90°).
Example
- Outputs the velocity direction for all timesteps in the results file.
res_to_res.exe -va -typeV results.xmdf
Concatenate
Input Switch: -con
Description
Concatenates (joins) two or more results files into one. Each results file must be from the same 1D/2D mesh.
Example
- Joins the water level results contained in the three files into a single file.
res_to_res.exe -con -typeH results_1.xmdf results_2.xmdf results_3.xmdf
Convert
Input Switch: -conv
Description
Converts between .dat and .xmdf format results. Not to be confused with -con (concatenate option described above)!
Examples
- Converts the maximum water level results in the xmdf file into .dat file format.
res_to_res.exe -conv -typeH -t99999 results.xmdf - Converts all datasets and times in the .xmdf file into .dat file format. This will output a number of .dat files.
res_to_res.exe -conv results.xmdf - Converts all times in the .dat file into xmdf file format.
res_to_res.exe -conv results_h.dat
Time of Increase
Input Switch: -toi<cutoff>
Calculates the time taken for the results to increase by the cutoff. For example if a value of 0.2 is used for a depth grid, the output result contains the time required for the depth to increase by 0.2m. If there are depth values greater than 0.2 initially (due to initial water level conditions), the output is the time for the depth to increase by 0.2m. For dry areas it is the time for the depth to reach 0.2m.
Example
- Extracts the time taken for the depth to increase by 0.2m.
res_to_res.exe -toi0.2 -typeD results.xmdf
Ensight (beta)
Input Switch: -ensight
Description
Converts an .xmdf file (.dat not yet supported) into Ensight Gold format.
If the input dataset is corner based (standard output) the Ensight results are output as scalar / vector per node (cell and triangle corners).
If the result is high resolution (Map Output Format == xmdf high res) then the Ensight results are per element. For 2D cells this is based on the cell centre output, for triangles (1D water level lines) this is based on an interpolation of the triangle vertices.
The conversion produces the following output files:
- Ensight case file;
- Ensight geometry file;
- Ensight results as either per node or per element depending on the input file.
This conversion is in its beta stage of development. This utility can currently only process 2D results. 1D channel result are currently not supported.
Any feedback regarding this utility function is welcome and can be sent to support@tuflow.com.
Example
- Converts all datasets in the xmdf file into Ensight format.
res_to_res.exe -ensight results.xmdf
General Options
Batch Mode
Input Switch: -b
Batch mode suppresses prompt to press Enter at end of processing. Used in .bat files where two or more files are to be processed in succession.
Output Filename
Input Switch: -out "output_filename"
Sets the output filename. This is not available for all outputs, particularly where multiple output files are required!
Time Search Tolerance
Input Switch: -dttol<search tolerance>
Allows the user to specify the time search tolerance. This is particularly useful for TUFLOW FV model results, as model uses an adaptive timestep the output time might not exactly match the desired output interval. If hourly output is requested the closest output might actually be 01:00:05 (HH:MM:SS). If extracting results at time 1, the requested time may not be found due to time search tolerance. The default value is 0.001.
XMDF Switches
When working with the .xmdf outputs from TUFLOW, there are some additional input switches are available. This is because the .xmdf file uses a folder structure and multiple output parameters are stored in the same .xmdf file. When converting you can control which dataset is converted using the switches below. These switches are not valid for .dat files as these contain a single parameter for each file. E.g. the _d.dat contains only depth information.
In the xmdf file, the data is stored in the following structure:
Simulation ID/Folder/Dataset. Some examples for simulation "M01_5m_001" are:
M01_5m_001/Maximums/ZAEM1
M01_5m_001/Temporal/Depth
The xmdf specific switches are outlined in the table below:
| Switch | Description |
|---|---|
| "-type<output type>" | Converts the specified output type in an xmdf file. Output types should be specified as per the output type in the .tcf e.g. h (water level), v (velocity), q (unit flow) or d (depth). Output types other than h, v, q and d are not predefined with the -type switch and should be called with -v and/or -s switch. |
| "-s<output id(integer)>" | Converts the specified scalar dataset in an xmdf file. For example, -s1 will convert the first scalar dataset. A list of the available datasets is listed within the DOS window when RES_to_RES is preprocessing results. Check XMDF Dataset Example. To keep the DOS window open write "pause" at the end of the processing batch file and remove -b switch. |
| "-v<output id(integer)>" | Converts the specified vector dataset in an xmdf file. For example, -v1 will convert the first vector dataset. A list of the available datasets is listed within the DOS window when RES_to_RES is preprocessing results. Check XMDF Dataset Example. To keep the DOS window open write "pause" at the end of the processing batch file and remove -b switch. |
| "-Folder<Folder Name>" | Converts all datasets within a particular xmdf file. For example, -Folder"Maximums" will convert all datasets in the \Maximums\ folder. |
| "-path<path name>" | Converts a dataset based on the path in the .xmdf file. For example, -path"Maximums/ZAEM1" would convert the dataset Maximum ZAEM1 dataset. This can be a full path in the .xmdf file or a partial match. E.g.: -path"Maximums/ZAEM1" M01_5m_001.xmdf |
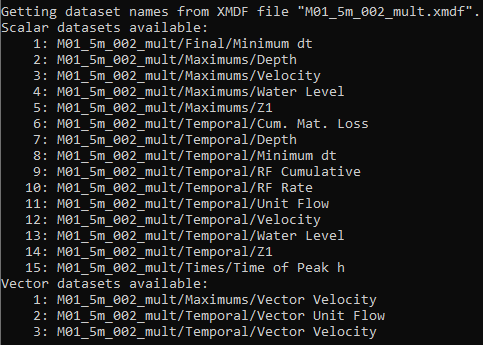
XMDF Dataset Example
Display the datasets available within an XMDF file in a DOS window by starting any operation.
To keep the DOS window open write "pause" at the end of the processing batch file and ensure -b switch is not included.
The list of available datasets will be displayed towards the start of the DOS window.
Examples
res_to_res.exe -xnfo results.xmdf
pause
Displays the following DOS window:
| Up |
|---|