GRID to GRID draft: Difference between revisions
Anne.Kolega (talk | contribs) m →Introduction: The |
|||
| (27 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Introduction= |
=Introduction= |
||
grid_to_grid.exe is a utility that can be used to perform a range of operations on gridded files. The input grids can be a combination of GeoTIFF (.tif), ESRI ASCII |
The grid_to_grid.exe is a utility that can be used to perform a range of operations on gridded files. The input grids can be a combination of GeoTIFF (.tif), ESRI ASCII (.asc), binary float (.flt) geopackage (.gpkg), NetCDF (.nc) and Cloud Optimised GeoTIFFs (.cog) grids, all of which can be input and output from TUFLOW and any of the format can be set as output from the utility.<br> |
||
For some options (such as processing maximums or differences) the input files must be of the same row/column dimensions.<br> |
For some options (such as processing maximums or differences) the input files must be of the same row/column dimensions.<br> |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
|"-src"||For use with -min,-max or various stat options to supress the source grid output. Will only output the minimum, maximum, mean, median, frac grid. The src_legend.csv is also supressed. |
|"-src"||For use with -min,-max or various stat options to supress the source grid output. Will only output the minimum, maximum, mean, median, frac grid. The src_legend.csv is also supressed. |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|"-grc"||For use with the "-classify" option and |
|"-grc"||For use with the "-classify" option and ASC format output. This creates a classified grid (uses name rather than number). This is only valid if using Vertical Mapper, neither QGIS or ArcMap will recognise this format. This can also be used with the -RGB option to specify the output colouring of the grid. |
||
|} |
|} |
||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
==Convert== |
==Convert== |
||
'''"-conv"'''<br> |
'''"-conv"'''<br> |
||
Converts |
Converts grid formats as specified by the output switch.<br> |
||
Example:<br> |
|||
*Converts all |
*Converts all FLT grids to TIF format.<br> |
||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -conv -tif *.flt</tt> |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -conv -tif *.flt</tt> |
||
*Converts the file "DEM.asc" to |
*Converts the file "DEM.asc" to FLT format.<br> |
||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -conv -flt DEM.asc</tt> |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -conv -flt DEM.asc</tt> |
||
* Converts an ASC grid to a GeoTIFF with an LZW compression and horizontal predictor.<br> |
* Converts an ASC grid to a GeoTIFF with an LZW compression and horizontal predictor, see <u>[[#Creation_Options | Creation Options]]</u>.<br> |
||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -conv -tif DEM_M01.asc -co COMPRESS=LZW -co PREDICTOR=2</tt> |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -conv -tif DEM_M01.asc -co COMPRESS=LZW -co PREDICTOR=2</tt> |
||
* Converts GeoTIFF to a Cloud Optimised GeoTIFF. Requires <tt>-out</tt> flag since the extension for COG is also |
* Converts GeoTIFF to a Cloud Optimised GeoTIFF. Requires <tt>-out</tt> flag since the extension for COG is also .tif and the default output file would be the same as the input file.<br> |
||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -conv -cog DEM_M01.tif -out DEM_M01_COG.tif</tt> |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -conv -cog DEM_M01.tif -out DEM_M01_COG.tif</tt> |
||
==Maximum== |
==Maximum== |
||
'''"-max"'''<br> |
'''"-max"'''<br> |
||
Determines the maximum value in all the input |
Determines the maximum value in all the input files. Two output grids are created:<br> |
||
*A numerical grid containing the maximum value.<br> |
*A numerical grid containing the maximum value.<br> |
||
*A classified grid with the |
*A classified grid with the suffix _src which contains the source grid for the maximum value.<br> |
||
Example:<br> |
|||
*Creates a new grid containing the maximum of the 3 input water level grids.<br> |
*Creates a new grid containing the maximum of the 3 input water level grids.<br> |
||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -max Q100_30min_h. |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -max Q100_30min_h.tif Q100_45min_h.tif Q100_60min_h.tif</tt><br> |
||
*As |
*As above, but specifies the output name "Q100_Max_Levels.tif".<br> |
||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -out Q100_Max_Levels. |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -out Q100_Max_Levels.tif -max Q100_30min_h.tif Q100_45min_h.tif Q100_60min_h.tif</tt><br> |
||
*Wildcard character "*" is supported in filenames.<br> |
*Wildcard character "*" is supported in filenames.<br> |
||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -out Q100_Max_Levels. |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -out Q100_Max_Levels.tif -max Q100_*min_h.tif</tt> |
||
* Runs a maximum operation on all FLT grids in a given location and outputs to a GeoPackage raster.<br> |
* Runs a maximum operation on all FLT grids in a given location and outputs to a GeoPackage raster.<br> |
||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -max -out "output_grids.gpkg >> maximum_h" *.flt</tt> |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -max -out "output_grids.gpkg >> maximum_h" *.flt</tt> |
||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
==Difference== |
==Difference== |
||
'''"-dif"'''<br> |
'''"-dif"'''<br> |
||
Takes the difference between the first two |
Takes the difference between the first two grids, the output is the first grid minus the second grid. If an optional third grid is specified, this is used as the output file, otherwise, grid_to_grid creates its own output filename using the names of the two input grids.<br> |
||
Two |
Two grids are output: |
||
*The first is the difference values between the |
*The first is the difference values between the grids. A difference value only occurs at grid cells that have a value in both grids. If the cell has a null value (i.e. the TUFLOW output was dry at that location) in either or both grids, a null value is output. |
||
*A second grid with a “_wd” suffix is output to indicate which |
*A second grid with a “_wd” suffix is output to indicate which grid cells were wet and now dry (value -99) or were dry and now wet (value +99). First grid to be the developed case and second grid to be the existing case. This grid is particularly useful for displaying areas that were previously inundated or previously flood-free.<br> |
||
Example: |
Example: |
||
*Creates new grids comparing the differences in flood levels and extents for: "difference.asc" = "after_h.asc" - "before_h.asc"<br> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
*Runs a difference operation on GeoTIFF outputs.<br> |
*Runs a difference operation on GeoTIFF outputs.<br> |
||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -dif proposed.tif existing.tif</tt> |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -dif proposed.tif existing.tif</tt> |
||
*As above with specified output name "difference.tif".<br> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* Runs a difference operation on GPKG outputs. The layer name needed is assumed to be the same as the database name.<br> |
* Runs a difference operation on GPKG outputs. The layer name needed is assumed to be the same as the database name.<br> |
||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -dif proposed.gpkg existing.gpkg</tt> |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -dif proposed.gpkg existing.gpkg</tt> |
||
* Runs a difference operation on GeoPackage outputs where the layer name is different than the database name.<br> |
* Runs a difference operation on GeoPackage outputs where the layer name is different than the database name, see <u>[[#GPKG_and_NetCDF | GPKG and NetCDF]]</u>.<br> |
||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -dif "proposed_grid_results.gpkg >> proposed_max_h" "existing_grid_results.gpkg >> existing_max_h"</tt> |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -dif "proposed_grid_results.gpkg >> proposed_max_h" "existing_grid_results.gpkg >> existing_max_h"</tt> |
||
| Line 89: | Line 89: | ||
*If two grids are specified, the first value is used for setting the cutoff depth and the values from the second grid are processed.<br> |
*If two grids are specified, the first value is used for setting the cutoff depth and the values from the second grid are processed.<br> |
||
*If three grids are specified, the third grid is used for setting the filename for the output grid. This is ignored if the "-out" option is used.<br> |
*If three grids are specified, the third grid is used for setting the filename for the output grid. This is ignored if the "-out" option is used.<br> |
||
Example: |
|||
Examples: |
|||
*Creates a new depth grid only where the depth is greater than 0.1m.<br> |
*Creates a new depth grid only where the depth is greater than 0.1m.<br> |
||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -cd0.1 depth. |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -cd0.1 depth.tif</tt> |
||
*Creates a new level grid only where the depth is greater than 0.1m.<br> |
*Creates a new level grid only where the depth is greater than 0.1m.<br> |
||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -cd0.1 depth. |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -cd0.1 depth.tif levels.tif</tt> |
||
*As per the example above, but sets the output name as "filtered_levels. |
*As per the example above, but sets the output name as "filtered_levels.tif".<br> |
||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -cd0.1 -out filtered_levels. |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -cd0.1 -out filtered_levels.tif depths.tif levels.tif</tt> |
||
==Resize== |
==Resize== |
||
'''"-resize<factor>"'''<br> |
'''"-resize<factor>"'''<br> |
||
Resize the grid based on the factor above. The factor must be an integer (greater than 1). The output grid has the same origin (lower left) coordinates as the input grid. The new cell size is the factor times the old cell size. |
Resize the grid based on the factor above. The factor must be an integer (greater than 1). The output grid has the same origin (lower left) coordinates as the input grid. The new cell size is the factor times the old cell size. For processing the grid three options are available: |
||
===Average (default)=== |
===Average (default)=== |
||
This is the defualt processing method, which can also be specified with the '''-rm_avg''' (resize method - average) input flag. When processing for each tile in the new grid, the average of all non-null values in the input grid is taken |
This is the defualt processing method, which can also be specified with the '''-rm_avg''' (resize method - average) input flag. When processing for each tile in the new grid, the average of all non-null values in the input grid is taken.<br> |
||
Example: |
Example: |
||
*Creates a new 10m DEM |
*Creates a new 10m DEM based on the the 2m DEM using an averaging approach.<br> |
||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -resize5 -out DEM_10m. |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -resize5 -out DEM_10m.tif DEM_2m.tif</tt> |
||
===Minimum=== |
===Minimum=== |
||
Alternative processing method for resize, specified with the '''-rm_min''' (resize method - minimum) flag. At each output grid the values |
Alternative processing method for resize, specified with the '''-rm_min''' (resize method - minimum) flag. At each output grid the values are the minimum of the values in the input grid.<br> |
||
Example: |
Example: |
||
*Creates a new 10m DEM |
*Creates a new 10m DEM based on the the 2m DEM using an minimum approach.<br> |
||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -resize5 -rm_min -out DEM_10m_min. |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -resize5 -rm_min -out DEM_10m_min.tif DEM_2m.tif</tt> |
||
===Maximum=== |
===Maximum=== |
||
Alternative processing method for resize, specified with the '''-rm_max''' (resize method - maximum) flag. At each output grid the values |
Alternative processing method for resize, specified with the '''-rm_max''' (resize method - maximum) flag. At each output grid the values are the maximum of the values in the input grid.<br> |
||
Example: |
Example: |
||
*Creates a new 10m DEM |
*Creates a new 10m DEM based on the the 2m DEM using an maximum approach.<br> |
||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -resize5 -rm_max -out DEM_10m_max. |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -resize5 -rm_max -out DEM_10m_max.tif DEM_2m.tif</tt> |
||
==Transform== |
==Transform== |
||
Transforms the values using a simple y = mx + c approach |
Transforms the values using a simple y = mx + c approach. The multiplier (m) is specified with flag '''-trans_m<value>'''. The add value (c) with flag '''-trans_c<value>'''. Only one value is required.<br> |
||
Example: |
|||
Examples: |
|||
*Multiplies all values by 0.3048.<br> |
*Multiplies all values by 0.3048.<br> |
||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -trans_m0.3048 DEM. |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -trans_m0.3048 DEM.tif</tt> |
||
*Multiplies all values by 0.3048 and then adds 10.0.<br> |
*Multiplies all values by 0.3048 and then adds 10.0.<br> |
||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -trans_m0.3048 -trans_c10 DEM. |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -trans_m0.3048 -trans_c10 DEM.tif</tt> |
||
==Decimal== |
==Decimal== |
||
Converts |
Converts grids with specified number of decimal spaces. For example ASC format created directly from TUFLOW comes only with three decimal spaces, FLT and TIF format has more decimal spaces.<br> |
||
Example: |
Example: |
||
*Converts all |
*Converts all TIF grids to ASC format with 5 decimal spaces.<br> |
||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -conv -decimal5 *. |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -conv -asc -decimal5 *.tif</tt> |
||
==Classify== |
==Classify== |
||
Classifies the grid based on the input classifications. |
Classifies the grid based on the input classifications. The output file is a classified grid. The classification .csv file should have two columns, cutoff value and name (in that order). The first line in .csv treated as a header line and ignored. Any values over the greatest cutoff with be outputted to class "above".<br> |
||
{| class="wikitable" |
{| class="wikitable" |
||
| Line 146: | Line 146: | ||
|} |
|} |
||
Example: |
|||
Examples: |
|||
*Outputs a classified grid, based on the cut off values and names in the "classifications.csv".<br> |
*Outputs a classified grid, based on the cut off values and names in the "classifications.csv".<br> |
||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -classify classifications.csv results_VMax. |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -classify classifications.csv results_VMax.tif</tt> |
||
*If using vertical mapper the -grc option can be used to create |
*If using vertical mapper the -grc option can be used to create flt file in classified grid format. In this format, rather than storing a numerical value when interrogating an area, a label is returned. This format is not recognised by ArcMap or QGIS. If using the grc option it is also possible to specify the desired RGB (red, green, blue) values for the output grid in the .csv file used for the classification. The RGB values should be specified in the 3-5th columns of the .csv file.<br> |
||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -RGB -grc -classify depth_classify.csv results_dMax. |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -RGB -grc -classify depth_classify.csv results_dMax.flt</tt><br> |
||
:{| class="wikitable" |
:{| class="wikitable" |
||
| Line 174: | Line 174: | ||
==Extract Breaklines from DEM== |
==Extract Breaklines from DEM== |
||
'''"-brkline <gis file in 2d_zsh format>"'''<br> |
'''"-brkline <gis file in 2d_zsh format>"'''<br> |
||
| ⚫ | Extracts elevations from a DEM for breaklines in the 2d_zsh format. This GIS input should have four attributes, z, dz, width and shape_options, as described in the <u>[https://docs.tuflow.com/classic-hpc/manual/latest/ TUFLOW Manual]</u>. For the utility the '''dz''', '''shape_width''' and the '''shape_options''' are used. Valid shape_options are "Max" and "Min" or blank (average used). The utility extracts an elevation at each vertex along the line.<br> |
||
This feature was added to the 2013-06-AA version of the utility.<br> |
|||
| ⚫ | Extracts elevations from a DEM for breaklines in the 2d_zsh format. This GIS input should have four attributes, z, dz, width and shape_options, as described in the <u>[https://docs.tuflow.com/classic-hpc/manual/latest/ TUFLOW Manual]</u>. For the utility the '''dz''', '''shape_width''' and the '''shape_options''' are used. Valid shape_options are "Max" and "Min" or blank (average used). The utility |
||
Depending on the line width and DEM cell size, the following methods are used:<br> |
Depending on the line width and DEM cell size, the following methods are used:<br> |
||
* If the width is set to 0, the closest DEM value to the vertex is used. If a "shape_option" is specified this is ignored. |
* If the width is set to 0, the closest DEM value to the vertex is used. If a "shape_option" is specified, this is ignored. |
||
* If the width is greater than 0, but less than 1.5 times the DEM cell size, the four DEM values surrounding the vertex are used. If max or min is specified in the "shape_option" the max or min of the four values is used. If max or min option is not specified (attribute is blank), the average of the four values is used. |
* If the width is greater than 0, but less than 1.5 times the DEM cell size, the four DEM values surrounding the vertex are used. If max or min is specified in the "shape_option" the max or min of the four values is used. If max or min option is not specified (attribute is blank), the average of the four values is used. |
||
* If the width is greater than 1.5 times the DEM cell size, at each vertex a buffer region (search radius) is created and all non null DEM values within the buffer object are processed. The diameter of the buffer region is equal to the width specified. If max or min option is not specified, the average of the values within the region is used. These buffer regions are outputted as a separate file, if '''"-check"''' switch is specified in the batch command.<br> |
* If the width is greater than 1.5 times the DEM cell size, at each vertex a buffer region (search radius) is created and all non null DEM values within the buffer object are processed. The diameter of the buffer region is equal to the width specified. If max or min option is not specified, the average of the values within the region is used. These buffer regions are outputted as a separate file, if '''"-check"''' switch is specified in the batch command.<br> |
||
| Line 183: | Line 182: | ||
'''NOTE:''' For the output GIS file, the '''dz''' attribute is set to 0.0 regardless of the value set in the input field. <br> |
'''NOTE:''' For the output GIS file, the '''dz''' attribute is set to 0.0 regardless of the value set in the input field. <br> |
||
Example: |
Example: |
||
*<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -brkline 2d_zsh_breaklines_L.shp DEM. |
*<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -brkline 2d_zsh_breaklines_L.shp DEM.flt</tt> |
||
*<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -brkline 2d_zsh_breaklines_L.gpkg DEM.tif</tt> |
*<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -brkline 2d_zsh_breaklines_L.gpkg DEM.tif</tt> |
||
==Fuzzy Map== |
==Fuzzy Map== |
||
'''"-fuzzy <input grids>"'''<br> |
'''"-fuzzy <input grids>"'''<br> |
||
This feature was added to the 2014-03-AB version of the utility.<br> |
|||
A fuzzy map can be used when comparing a large number of simulations.<br> |
A fuzzy map can be used when comparing a large number of simulations.<br> |
||
For each input grid (or scenario) the grid is classed as either 1 if the results grid is wet or 0 if dry. |
For each input grid (or scenario) the grid is classed as either 1 if the results grid is wet or 0 if dry. The total score for each grid cell is calculated and then divided by the total number of input grids. A value of 1 indicates that the cell was wet in each simulation ,a value of 0 is dry in all simulations. Grids with a value of 0.5 are most sensitive.<br> |
||
This can be useful for quantifying the sensitivity of the model to parameters.<br> |
This can be useful for quantifying the sensitivity of the model to parameters.<br> |
||
Example: |
Example: |
||
*Create a fuzzy map from all maximum depth grids in the directory.<br> |
*Create a fuzzy map from all maximum depth grids in the directory.<br> |
||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -fuzzy *_d_Max. |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -fuzzy *_d_Max.tif</tt> |
||
==Histogram== |
==Histogram== |
||
'''"-histogram bins.csv <input grid>"'''<br> |
'''"-histogram bins.csv <input grid>"'''<br> |
||
This feature was added to the 2014-03-AB version of the utility.<br> |
|||
Calculates the number of cells and percentage of cells that fall in each range. Requires and input .csv file containing the bin values.<br> |
Calculates the number of cells and percentage of cells that fall in each range. Requires and input .csv file containing the bin values.<br> |
||
Example: |
|||
Examples: |
|||
*An example inputs bin file is:<br> |
*An example inputs bin file is:<br> |
||
:{| class="wikitable" |
:{| class="wikitable" |
||
| Line 242: | Line 239: | ||
|Above 5.0|| Above 5.0 || 973 || 0.06 |
|Above 5.0|| Above 5.0 || 973 || 0.06 |
||
|} |
|} |
||
*Example |
*Example: |
||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe –histogram histogram_bins.csv results_d_Max. |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe –histogram histogram_bins.csv results_d_Max.tif</tt> |
||
==Extract 1D Model Inputs== |
==Extract 1D Model Inputs== |
||
'''"-egc control_file.egc"'''<br> |
'''"-egc control_file.egc"'''<br> |
||
This allows 1D Network (1d_nwk) and/or 1D |
This allows 1D Network (1d_nwk) and/or 1D cross-sections to be extracted from a series of grids.<br> |
||
A simple input file similar to the TUFLOW geometry control file is input into the utility. This is nominally given the extension .egc (Estry Geometry Control).<br> |
A simple input file similar to the TUFLOW geometry control file is input into the utility. This is nominally given the extension .egc (Estry Geometry Control).<br> |
||
<br> |
<br> |
||
| Line 307: | Line 304: | ||
|Read GIS XS == <1d_cut GIS file>|| Reads the cross-section cut lines, these are described above. |
|Read GIS XS == <1d_cut GIS file>|| Reads the cross-section cut lines, these are described above. |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|Read GIS FLC == <GIS file>|| Optional GIS layer of polygons that can be used to specify form loss coefficients to the 1d_nwk layer. A single GIS (float) attribute is required. A FLC value of greater than 0 will be split between all 1d_nwk channels within the region. A FLC value of less than 0, will apply the absolute value to all channels within the polygon. For example if an FLC value of -0.1 is specified, all channels that fall within the polygon will have a form_loss attribute of 0.1. If a channel falls within multiple polygons, the form loss values will be added. |
|Read GIS FLC == <GIS file>|| Optional GIS layer of polygons that can be used to specify form loss coefficients to the 1d_nwk layer. A single GIS (float) attribute is required. A FLC value of greater than 0 will be split between all 1d_nwk channels within the region. A FLC value of less than 0, will apply the absolute value to all channels within the polygon. For example if an FLC value of -0.1 is specified, all channels that fall within the polygon will have a form_loss attribute of 0.1. If a channel falls within multiple polygons, the form loss values will be added. |
||
Reads the polygons off losses from GIS layer. cross-section cut lines, these are described above. |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
|Set XS dx == <distance>|| Sets the default distance across section to extract elevations and materials data. This can be specified on the cut lines as detailed above. |
|Set XS dx == <distance>|| Sets the default distance across section to extract elevations and materials data. This can be specified on the cut lines as detailed above. |
||
| Line 332: | Line 328: | ||
|FLC per Unit Length == <form loss per unit length> || The form loss per unit length is written to the "exit_loss" attribute of all 1d_nwk channels. |
|FLC per Unit Length == <form loss per unit length> || The form loss per unit length is written to the "exit_loss" attribute of all 1d_nwk channels. |
||
|} |
|} |
||
Example |
Example: |
||
*<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -egc MR_1d_001.egc</tt> |
*<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -egc MR_1d_001.egc</tt> |
||
| Line 347: | Line 343: | ||
Set XS Mat == 1 !default Material ID of 1 |
Set XS Mat == 1 !default Material ID of 1 |
||
Read Grid Mat == grid\grid_5m_2d_mat_MR_001. |
Read Grid Mat == grid\grid_5m_2d_mat_MR_001.tif |
||
Set XS Z == 99 |
Set XS Z == 99 |
||
Read Grid Z == grid\dem_5m_regional. |
Read Grid Z == grid\dem_5m_regional.tif |
||
Read Grid Z == grid\dem_1m_bathymetry. |
Read Grid Z == grid\dem_1m_bathymetry.tif |
||
Read Grid Z == grid\dem_1m_survey. |
Read Grid Z == grid\dem_1m_survey.tif |
||
</pre> |
</pre> |
||
| Line 360: | Line 356: | ||
The input GIS region file should have the same attributes as the 1d_tab file format produced by TUFLOW. The first attribute ("Source" ) should contain a valid .csv file name.<br> |
The input GIS region file should have the same attributes as the 1d_tab file format produced by TUFLOW. The first attribute ("Source" ) should contain a valid .csv file name.<br> |
||
The out nodal area table extends from the minimum to the maximum elevation in the DEM. A user defined minimum value can be specified using the "Skew" attribute of the GIS region.<br> |
The out nodal area table extends from the minimum to the maximum elevation in the DEM. A user defined minimum value can be specified using the "Skew" attribute of the GIS region.<br> |
||
Example |
Example: |
||
*<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -na |
*<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -na storage_R.shp DEM_1m.tif</tt> |
||
==Calibration Points== |
==Calibration Points== |
||
'''"-cp <cp_file>"'''<br> |
'''"-cp <cp_file>"'''<br> |
||
For appending the value from a |
For appending the value from a grid file to a .mif or .shp file. The cp_file contains points representing locations where results are extracted from TUFLOW. The file format includes two attributes. The first attribute is a numeric field containing the recorded value. The second field is a char(100) text field containing the cp name.<br> |
||
'''"-config <config_file>"''' (optional)<br> |
'''"-config <config_file>"''' (optional)<br> |
||
Points to a csv file containing accuracy thresholds and style control options, e.g. symbol, colour and size.<br> |
Points to a csv file containing accuracy thresholds and style control options, e.g. symbol, colour and size.<br> |
||
| Line 372: | Line 368: | ||
'''"-cpmm<mm>"''' (optional)<br> |
'''"-cpmm<mm>"''' (optional)<br> |
||
The second search radius used to search for maximum and minimum values in meters.<br> |
The second search radius used to search for maximum and minimum values in meters.<br> |
||
Example |
Example: |
||
*<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -cp Flood_Marks.MIF -config diff_config.csv -cpsd100 -cpmm50 results_h_Max. |
*<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -cp Flood_Marks.MIF -config diff_config.csv -cpsd100 -cpmm50 results_h_Max.tif</tt><br> |
||
==Statistics== |
==Statistics== |
||
<big>'''"-stat<type>"'''</big> |
<big>'''"-stat<type>"'''</big> |
||
The grid_to_grid.exe utility allows the user to perform a number of statistical analyses on a group of input grids. This is particularly useful when extracting information from assessments that produce multiple result files for a single event, for example, processing grids from an ensemble assessment with numerous temporal pattern arrangements. |
|||
The available options are: |
The available options are: |
||
| Line 396: | Line 392: | ||
* A value grid: the resulting median value |
* A value grid: the resulting median value |
||
* An SRC grid: a grid listing which source input grid the median result value came from (a corresponding .csv file is also written as a legend)<br> |
* An SRC grid: a grid listing which source input grid the median result value came from (a corresponding .csv file is also written as a legend)<br> |
||
Example |
Example: |
||
*<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -statMedian Q100_30min_TP1_h. |
*<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -statMedian Q100_30min_TP1_h.tif Q100_30min_TP2_h.tif Q100_30min_TP3_h.tif Q100_30min_TP4_h.tif ... Q100_30min_TP10_h.tif </tt><br> |
||
[[File: asc_to_asc_statsMedian_eg.PNG|1000px|]]<br> |
[[File: asc_to_asc_statsMedian_eg.PNG|1000px|]]<br> |
||
<br> |
<br> |
||
Note, the median value for |
Note, the median value for the example below is a 'NULL' value, the output is a dry cell. 7 out of the 10 inputs are dry at this particular cell. Once the outputs are ordered (with NULL showing at the lowest spots), the median (6th) value for the cell is 'NULL' (dry) and '8' is the source grid output. |
||
<br> |
<br> |
||
[[File:A2A median.png|400px]]<br> |
[[File:A2A median.png|400px]]<br> |
||
| Line 410: | Line 406: | ||
* A value grid: the resulting value |
* A value grid: the resulting value |
||
* An SRC grid: a grid listing which source input grid the result value came from or was the next above (a corresponding .csv file is also written as a legend)<br> |
* An SRC grid: a grid listing which source input grid the result value came from or was the next above (a corresponding .csv file is also written as a legend)<br> |
||
Example |
Example: |
||
*<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -statMean Q100_30min_*_h. |
*<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -statMean Q100_30min_*_h.tif</tt><br> |
||
==="-statFrac"=== |
==="-statFrac"=== |
||
| Line 417: | Line 413: | ||
The utility outputs one grid: |
The utility outputs one grid: |
||
* A Frac grid: the resulting |
* A Frac grid: the resulting fraction value<br> |
||
Example |
Example: |
||
*<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -statFrac Q100_30min_*_h. |
*<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -statFrac Q100_30min_*_h.tif</tt><br> |
||
==="-statMin"=== |
==="-statMin"=== |
||
The -statMin flag outputs the minimum value at each grid cell from all the input grids. |
The -statMin flag outputs the minimum value at each grid cell from all the input grids. This flag is analogous with the [[#Minimum|-Min]] operation flag. |
||
The utility outputs two grids: |
The utility outputs two grids: |
||
* A value grid: the resulting value |
* A value grid: the resulting value |
||
* An SRC grid: a grid listing which source input grid the minimum result value came from (a corresponding .csv file is also written as a legend)<br> |
* An SRC grid: a grid listing which source input grid the minimum result value came from (a corresponding .csv file is also written as a legend)<br> |
||
Example |
Example: |
||
*<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -statMin Q100_30min_*_h. |
*<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -statMin Q100_30min_*_h.tif</tt><br> |
||
==="-statMax"=== |
==="-statMax"=== |
||
| Line 436: | Line 432: | ||
* A value grid: the resulting value |
* A value grid: the resulting value |
||
* An SRC grid: a grid listing which source input grid the maximum result value came from (a corresponding .csv file is also written as a legend)<br> |
* An SRC grid: a grid listing which source input grid the maximum result value came from (a corresponding .csv file is also written as a legend)<br> |
||
Example |
Example: |
||
*<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -statMax Q100_30min_*_h. |
*<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -statMax Q100_30min_*_h.tif</tt><br> |
||
==="-statAll"=== |
==="-statAll"=== |
||
| Line 446: | Line 442: | ||
* An SRC grid: for the median, mean, min and max calculations (calculation of source grids as detailed above) |
* An SRC grid: for the median, mean, min and max calculations (calculation of source grids as detailed above) |
||
* A .csv file that contains the legend for all SRC grids<br> |
* A .csv file that contains the legend for all SRC grids<br> |
||
Example |
Example: |
||
*<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -statAll Q100_30min_*_h. |
*<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -statAll Q100_30min_*_h.tif</tt><br> |
||
==="-statRank<integer id>"=== |
==="-statRank<integer id>"=== |
||
The -statRank<integer> flag outputs the |
The -statRank<integer> flag outputs the n<integer> ranked value at each grid cell from all the input grids. All the input grids are considered, regardless of if the grid cell is dry in some of the input grids (dry areas are still ranked as low e.g. Rank1, Rank2 and so on). For example, if the number of input grids is 10, at each grid cell the values are ranked lowest to highest (from 1 to 10). -statRank8 will output results taken from the 8th ranked grid. In this example, -statRank1 is equivalent to Min, -statRank10 is equivalent to Max, and -statRank6 is equivalent to Median. The Rank flag allows additional functionality that lets users extract results in between those that are pre-programmed. |
||
The utility outputs two grids: |
The utility outputs two grids: |
||
* A value grid: the resulting value |
* A value grid: the resulting value |
||
* An SRC grid: a grid listing which source input grid the ranked result value came from (a corresponding .csv file is also written as a legend)<br> |
* An SRC grid: a grid listing which source input grid the ranked result value came from (a corresponding .csv file is also written as a legend)<br> |
||
Example |
Example: |
||
*<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -statRank5 Q100_30min_*_h. |
*<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -statRank5 Q100_30min_*_h.tif</tt><br> |
||
==Flood Extent== |
==Flood Extent== |
||
| ⚫ | |||
Returns a simple grid with value of 1 where the input grid has an active, non-zero value.<br> |
Returns a simple grid with value of 1 where the input grid has an active, non-zero value.<br> |
||
Example |
Example: |
||
*<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -fe results_dMax. |
*<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -fe results_dMax.tif</tt><br> |
||
==Remap== |
==Remap== |
||
| ⚫ | |||
Remaps coarser resolution water level grid to a finer resolution DEM.<br> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
Sets the coarser resolution water level grid to remap from.<br> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
Sets the finer resolution DEM.<br> |
|||
The default interpolation method is TIN. But "-idw_npt<number of points>" flag can be used to change the interpolation method to IDW and set the number of points used for IDW interpolation (default is 12).<br> |
The default interpolation method is TIN. But "-idw_npt<number of points>" flag can be used to change the interpolation method to IDW and set the number of points used for IDW interpolation (default is 12).<br> |
||
Example: |
|||
Examples: |
|||
* |
*Remaps water level grid to the resolution of the DEM file:<br> |
||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -remap -wl lowres_h. |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -remap -wl lowres_h.tif -dem DEM_highres.tif</tt> |
||
*The utility can also |
*The utility can also remap depth output grids to the resolution of the DEM file:<br> |
||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -remap -wl lowres_h. |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -remap -wl lowres_h.tif -dem DEM_highres.tif lowres_d.tif</tt> |
||
*The utility can also apply a buffer distance or add a freeboard. The below applies a buffer distance of 20m, and adds a freeboard of 0.2m to the original water level grid.<br> |
|||
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -remap -fb0.2 -bd20 -wl lowres_h. |
:<tt>grid_to_grid.exe -remap -fb0.2 -bd20 -wl lowres_h.tif -dem DEM_highres.tif</tt> |
||
| ⚫ | Note |
||
| ⚫ | Note, for any output types other than depth, this utility does NOT interpolate the result from the coarser grid to the finer grid, but only extends/reduces the output extent to the dry/wet extent. More discussions on this function is documented here <u>[[TUFLOW_Remapping | TUFLOW Remapping Tool]]</u>.<br> |
||
=GPKG and NetCDF= |
=GPKG and NetCDF= |
||
| Line 490: | Line 484: | ||
=Creation Options= |
=Creation Options= |
||
The grid_to_grid.exe supports GDAL style creation options. Creation options can be passed in using the -co flag then the name of the creation option and the value:<Br> |
The grid_to_grid.exe supports GDAL style creation options. Creation options can be passed in using the "-co" flag then the name of the creation option and the value:<Br> |
||
<pre>-co COMPRESS=DEFLATE</pre> |
<pre>-co COMPRESS=DEFLATE</pre> |
||
Multiple creation options can be used (each will require its own -co flag).<Br> |
Multiple creation options can be used (each will require its own "-co" flag).<Br> |
||
<Br> |
<Br> |
||
The creation options have adopted the same naming as GDAL (more information on the options can be found at <b><u>[https://gdal.org https://gdal.org]</u></b>), however, not all options in GDAL are supported in the grid_to_grid.exe utility. The following creation options are supported:<Br> |
The creation options have adopted the same naming as GDAL (more information on the options can be found at <b><u>[https://gdal.org https://gdal.org]</u></b>), however, not all options in GDAL are supported in the grid_to_grid.exe utility. The following creation options are supported:<Br> |
||
| Line 511: | Line 505: | ||
====NetCDF==== |
====NetCDF==== |
||
* COMPRESS=NONE/DEFLATE- output compression. Default - DEFLATE |
* COMPRESS=NONE/DEFLATE- output compression. Default - DEFLATE |
||
* ZLEVEL=[0-9] - Compression level. Zero is no compression, 9 is |
* ZLEVEL=[0-9] - Compression level. Zero is no compression, 9 is highest compression. Only supported for DEFLATE compression method. Default - 9. |
||
====ASC==== |
====ASC==== |
||
* DECIMAL_PRECISION=N - The number of decimal places in the output. This option is analogous to the <tt>"-decimal[N]"</tt> switch. Default - 3. |
* DECIMAL_PRECISION=N - The number of decimal places in the output. This option is analogous to the <tt>"-decimal[N]"</tt> switch. Default - 3. |
||
Latest revision as of 09:06, 27 November 2024
Introduction
The grid_to_grid.exe is a utility that can be used to perform a range of operations on gridded files. The input grids can be a combination of GeoTIFF (.tif), ESRI ASCII (.asc), binary float (.flt) geopackage (.gpkg), NetCDF (.nc) and Cloud Optimised GeoTIFFs (.cog) grids, all of which can be input and output from TUFLOW and any of the format can be set as output from the utility.
For some options (such as processing maximums or differences) the input files must be of the same row/column dimensions.
Output Switches
| Switch | Description |
|---|---|
| "-tif" | Output to GeoTIFF format. |
| "-asc" | Output to ASC format. |
| "-flt" | Output to FLT format. |
| "-gpkg" | Output to GeoPackage format, see GPKG and NetCDF. |
| "-nc" | Output to NetCDF format, specifies that the output format should be NetCDF for all operations, see GPKG and NetCDF. |
| "-cog" | Output to Cloud Optimised GeoTIFF format, overviews (pyramids) for GPKG rasters. |
| "-out <output_name/output_name.ext>" | Specifies output file name. When output extension is included in the name it also specifies output extension. A space is required between the -out and the filename. |
| "-co" | Creation option switch, see Creation Options. |
| "-b" | Run the utility in batch mode, this suppresses the prompt to press enter at the end of processing. Used in .bat files where two or more files are to be processed. The -b flag should be placed after the grid_to_grid.exe call, before the function command. For example: grid_to_grid.exe -b -brkline 2d_zsh_breaklines_L.gpkg DEM.tif |
| "-check" | This creates check files for the data processing if applicable. |
| "-src" | For use with -min,-max or various stat options to supress the source grid output. Will only output the minimum, maximum, mean, median, frac grid. The src_legend.csv is also supressed. |
| "-grc" | For use with the "-classify" option and ASC format output. This creates a classified grid (uses name rather than number). This is only valid if using Vertical Mapper, neither QGIS or ArcMap will recognise this format. This can also be used with the -RGB option to specify the output colouring of the grid. |
Operations
Convert
"-conv"
Converts grid formats as specified by the output switch.
Example:
- Converts all FLT grids to TIF format.
- grid_to_grid.exe -conv -tif *.flt
- Converts the file "DEM.asc" to FLT format.
- grid_to_grid.exe -conv -flt DEM.asc
- Converts an ASC grid to a GeoTIFF with an LZW compression and horizontal predictor, see Creation Options.
- grid_to_grid.exe -conv -tif DEM_M01.asc -co COMPRESS=LZW -co PREDICTOR=2
- Converts GeoTIFF to a Cloud Optimised GeoTIFF. Requires -out flag since the extension for COG is also .tif and the default output file would be the same as the input file.
- grid_to_grid.exe -conv -cog DEM_M01.tif -out DEM_M01_COG.tif
Maximum
"-max"
Determines the maximum value in all the input files. Two output grids are created:
- A numerical grid containing the maximum value.
- A classified grid with the suffix _src which contains the source grid for the maximum value.
Example:
- Creates a new grid containing the maximum of the 3 input water level grids.
- grid_to_grid.exe -max Q100_30min_h.tif Q100_45min_h.tif Q100_60min_h.tif
- As above, but specifies the output name "Q100_Max_Levels.tif".
- grid_to_grid.exe -out Q100_Max_Levels.tif -max Q100_30min_h.tif Q100_45min_h.tif Q100_60min_h.tif
- Wildcard character "*" is supported in filenames.
- grid_to_grid.exe -out Q100_Max_Levels.tif -max Q100_*min_h.tif
- Runs a maximum operation on all FLT grids in a given location and outputs to a GeoPackage raster.
- grid_to_grid.exe -max -out "output_grids.gpkg >> maximum_h" *.flt
Difference
"-dif"
Takes the difference between the first two grids, the output is the first grid minus the second grid. If an optional third grid is specified, this is used as the output file, otherwise, grid_to_grid creates its own output filename using the names of the two input grids.
Two grids are output:
- The first is the difference values between the grids. A difference value only occurs at grid cells that have a value in both grids. If the cell has a null value (i.e. the TUFLOW output was dry at that location) in either or both grids, a null value is output.
- A second grid with a “_wd” suffix is output to indicate which grid cells were wet and now dry (value -99) or were dry and now wet (value +99). First grid to be the developed case and second grid to be the existing case. This grid is particularly useful for displaying areas that were previously inundated or previously flood-free.
Example:
- Runs a difference operation on GeoTIFF outputs.
- grid_to_grid.exe -dif proposed.tif existing.tif
- As above with specified output name "difference.tif".
- grid_to_grid.exe -out difference.tif -dif proposed.tif existing.tif
- Runs a difference operation on GPKG outputs. The layer name needed is assumed to be the same as the database name.
- grid_to_grid.exe -dif proposed.gpkg existing.gpkg
- Runs a difference operation on GeoPackage outputs where the layer name is different than the database name, see GPKG and NetCDF.
- grid_to_grid.exe -dif "proposed_grid_results.gpkg >> proposed_max_h" "existing_grid_results.gpkg >> existing_max_h"
Secondary options (only one can be used):
- "-nowetdry" does not carry out a wet/dry test. If both cells are active a difference is calculated.
- "-change" calculates change even if one cell is null (wet / dry areas). Assumes a "dry" cell has a value of zero. Can be used to calculate depth change.
Cutoff Depth
"-cd<cutoff value>"
Outputs a new file only where the value is greater than the cutoff value.
- If only one grid is specified this grid is processed.
- If two grids are specified, the first value is used for setting the cutoff depth and the values from the second grid are processed.
- If three grids are specified, the third grid is used for setting the filename for the output grid. This is ignored if the "-out" option is used.
Example:
- Creates a new depth grid only where the depth is greater than 0.1m.
- grid_to_grid.exe -cd0.1 depth.tif
- Creates a new level grid only where the depth is greater than 0.1m.
- grid_to_grid.exe -cd0.1 depth.tif levels.tif
- As per the example above, but sets the output name as "filtered_levels.tif".
- grid_to_grid.exe -cd0.1 -out filtered_levels.tif depths.tif levels.tif
Resize
"-resize<factor>"
Resize the grid based on the factor above. The factor must be an integer (greater than 1). The output grid has the same origin (lower left) coordinates as the input grid. The new cell size is the factor times the old cell size. For processing the grid three options are available:
Average (default)
This is the defualt processing method, which can also be specified with the -rm_avg (resize method - average) input flag. When processing for each tile in the new grid, the average of all non-null values in the input grid is taken.
Example:
- Creates a new 10m DEM based on the the 2m DEM using an averaging approach.
- grid_to_grid.exe -resize5 -out DEM_10m.tif DEM_2m.tif
Minimum
Alternative processing method for resize, specified with the -rm_min (resize method - minimum) flag. At each output grid the values are the minimum of the values in the input grid.
Example:
- Creates a new 10m DEM based on the the 2m DEM using an minimum approach.
- grid_to_grid.exe -resize5 -rm_min -out DEM_10m_min.tif DEM_2m.tif
Maximum
Alternative processing method for resize, specified with the -rm_max (resize method - maximum) flag. At each output grid the values are the maximum of the values in the input grid.
Example:
- Creates a new 10m DEM based on the the 2m DEM using an maximum approach.
- grid_to_grid.exe -resize5 -rm_max -out DEM_10m_max.tif DEM_2m.tif
Transform
Transforms the values using a simple y = mx + c approach. The multiplier (m) is specified with flag -trans_m<value>. The add value (c) with flag -trans_c<value>. Only one value is required.
Example:
- Multiplies all values by 0.3048.
- grid_to_grid.exe -trans_m0.3048 DEM.tif
- Multiplies all values by 0.3048 and then adds 10.0.
- grid_to_grid.exe -trans_m0.3048 -trans_c10 DEM.tif
Decimal
Converts grids with specified number of decimal spaces. For example ASC format created directly from TUFLOW comes only with three decimal spaces, FLT and TIF format has more decimal spaces.
Example:
- Converts all TIF grids to ASC format with 5 decimal spaces.
- grid_to_grid.exe -conv -asc -decimal5 *.tif
Classify
Classifies the grid based on the input classifications. The output file is a classified grid. The classification .csv file should have two columns, cutoff value and name (in that order). The first line in .csv treated as a header line and ignored. Any values over the greatest cutoff with be outputted to class "above".
| Cutoff Value | Name |
|---|---|
| 0.5 | Less than 0.5 |
| 1.0 | 0.5 to 1.0 |
| 2.0 | 1.0 to 2.0 |
Example:
- Outputs a classified grid, based on the cut off values and names in the "classifications.csv".
- grid_to_grid.exe -classify classifications.csv results_VMax.tif
- If using vertical mapper the -grc option can be used to create flt file in classified grid format. In this format, rather than storing a numerical value when interrogating an area, a label is returned. This format is not recognised by ArcMap or QGIS. If using the grc option it is also possible to specify the desired RGB (red, green, blue) values for the output grid in the .csv file used for the classification. The RGB values should be specified in the 3-5th columns of the .csv file.
- grid_to_grid.exe -RGB -grc -classify depth_classify.csv results_dMax.flt
Cutoff Value Name R G B 0.5 Less than 0.5 0 0 192 1.0 0.5 to 1.0 0 0 128 2.0 1.0 to 2.0 0 0 64
In the image below two grids are shown in MapInfo / Vertical Mapper, one is classified without the -grc option and a class number is returned for the grid. The second grid has been created with the -grc option shown, when querying this the label is returned instead.

Extract Breaklines from DEM
"-brkline <gis file in 2d_zsh format>"
Extracts elevations from a DEM for breaklines in the 2d_zsh format. This GIS input should have four attributes, z, dz, width and shape_options, as described in the TUFLOW Manual. For the utility the dz, shape_width and the shape_options are used. Valid shape_options are "Max" and "Min" or blank (average used). The utility extracts an elevation at each vertex along the line.
Depending on the line width and DEM cell size, the following methods are used:
- If the width is set to 0, the closest DEM value to the vertex is used. If a "shape_option" is specified, this is ignored.
- If the width is greater than 0, but less than 1.5 times the DEM cell size, the four DEM values surrounding the vertex are used. If max or min is specified in the "shape_option" the max or min of the four values is used. If max or min option is not specified (attribute is blank), the average of the four values is used.
- If the width is greater than 1.5 times the DEM cell size, at each vertex a buffer region (search radius) is created and all non null DEM values within the buffer object are processed. The diameter of the buffer region is equal to the width specified. If max or min option is not specified, the average of the values within the region is used. These buffer regions are outputted as a separate file, if "-check" switch is specified in the batch command.
If a dz value is specified this can be used to control the spacing of vertices along the line. If a dz value of 100 is specified the maximum spacing along the line is 100 (metres or feet), if the existing vertices along the line are greater than 100 (m or ft) apart additional vertices are inserted. The method for inserting additional vertices creates equally spaced vertices. For example, if two vertices along a line are spaced 250m apart and a dz attribute of 100m is specified three line segments of 83.3m will be created as opposed to two segments of 100m and one segment of 50m.
NOTE: For the output GIS file, the dz attribute is set to 0.0 regardless of the value set in the input field.
Example:
- grid_to_grid.exe -brkline 2d_zsh_breaklines_L.shp DEM.flt
- grid_to_grid.exe -brkline 2d_zsh_breaklines_L.gpkg DEM.tif
Fuzzy Map
"-fuzzy <input grids>"
A fuzzy map can be used when comparing a large number of simulations.
For each input grid (or scenario) the grid is classed as either 1 if the results grid is wet or 0 if dry. The total score for each grid cell is calculated and then divided by the total number of input grids. A value of 1 indicates that the cell was wet in each simulation ,a value of 0 is dry in all simulations. Grids with a value of 0.5 are most sensitive.
This can be useful for quantifying the sensitivity of the model to parameters.
Example:
- Create a fuzzy map from all maximum depth grids in the directory.
- grid_to_grid.exe -fuzzy *_d_Max.tif
Histogram
"-histogram bins.csv <input grid>"
Calculates the number of cells and percentage of cells that fall in each range. Requires and input .csv file containing the bin values.
Example:
- An example inputs bin file is:
Bin Label 0.25 Less than 0.25 0.5 0.25 to 0.50 1.0 0.5 to 1.0 2.0 1.0 to 2.0 3.0 2.0 to 3.0 5.0 3.0 to 5.0
- An example output looks like the below:
Bin Label Count Percentage 0.25 Less than 0.25 986,434 58.61 0.5 0.25 to 0.50 334,422 19.87 1.0 0.5 to 1.0 216,449 12.86 2.0 1.0 to 2.0 118,452 7.04 3.0 2.0 to 3.0 10,206 0.61 5.0 3.0 to 5.0 15,998 0.95 Above 5.0 Above 5.0 973 0.06
- Example:
- grid_to_grid.exe –histogram histogram_bins.csv results_d_Max.tif
Extract 1D Model Inputs
"-egc control_file.egc"
This allows 1D Network (1d_nwk) and/or 1D cross-sections to be extracted from a series of grids.
A simple input file similar to the TUFLOW geometry control file is input into the utility. This is nominally given the extension .egc (Estry Geometry Control).
Two input GIS layers can be used, these are the branch lines (channels) and cut lines (cross sections). The branch line is split into the 1d_nwk layer, a new 1D channel is created for each section. The GIS attributes of these are defined in the sections below.
Branch Lines
The branch lines are split into channels using the cross-section cut lines detailed below. A number of channel characteristics can be set for branch lines. The required attribute names and data types for branch line are as follows:
| Attribute (type) | Description |
|---|---|
| Name (character 10) | Sets the branch name, unique chainage identifier is added to all output channels. |
| n_or_nF (float) | Sets the output "n_or_nF" attribute for all output channels in the 1d_nwk layer. |
| UCS (float) | Sets the "UCS" attribute for all output channels in the 1d_nwk layer. |
| FLC (float) | Sets the "FLC" attribute for all output channels in the 1d_nwk layer. If a value of greater than 0 is specified the FLC is split between channels within the branch. For example if 0.5 is specified and the branch is split into 10 channels, each channel will have an output "Form_Loss" of 0.05. |
| ChanType (character 4) | Sets the "Type" attribute for all output channels in the 1d_nwk layer. If left blank a default channel type of "S" is applied. |
Cut Lines
For each line in the cut line layer a cross-section will be extracted and output into .csv file format ready for use in TUFLOW. A number of cross section characteristics can be set for each cut line. The required attributes for the cross-section cut line are:
| Attribute (type) | Description |
|---|---|
| Source (character 50) | Optional output cross-section file name. If left blank the name and chainage of the branch the cross-section intersects is used. |
| Distance (float) | Optional distance along the line for sampling from grids. If not specified the value specified in the .egc file is used. |
| Split (character 1) | "T" (True) or "F" (False) for splitting the branch, set to false and the branch will not be split (used for centre sections) |
| Extract_XS (character 1) | "T" (True) or "F" (False) for cross-section extraction. If set to "F" no cross-section is extracted for the cut line. |
| Extract_Method (character 50) | Specify the method for extract the elevations from the grid (does not apply to Material grids). Options are:
|
| Buffer_Method (character 50) | Optional method for extracting the elevations from the grid (does not apply to Material grids) values from grid. Options are:
|
| Buffer_Distance (float) | Sets the distance for when using the "Buffer" or "Perpendicular" methods above. |
EGC commands
The .egc file is read in a similar manner to the .tgc (TUFLOW geometry control) file. This file is read in a sequential order and for repeated commands the final one prevails.
A full list of the availble .egc commands is detailed in the table below.
| Attribute (type) | Description |
|---|---|
| Read GIS Branch == <1d_br GIS file> | Reads the branch lines, these are described above. |
| Read GIS XS == <1d_cut GIS file> | Reads the cross-section cut lines, these are described above. |
| Read GIS FLC == <GIS file> | Optional GIS layer of polygons that can be used to specify form loss coefficients to the 1d_nwk layer. A single GIS (float) attribute is required. A FLC value of greater than 0 will be split between all 1d_nwk channels within the region. A FLC value of less than 0, will apply the absolute value to all channels within the polygon. For example if an FLC value of -0.1 is specified, all channels that fall within the polygon will have a form_loss attribute of 0.1. If a channel falls within multiple polygons, the form loss values will be added. |
| Set XS dx == <distance> | Sets the default distance across section to extract elevations and materials data. This can be specified on the cut lines as detailed above. |
| Set XS Z == <elevation> | Sets the elevation for all points in all cross-sections. |
| Set XS Mat == <Material ID> | Sets the material ID for all points in all cross-sections. |
| Read Grid Z == <grid layer of elevations> | Read elevations from DEM and assign this to all cross-section extraction points that fall within active DEM pixels. |
| Read Grid Mat == <grid layer of Material IDs> | Read material IDs from raster grid and assign this to all cross-section extraction points that fall within active DEM pixels. This should be an integer grid. |
| Write XS == ON or OFF | Turns on or off the writing of the 1d_xs layer. The default is off. |
| Write NWK == ON or OFF | Turns on or off the writing of the 1d_nwk layer. The default is off. |
| Output XS == <output gis layer> | Sets the output GIS layer for the 1D cross-sections. |
| Output NWK == <output gis layer> | Sets the output GIS layer for the 1D channel cross-sections. |
| Output NWK == <output gis layer> | Sets the output GIS layer for the 1D channel cross-sections. |
| FLC per Unit Length == <form loss per unit length> | The form loss per unit length is written to the "exit_loss" attribute of all 1d_nwk channels. |
Example:
- grid_to_grid.exe -egc MR_1d_001.egc
An example .egc file is:
Read GIS Branch == 1d_br_MR_001.MIF Read GIS XS == 1d_cut_MR_001.MIF Output Nwk == 1d_nwk_MR_001.MIF Output XS == 1d_xs_MR_001.MIF Write NWK == ON !Write 1d_nwk layer Write XS == ON !Write 1d_xs layer Set XS dx == 5 !set default spacing, can be specified on xs or cut line Set XS Mat == 1 !default Material ID of 1 Read Grid Mat == grid\grid_5m_2d_mat_MR_001.tif Set XS Z == 99 Read Grid Z == grid\dem_5m_regional.tif Read Grid Z == grid\dem_1m_bathymetry.tif Read Grid Z == grid\dem_1m_survey.tif
Extract 1D Nodal Area Tables from Grid
"-na <gis_region_file> <input grid>"
Can be used to extract nodal-area (elevation-area) tables from a DEM, and output these in a .csv file format suitable for input into the 1D domain of a TUFLOW model.
The input GIS region file should have the same attributes as the 1d_tab file format produced by TUFLOW. The first attribute ("Source" ) should contain a valid .csv file name.
The out nodal area table extends from the minimum to the maximum elevation in the DEM. A user defined minimum value can be specified using the "Skew" attribute of the GIS region.
Example:
- grid_to_grid.exe -na storage_R.shp DEM_1m.tif
Calibration Points
"-cp <cp_file>"
For appending the value from a grid file to a .mif or .shp file. The cp_file contains points representing locations where results are extracted from TUFLOW. The file format includes two attributes. The first attribute is a numeric field containing the recorded value. The second field is a char(100) text field containing the cp name.
"-config <config_file>" (optional)
Points to a csv file containing accuracy thresholds and style control options, e.g. symbol, colour and size.
"-cpsd<sd>" (optional)
The search radius for finding calibration points in meters.
"-cpmm<mm>" (optional)
The second search radius used to search for maximum and minimum values in meters.
Example:
- grid_to_grid.exe -cp Flood_Marks.MIF -config diff_config.csv -cpsd100 -cpmm50 results_h_Max.tif
Statistics
"-stat<type>" The grid_to_grid.exe utility allows the user to perform a number of statistical analyses on a group of input grids. This is particularly useful when extracting information from assessments that produce multiple result files for a single event, for example, processing grids from an ensemble assessment with numerous temporal pattern arrangements.
The available options are:
- Median
- Mean
- Frac
- Min
- Max
- All
- Rank<integer id>
The below gives a description on each option as well as an example. It is also useful to consider using wildcards in the batch file to supplement typing out each input grid file individually. Several of the examples below utilise this ability to demonstrate how it can be done.
"-statMedian"
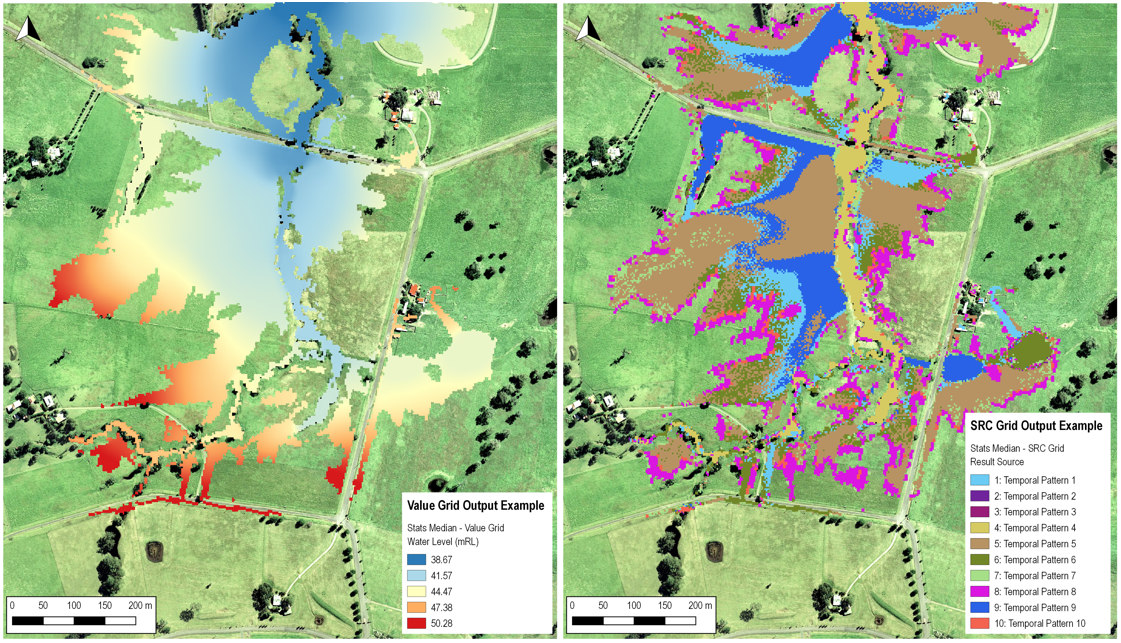
The -statMedian flag outputs the median value at each grid cell from all the input grids. All the input grids are considered, regardless of if the grid cell is dry in some of the input grids (dry areas are still ranked as low e.g. Rank1, Rank2 and so on).
If the number of input grids is an even number, the median value is taken from the grid that is ranked n / 2 + 1 (where n is the number of input grids). For example if the number of input grids is 10, at each grid cell the values are ranked lowest to highest (from 1 to 10). The result is taken from the 6th ranked grid. The median command outputs two grids:
- A value grid: the resulting median value
- An SRC grid: a grid listing which source input grid the median result value came from (a corresponding .csv file is also written as a legend)
Example:
- grid_to_grid.exe -statMedian Q100_30min_TP1_h.tif Q100_30min_TP2_h.tif Q100_30min_TP3_h.tif Q100_30min_TP4_h.tif ... Q100_30min_TP10_h.tif
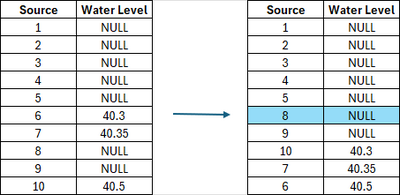
Note, the median value for the example below is a 'NULL' value, the output is a dry cell. 7 out of the 10 inputs are dry at this particular cell. Once the outputs are ordered (with NULL showing at the lowest spots), the median (6th) value for the cell is 'NULL' (dry) and '8' is the source grid output.
"-statMean"
The -statMean flag outputs the mean value at each grid cell. Unlike the median, the mean is only calculated at grid cells that are wet (that show flooding) in all input grids. Please note that the source grid is the next grid above the mean value. The mean command outputs two grids:
- A value grid: the resulting value
- An SRC grid: a grid listing which source input grid the result value came from or was the next above (a corresponding .csv file is also written as a legend)
Example:
- grid_to_grid.exe -statMean Q100_30min_*_h.tif
"-statFrac"
The -statFrac flag outputs a value at each grid cell that represents the fraction of the events that the grid cell is wet in. For example, if the number of input grids is 10, and a value of 0.2 is returned, this means this grid cell experienced flooding in 2 out of the 10 events. A value of 1.0 means that the grid cell was wet in all events.
The utility outputs one grid:
- A Frac grid: the resulting fraction value
Example:
- grid_to_grid.exe -statFrac Q100_30min_*_h.tif
"-statMin"
The -statMin flag outputs the minimum value at each grid cell from all the input grids. This flag is analogous with the -Min operation flag.
The utility outputs two grids:
- A value grid: the resulting value
- An SRC grid: a grid listing which source input grid the minimum result value came from (a corresponding .csv file is also written as a legend)
Example:
- grid_to_grid.exe -statMin Q100_30min_*_h.tif
"-statMax"
The -statMax flag outputs the maximum value at each grid cell from all the input grids. This flag is analogous with the -Max operation flag.
The utility outputs two grids:
- A value grid: the resulting value
- An SRC grid: a grid listing which source input grid the maximum result value came from (a corresponding .csv file is also written as a legend)
Example:
- grid_to_grid.exe -statMax Q100_30min_*_h.tif
"-statAll"
The -statAll flag undertakes and creates results for all the statistic operations mentioned above.
The utility outputs 9 grids:
- A median, mean, max, min and frac grid (as detailed above)
- An SRC grid: for the median, mean, min and max calculations (calculation of source grids as detailed above)
- A .csv file that contains the legend for all SRC grids
Example:
- grid_to_grid.exe -statAll Q100_30min_*_h.tif
"-statRank<integer id>"
The -statRank<integer> flag outputs the n<integer> ranked value at each grid cell from all the input grids. All the input grids are considered, regardless of if the grid cell is dry in some of the input grids (dry areas are still ranked as low e.g. Rank1, Rank2 and so on). For example, if the number of input grids is 10, at each grid cell the values are ranked lowest to highest (from 1 to 10). -statRank8 will output results taken from the 8th ranked grid. In this example, -statRank1 is equivalent to Min, -statRank10 is equivalent to Max, and -statRank6 is equivalent to Median. The Rank flag allows additional functionality that lets users extract results in between those that are pre-programmed.
The utility outputs two grids:
- A value grid: the resulting value
- An SRC grid: a grid listing which source input grid the ranked result value came from (a corresponding .csv file is also written as a legend)
Example:
- grid_to_grid.exe -statRank5 Q100_30min_*_h.tif
Flood Extent
"-fe"
Returns a simple grid with value of 1 where the input grid has an active, non-zero value.
Example:
- grid_to_grid.exe -fe results_dMax.tif
Remap
"-wl <wl_file> -dem <dem_file>"
Remaps coarser resolution water level grid to a finer resolution DEM.
The default interpolation method is TIN. But "-idw_npt<number of points>" flag can be used to change the interpolation method to IDW and set the number of points used for IDW interpolation (default is 12).
Example:
- Remaps water level grid to the resolution of the DEM file:
- grid_to_grid.exe -remap -wl lowres_h.tif -dem DEM_highres.tif
- The utility can also remap depth output grids to the resolution of the DEM file:
- grid_to_grid.exe -remap -wl lowres_h.tif -dem DEM_highres.tif lowres_d.tif
- The utility can also apply a buffer distance or add a freeboard. The below applies a buffer distance of 20m, and adds a freeboard of 0.2m to the original water level grid.
- grid_to_grid.exe -remap -fb0.2 -bd20 -wl lowres_h.tif -dem DEM_highres.tif
Note, for any output types other than depth, this utility does NOT interpolate the result from the coarser grid to the finer grid, but only extends/reduces the output extent to the dry/wet extent. More discussions on this function is documented here TUFLOW Remapping Tool.
GPKG and NetCDF
GeoPackage and NetCDF are database formats and are able to contain multiple layers in a single file. When passing in an input or output reference to a GeoPackage or NetCDF file the layer name is assumed to be the same as the database name unless otherwise specified. To give the layer a different name than the database, the following syntax "database.ext >> layer" can be used:
grid_to_grid.exe -dif "database.gpkg >> raster1" "database.gpkg >> raster2"
Notes:
- Quotes will always be required when using this syntax.
- GPKG output paths can be either a new or existing database i.e. the utility supports writing new layers into an existing database.
- NetCDF outputs will overwrite any existing NetCDF file.
- Typically outputs to the GPKG or NetCDF format will be grouped together into a single output file.
Creation Options
The grid_to_grid.exe supports GDAL style creation options. Creation options can be passed in using the "-co" flag then the name of the creation option and the value:
-co COMPRESS=DEFLATE
Multiple creation options can be used (each will require its own "-co" flag).
The creation options have adopted the same naming as GDAL (more information on the options can be found at https://gdal.org), however, not all options in GDAL are supported in the grid_to_grid.exe utility. The following creation options are supported:
GeoTIFF
- COMPRESS=NONE/DEFLATE/LZW - output compression. Default - DEFLATE.
- ZLEVEL=[0-9] - Compression level. Zero is no compression, 9 is hightest compression. Only supported for DEFLATE compression method. Default - 9.
- PREDICTOR=1/2 - Compression predictor. Supported options are none [1] and horizontal differencing [2]. Default - 2.
- NUM_THREADS=[N]/ALL_CPUS - Number of threads to use when processing GeoTIFFs. Default - ALL_CPUS.
- BIGTIFF=YES/NO/IF_NEEDED - Controls whether the ouput file uses the BigTIFF format or classic TIFF. Default - IF_NEEDED.
- TILED=YES/NO - Controls whether the output GeoTIFF should use tiles or strips. Default - NO.
- OVERVIEWS=YES/NO - Controls whether overviews (also known as pyramids) should be created. The grid_to_grid tool only supports internal overviews and therefore this option is only supported for tiled GeoTIFFs. Default - NO.
Cloud Optimised GeoTIFF (COG)
Same options as GeoTIFF however will automatically use 'TILED=YES' and 'OVERVIEWS=YES' creation options.
GeoPackage
- COMPRESS=NONE/LZW - output compression. Default - LZW
- PREDICTOR=1/2 - Compression predictor. Supported options are none [1] and horizontal differencing [2]. Default - 2.
- OVERVIEWS=YES/NO - Controls whether overviews (also known as pyramids) should be created. Default - NO.
NetCDF
- COMPRESS=NONE/DEFLATE- output compression. Default - DEFLATE
- ZLEVEL=[0-9] - Compression level. Zero is no compression, 9 is highest compression. Only supported for DEFLATE compression method. Default - 9.
ASC
- DECIMAL_PRECISION=N - The number of decimal places in the output. This option is analogous to the "-decimal[N]" switch. Default - 3.
| Up |
|---|