TUFLOW Setup with Kart QGIS Plugin: Difference between revisions
Tuflowduncan (talk | contribs) |
Tuflowduncan (talk | contribs) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
All of these are useful from a quality assurance perspective, allowing a history of the development of a TUFLOW model geometry files to be understood and analysed. Kart is very easy to use once it is set up. The set up of Kart to be used with TUFLOW is a little cumbersome but the steps below provide information of how to set up the Kart QGIS Plugin, set up the TUFLOW folders and initialise the Kart repository. |
All of these are useful from a quality assurance perspective, allowing a history of the development of a TUFLOW model geometry files to be understood and analysed. Kart is very easy to use once it is set up. The set up of Kart to be used with TUFLOW is a little cumbersome but the steps below provide information of how to set up the Kart QGIS Plugin, set up the TUFLOW folders and initialise the Kart repository. |
||
== |
== Installing the Kart Plugin == |
||
The first step is to install the Kart QGIS plugin. This is done using the '''Manage and Install Plugins''' tool within QGIS. Search for Kart and install the plugin. |
The first step is to install the Kart QGIS plugin. This is done using the '''Manage and Install Plugins''' tool within QGIS. Search for Kart and install the plugin. |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
[[File:Kart Repository.png|thumb|Initial Kart Repository|alt=|none|465x465px]] |
[[File:Kart Repository.png|thumb|Initial Kart Repository|alt=|none|465x465px]] |
||
== |
== Setting up the TUFLOW Model and Initialise Kart Repository == |
||
With Kart set up, we can now move towards setting up your TUFLOW model. To use Kart, you would need to be using a Geopackage GIS Format. We will start at the beginning of a TUFLOW model build but it would be possible to set up kart with an existing model with a similar workflow. However, in this instance, commits and changes would only be tracked for edits to the geometry data after the TUFLOW model is initialised within a Kart folder. |
With Kart set up, we can now move towards setting up your TUFLOW model. To use Kart, you would need to be using a Geopackage GIS Format. We will start at the beginning of a TUFLOW model build but it would be possible to set up kart with an existing model with a similar workflow. However, in this instance, commits and changes would only be tracked for edits to the geometry data after the TUFLOW model is initialised within a Kart folder. |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
With the TUFLOW folders set up, there is now some fiddly steps to go through so that we can set up a Kart repository. This is because a Kart repository can only be set up for an empty folder but our GIS folder has an empty folder and a geopackage in it already. We also want to initialise Kart using the TUFLOW model name rather than have a geopackage called gis, which is based on the GIS folder. The below steps are one way to get address these and provide a neat GIS folder, with a geopackage name that matches the model, which is initialised as a Kart repository. |
With the TUFLOW folders set up, there is now some fiddly steps to go through so that we can set up a Kart repository. This is because a Kart repository can only be set up for an empty folder but our GIS folder has an empty folder and a geopackage in it already. We also want to initialise Kart using the TUFLOW model name rather than have a geopackage called gis, which is based on the GIS folder. The below steps are one way to get address these and provide a neat GIS folder, with a geopackage name that matches the model, which is initialised as a Kart repository. |
||
[[File:GIS Folder.png|none|thumb| |
[[File:GIS Folder.png|none|thumb|390x390px|The Desired TUFLOW GIS Folder Initialised as a Kart Repository|alt=]] |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
* Cut and paste the '''empty''' folder and the model Geopackage file from the '''TUFLOW\Model\GIS''' folder to TUFLOW\Model. This is because Kart can not initialise a repository if the folder is not empty. |
* Cut and paste the '''empty''' folder and the model Geopackage file from the '''TUFLOW\Model\GIS''' folder to TUFLOW\Model. This is because Kart can not initialise a repository if the folder is not empty. |
||
* Rename the ' |
* Rename the ''''GIS'''<nowiki/>' folder to ''''*Model_Name*'''<nowiki/>' where '*Model_Name*' is the same as your Geopackage name. |
||
* Use the Kart Create new repository tool to create a new Kart repository. |
* Use the Kart Create new repository tool to create a new Kart repository. |
||
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
== Using Remote Repositories == |
== Using Remote Repositories == |
||
The above steps are for a local Kart repository. However, it is possible to use Kart with remote repositories. This |
The above steps are for a local Kart repository. However, it is possible to use Kart with remote repositories. This allows access from multiple machines as well as multiple users. |
||
[[File:Remote repository.png|none|Kart Push/Pull Functions to Remote Repository|alt=|thumb|400x400px]]It should be noted that the TUFLOW team have not made sufficient use of Kart with remote repository so cannot suggest that it is a recommended approach. |
|||
This can be done by cloning a remote respository on Gitlab/Github or similar or pushing the local repository to Gitlab/Github or similar. |
|||
To do push a local repository to Gitlab or Github, firstly create the remote repository in Gitlab/Github. Don’t initialise the project with a readme file as this can cause issues. Once set up, got to the Kart plugin within QGIS, navigate to the local repository you would like to upload and right click on the repository and choose to ‘push’ changes. |
|||
[[File:Kart Push.png|none|thumb|400x400px]] |
|||
Choose to ‘Manage remotes’. Within the resulting dialogue, add the remote name and URL. It is recommended to use SSH Keys for authentication. When using SSH keys the form of the url would be git@gitlab.com: 'username' 'git repository.git' where username would be your own Gitlab user name and the git repository would be the remote repository ID. |
|||
[[File:Kart Manage Remotes.png|none|thumb|400x400px]] |
|||
Choose Add New/Save to save the options. In the next dialogue, select OK. If the permissions are set up correctly, the repository should be pushed to the remote repository and a message will pop up within QGIS indicating success. |
|||
An example of the TUFLOW Tutorial Geopackage dataset from modules 1 and 2, is available from the [https://gitlab.com/tuflow-user-group TUFLOW Gitlab User Group] at following location: https://gitlab.com/tuflow-user-group/third-party-tools/other/tuflow_tutorial_model_kart. |
|||
This can be cloned using Kart by selecting Clone Repository. |
|||
[[File:Kart CLone.png|none|thumb|400x400px]] |
|||
If using SSH keys the URL for the repository would be: git@gitlab.com: tuflow-user-group/third-party-tools/other/tuflow_tutorial_model_kart.git. Choose a suitable location to save the repository locally. |
|||
[[File:Kart CLone 2.png|none|thumb|400x400px]] |
|||
The repository will then appear within Kart in the list of repositories and can be interrogated with the above tools. A remote repository can also allow multi-user editing, providing the opportunity for conflicts which can be dealt with. See the [https://docs.kartproject.org/en/latest/ Kart documentation] for more details. |
|||
{{Tips Navigation |
{{Tips Navigation |
||
Latest revision as of 23:55, 24 July 2025
Introduction
Kart is a version control tool which stores geospatial data (and tabular data) in Git, providing a neat version control system whilst building TUFLOW models. Despite using Git, there is no requirement for the user to have a thorough understanding of Git, it's processes and commands. The Kart QGIS plugin provides a user interface for Kart which provides tools for reviewing changes to geospatial data as it is iteratively edited. This page describes a workflow for setting up a TUFLOW project, utilising Kart, and provides some of the benefits of using the Kart tools for version control. Kart can be used with remote repositories to allow multiple users to access the data and work simultaneously with merge control, however, the example below is a local repository for the purposes of version control and ease of quality assurance checking.
Benefits of using Kart
The video below shows an initial model build with some a number of TUFLOW model layers and where the layer geometry has undergone a number of iterative changes. The video shows:
- The Kart commit history table.
- Tags for specific commits. For instance for models that have undergone QA, been sent to a client or sent to support@tuflow.com.
- The evaluation in differences between commit versions both in text form and in geometry form.
All of these are useful from a quality assurance perspective, allowing a history of the development of a TUFLOW model geometry files to be understood and analysed. Kart is very easy to use once it is set up. The set up of Kart to be used with TUFLOW is a little cumbersome but the steps below provide information of how to set up the Kart QGIS Plugin, set up the TUFLOW folders and initialise the Kart repository.
Installing the Kart Plugin
The first step is to install the Kart QGIS plugin. This is done using the Manage and Install Plugins tool within QGIS. Search for Kart and install the plugin.
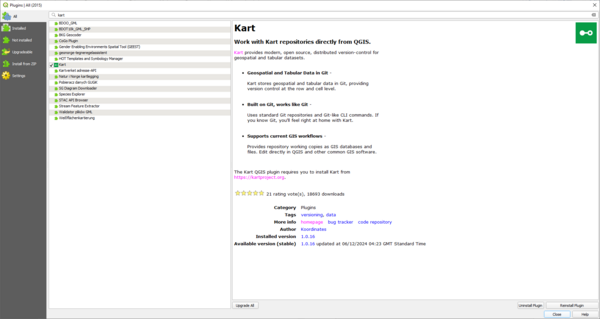
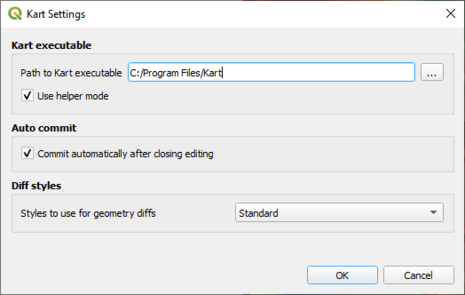
The plugin requires that you install Kart from https://kartproject.org/ Once the plugin and Kart is installed, there is a Kart menu within QGIS with some settings. Specify the path to the installed Kart executable. There's an option to Auto Commit which will commit your changes to the repository when you 'Toggle editing' off within QGIS. This can be a useful option, although the drawback is that you are not prompted to add a commit message.
The Kart Repositories panel should show something similar to the following, with no repositories showing.
Setting up the TUFLOW Model and Initialise Kart Repository
With Kart set up, we can now move towards setting up your TUFLOW model. To use Kart, you would need to be using a Geopackage GIS Format. We will start at the beginning of a TUFLOW model build but it would be possible to set up kart with an existing model with a similar workflow. However, in this instance, commits and changes would only be tracked for edits to the geometry data after the TUFLOW model is initialised within a Kart folder.
Firstly, we'll set up our TUFLOW folder structure and template files. To set up your TUFLOW folders, you can use your chosen method of either the TUFLOW Create Project tool or the Create TUFLOW Project tool.
With the TUFLOW folders set up, there is now some fiddly steps to go through so that we can set up a Kart repository. This is because a Kart repository can only be set up for an empty folder but our GIS folder has an empty folder and a geopackage in it already. We also want to initialise Kart using the TUFLOW model name rather than have a geopackage called gis, which is based on the GIS folder. The below steps are one way to get address these and provide a neat GIS folder, with a geopackage name that matches the model, which is initialised as a Kart repository.
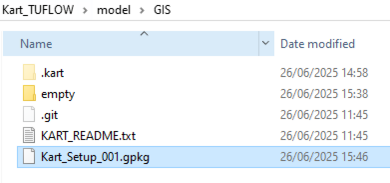
Kart probably works best with a single Geopackage for the whole TUFLOW model, although it would be possible to use with seperate Geopackages. The steps below are for a single Geopackage.
- Cut and paste the empty folder and the model Geopackage file from the TUFLOW\Model\GIS folder to TUFLOW\Model. This is because Kart can not initialise a repository if the folder is not empty.
- Rename the 'GIS' folder to '*Model_Name*' where '*Model_Name*' is the same as your Geopackage name.
- Use the Kart Create new repository tool to create a new Kart repository.
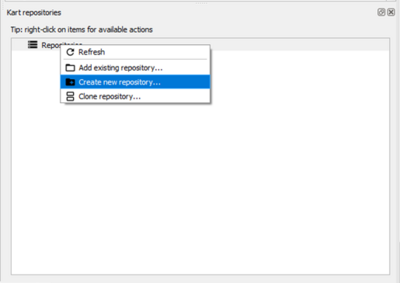
- Select the TUFLOW\Model\Model_Name folder and ensure 'Geopackage in repository folder' is selected in the Storage type option. Click OK.
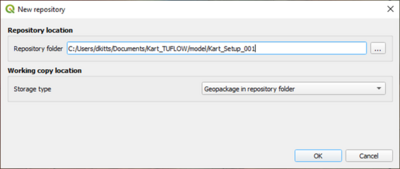
- Cut and paste the 'empty' folder from TUFLOW\Model to the TUFLOW\Model\Model_Name folder.
- Rename the 'Model_Name' folder to 'GIS'
- We will now remap the repository to the GIS folder. In the Kart repositories panel, highlight the current repositiry and choose to 'remove this repository'. Click Yes when the prompt dialogue comes up.
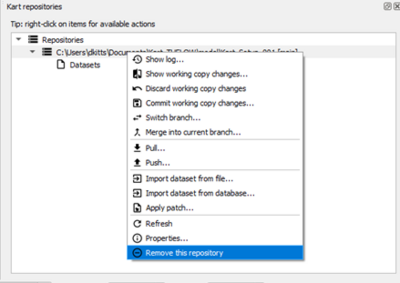
- We now need to add the renamed folder as an existing repository. Right click on the repositories option and select 'Add existing repository'. Navigate to the TUFLOW\Model\GIS folder and choose select folder.
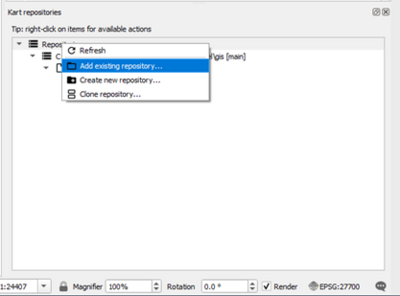
- We can now import the Model_Name.gpkg into the repository. This is done by right clicking on the repository and selecting 'Import dataset from file'. Navigate to the TUFLOW\Model\Model_Name.gpkg and select open.

- The repository will now show the Geopackage layers, which at present is only the projection layer generate during the create TUFLOW project step.
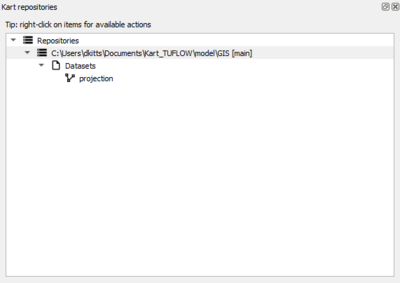
- Finally, the Model_Name.gpkg can be deleted from the TUFLOW\Model folder.
The above steps are by far and away the fiddliest steps with the TUFLOW model Kart set up. Now we can start building the TUFLOW model and utilising Kart.
TUFLOW Model Build
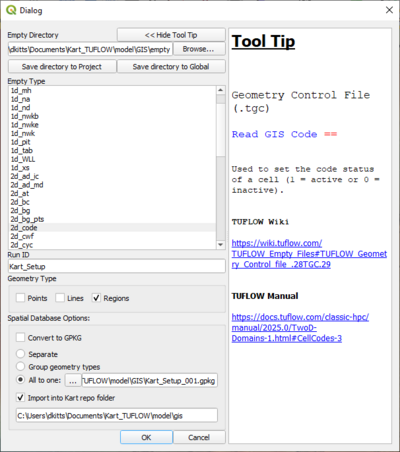
We can now start to build our TUFLOW model using the traditional steps of the Import Empty File tool within the QGIS TUFLOW Plugin. When importing the empty files, we can import to the gpkg in Kart repository using the options in the following image, ensuring to select the 'All to one' option and choosing to 'Import into Kart repo folder'.
Once the empty file is imported, you can refresh the Kart Repository, and see the additional layers with there.
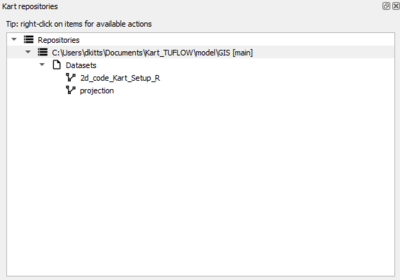
We can now build the TUFLOW model geometry as we would do usually. As we add additional layers to the geodatabase, they will start to appear in the Kart repositories panel.
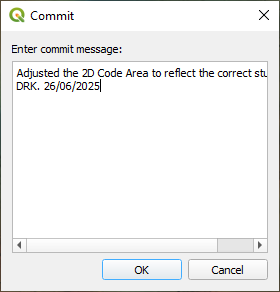
If the option to 'Commit automatically after closing editing' then the changes will be automatically committed. This is useful to avoid forgetting to commit, similar to how an autosave can be beneficial. Alternatively, it is possible to commit manually, either by clicking the repository or the individual layers and using the 'Commit working copy changes' or 'Commit working copy changes for this dataset' option respectively. The benefit of the latter approach is that there are less frequent commits and the user is prompted for a commit message prior to committing the working changes.
If you select the Kart repository or an individual layer dataset then you can choose to 'Show log' which provides a table of the commit history.
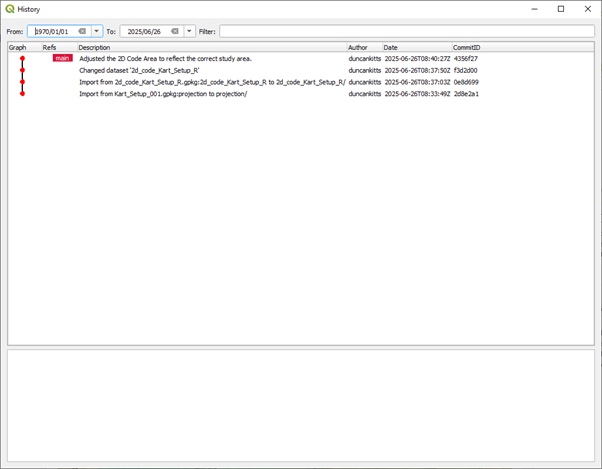
The commit history can then be interrogated to show the details of the commits, the differences between versions, adding tags and other git like tools such as branching, merging, reverting back to older versions as well as replacing working copy changes.It is also possible to apply temporal filters for changes. For a full list of Kart tools, the user is recommended to consult the Kart documentation here.
Using Remote Repositories
The above steps are for a local Kart repository. However, it is possible to use Kart with remote repositories. This allows access from multiple machines as well as multiple users.
This can be done by cloning a remote respository on Gitlab/Github or similar or pushing the local repository to Gitlab/Github or similar.
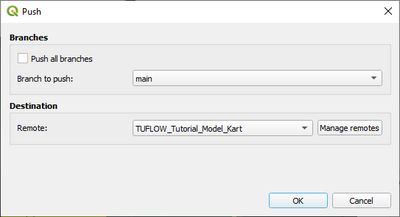
To do push a local repository to Gitlab or Github, firstly create the remote repository in Gitlab/Github. Don’t initialise the project with a readme file as this can cause issues. Once set up, got to the Kart plugin within QGIS, navigate to the local repository you would like to upload and right click on the repository and choose to ‘push’ changes.
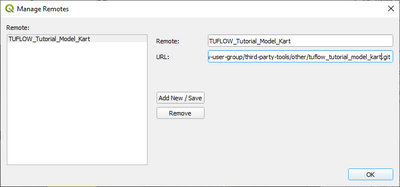
Choose to ‘Manage remotes’. Within the resulting dialogue, add the remote name and URL. It is recommended to use SSH Keys for authentication. When using SSH keys the form of the url would be git@gitlab.com: 'username' 'git repository.git' where username would be your own Gitlab user name and the git repository would be the remote repository ID.
Choose Add New/Save to save the options. In the next dialogue, select OK. If the permissions are set up correctly, the repository should be pushed to the remote repository and a message will pop up within QGIS indicating success.
An example of the TUFLOW Tutorial Geopackage dataset from modules 1 and 2, is available from the TUFLOW Gitlab User Group at following location: https://gitlab.com/tuflow-user-group/third-party-tools/other/tuflow_tutorial_model_kart.
This can be cloned using Kart by selecting Clone Repository.

If using SSH keys the URL for the repository would be: git@gitlab.com: tuflow-user-group/third-party-tools/other/tuflow_tutorial_model_kart.git. Choose a suitable location to save the repository locally.

The repository will then appear within Kart in the list of repositories and can be interrogated with the above tools. A remote repository can also allow multi-user editing, providing the opportunity for conflicts which can be dealt with. See the Kart documentation for more details.
| Up |
|---|