Advection Dispersion Modelling: Difference between revisions
Tuflowduncan (talk | contribs) |
Tuflowduncan (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Introduction= |
=Introduction= |
||
TUFLOW’s Advection Dispersion (AD) Module is an extension of the TUFLOW Classic/HPC engines. It adds |
TUFLOW’s Advection Dispersion (AD) Module is an extension of the TUFLOW Classic/HPC engines. It adds to the hydrodynamic capabilities of TUFLOW Classic/HPC by simulating depth-averaged, two and one-dimensional constituent fate and transport. An example of such a constituent might include salinity. Both dissolved and particulate constituents can be simulated. TUFLOW AD takes depth and velocity fields computed by the TUFLOW Classic and HPC solvers and uses this information, together with initial and boundary conditions, to simulate the advection and dispersion of user-defined constituents. |
||
TUFLOW AD is specifically oriented towards such analyses in systems including coastal waters, estuaries, rivers, floodplains and urban areas. The AD module is discussed in detail in the TUFLOW Advection Dispersion Manual. |
TUFLOW AD is specifically oriented towards such analyses in systems including coastal waters, estuaries, rivers, floodplains and urban areas. The AD module is discussed in detail in the [https://downloads.tuflow.com/TUFLOW/Releases/2020-10/TUFLOW%20AD%20Manual.2020-10-AF.pdf TUFLOW Advection Dispersion Manual]. |
||
=Model Development= |
=Model Development= |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
<ol> |
<ol> |
||
<li>Create a TUFLOW AD control file |
<li>Create a TUFLOW AD control file with the extension .adcf |
||
<li>Use a text editor to create an empty .adcf file and save it to the “runs” folder. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
<li>Set up the AD global database (.csv file). |
|||
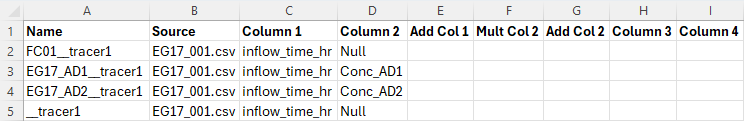
<li>Set up the TUFLOW AD global database in the “bc_dbase” folder which defines the constituent of interest and a number of characteristics, for example the decay rate and dispersion coefficient. The resulting file should look similar to the below:<br> |
|||
[[File:EG17 AD Consit 001.png]]<br> |
[[File:EG17 AD Consit 001.png]]<br> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
<font color="blue"><tt>AD Global Database</tt></font><font color="red"><tt> == </tt></font><font color="black"><tt>..\bc dbase\my_ad_global_dbase.csv</tt></font></ol> |
|||
<li>Setup up the boundary condition tables (.csv file(s)) |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
<li>Setup up the boundary condition database (.csv file) |
|||
<li>Set up the boundary condition tables (.csv file(s)) to define the time-varying constituent concentrations at any input boundaries. |
|||
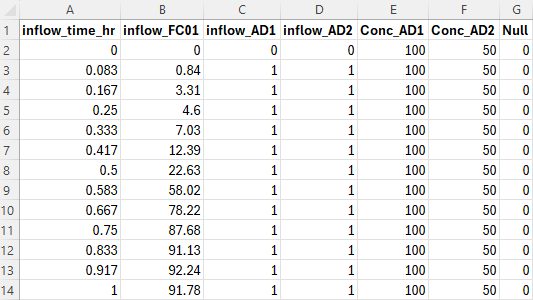
<ul><li>Set up the constituent boundary condition table(s) in the “bc_dbase” folder . For example in the below, the time-varying concentration of constituents Conc_AD1 and Conc_AD2 are set:<br> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
[[File:EG17 AD 001.png]]<br> |
[[File:EG17 AD 001.png]]<br> |
||
<li>In the .adcf file use the "AD BC Database" command to set the location of the bc database as follows.<br> |
<li>In the .adcf file use the "AD BC Database" command to set the location of the bc database as follows.<br><font color="blue"><tt>AD BC Database</tt></font><font color="red"><tt> == </tt></font><font color="black"><tt>..\bc dbase\my_ad_bc_dbase.csv</tt></font></ul> |
||
<font color="blue"><tt>AD BC Database</tt></font><font color="red"><tt> == </tt></font><font color="black"><tt>..\bc dbase\my_ad_bc_dbase.csv</tt></font></ol> |
|||
<li>Setup up TUFLOW to activate the AD module (.tcf file) |
<li>Setup up TUFLOW to activate the AD module (.tcf file) |
||
< |
<ul><li>In the .tcf file use the command "AD Control File" to set the location of the adcf and activate execution of the AD module as follows.<br><font color="blue"><tt>AD Control File</tt></font><font color="red"><tt> == </tt></font><font color="black"><tt>ad_run.adcf</tt></font></ul> |
||
<font color="blue"><tt>AD Control File</tt></font><font color="red"><tt> == </tt></font><font color="black"><tt>ad_run.adcf</tt></font></ol> |
|||
<li>Run the model |
<li>Run the model |
||
<li>Run TUFLOW as normal. The AD module will be called and appropriate constituent result output files written. |
|||
</ol> |
</ol> |
||
Revision as of 21:38, 18 March 2024
Introduction
TUFLOW’s Advection Dispersion (AD) Module is an extension of the TUFLOW Classic/HPC engines. It adds to the hydrodynamic capabilities of TUFLOW Classic/HPC by simulating depth-averaged, two and one-dimensional constituent fate and transport. An example of such a constituent might include salinity. Both dissolved and particulate constituents can be simulated. TUFLOW AD takes depth and velocity fields computed by the TUFLOW Classic and HPC solvers and uses this information, together with initial and boundary conditions, to simulate the advection and dispersion of user-defined constituents.
TUFLOW AD is specifically oriented towards such analyses in systems including coastal waters, estuaries, rivers, floodplains and urban areas. The AD module is discussed in detail in the TUFLOW Advection Dispersion Manual.
Model Development
Setting Up a New Model
The steps below describe the process for setting up a TUFLOW AD model. It is assumed that the user is familiar with TUFLOW Classic/HPC and that the folder structure for TUFLOW has been setup with all required files. The user should run the TUFLOW Classic/HPC model without the AD module first to make sure that it is appropriately configured and stable.
- Create a TUFLOW AD control file with the extension .adcf
- Use a text editor to create an empty .adcf file and save it to the “runs” folder.
- Set up the AD global database (.csv file).
- Set up the TUFLOW AD global database in the “bc_dbase” folder which defines the constituent of interest and a number of characteristics, for example the decay rate and dispersion coefficient. The resulting file should look similar to the below:

- In the .adcf file use the "AD Global Database" command to set the location of the global database as follows.
AD Global Database == ..\bc dbase\my_ad_global_dbase.csv - Set up the boundary condition tables (.csv file(s)) to define the time-varying constituent concentrations at any input boundaries.
- Set up up the boundary condition database (.csv file)
- Setup up TUFLOW to activate the AD module (.tcf file)
- In the .tcf file use the command "AD Control File" to set the location of the adcf and activate execution of the AD module as follows.
AD Control File == ad_run.adcf
- In the .tcf file use the command "AD Control File" to set the location of the adcf and activate execution of the AD module as follows.
- Run the model
- Run TUFLOW as normal. The AD module will be called and appropriate constituent result output files written.
Example Models
Example TUFLOW AD models, including settling and decay, are available via the TUFLOW Example Model Dataset.