|
|
| (136 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| − | <font size = 18>Page Under Construction - Expected Finalization date: 23 February 2024 </font>
| |
| | = Introduction = | | = Introduction = |
| − | This Wiki page outlines recommended steps for conversion of an XPSWMM model to TUFLOW. <br> | + | This Wiki page outlines recommended steps for the conversion of an XPSWMM model to TUFLOW. <br> |
| − | | |
| − | XPSWMM is a flood and urban stormwater drainage modeling software developed by Autodesk (previously Innovyze and XP Solutions). The XPSWMM solution uses EPA SWMM for its 1D calculations, dynamically linked to TUFLOW for its 2D calculations. The software functions within a custom build Graphical User interface (GUI). During simulation, XPSWMM calls a TUFLOW dynamic library for the 2D calculations. As XPSWMM uses TUFLOW for its 2D engine, XPSWMM and TUFLOW use the same 2D solution and will achieve identical results if configured in a like-for-like way.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Common user feedback suggests the XPSWMM GUI is useful for simple modeling projects; however, it can become cumbersome and inefficient in workflow when dealing with larger datasets and/or a large volume of different scenario and event simulations. In response to requests from USA XPSWMM users who want to convert XPSWMM models into a native TUFLOW format, TUFLOW linkage with 1D EPA Storm Water Management Model (SWMM) was added as a supported feature in TUFLOW 2023-03-AD release. The modeling workflow in TUFLOW differs from XPSWMM, as TUFLOW modeling is integrated with QGIS (Geographical Information System) GIS software. This GIS integration is well-suited for working with larger datasets. Additionally, the structural design associated with TUFLOW modeling makes its general workflow extremely efficient, particularly for the automated management of multiple scenarios and events.
| |
| | | | |
| | + | XPSWMM is a flood and urban stormwater drainage modeling software developed by Autodesk (previously Innovyze and XP Solutions). The XPSWMM solution uses EPA SWMM for its 1D calculations, dynamically linked to TUFLOW for its 2D calculations. The software functions within a custom build Graphical User Interface (GUI). Unknown to many XPSWMM modelers, during simulation, XPSWMM processes its inputs into TUFLOW files and also calls TUFLOW for the 2D calculations. As XPSWMM uses TUFLOW for its 2D engine, like-for-like results can be achieved using this software. The modeling workflow in TUFLOW differs from XPSWMM, as TUFLOW modeling is integrated with QGIS (Geographical Information System) GIS software instead of embedded within a software specific Graphical User Interface. |
| | | | |
| | If you are building a TUFLOW SWMM model from scratch, not from XPSWMM, please refer to the <u>[[TUFLOW_SWMM_Tutorial_Introduction | TUFLOW SWMM Tutorials]]</u>. Tutorials are provided for the following topics: | | If you are building a TUFLOW SWMM model from scratch, not from XPSWMM, please refer to the <u>[[TUFLOW_SWMM_Tutorial_Introduction | TUFLOW SWMM Tutorials]]</u>. Tutorials are provided for the following topics: |
| Line 13: |
Line 9: |
| | * <u>[[TUFLOW SWMM Tutorial M03 | TUFLOW SWMM Module 3]]</u> - 1D SWMM Pipe Network / 1D SWMM Urban Hydrology | | * <u>[[TUFLOW SWMM Tutorial M03 | TUFLOW SWMM Module 3]]</u> - 1D SWMM Pipe Network / 1D SWMM Urban Hydrology |
| | * <u>[[TUFLOW SWMM Tutorial M04 | TUFLOW SWMM Module 4]]</u> - 1D SWMM Pipe Network / 1D SWMM Urban Hydrology: Executing multiple different event simulations from a single model control file. | | * <u>[[TUFLOW SWMM Tutorial M04 | TUFLOW SWMM Module 4]]</u> - 1D SWMM Pipe Network / 1D SWMM Urban Hydrology: Executing multiple different event simulations from a single model control file. |
| − | <br>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | == TUFLOW Licensing / XPSWMM Discount ==
| |
| − | If you are an existing / or past XPSWMM perpetual license owner who would like to purchase a TUFLOW license, please contact <u>[mailto::sales@tuflow.com sales@tuflow.com]</u>. You may be eligible for an XPSWMM / TUFLOW discount in recognition of past royalties Autodesk paid TUFLOW when you purchased an XPSWMM perpetual license. <br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| | | | |
| − | = XPSWMM to TUFLOW Model Conversion=
| |
| | == Dataset Download == | | == Dataset Download == |
| − | The XPSWMM model used for this model conversion demonstration is available for download here: <u>[https://downloads.tuflow.com/SWMM/XPSWMM_to_TUFLOW_Model_Conversion.zip XPSWMM to TUFLOW Model Conversion Dataset]</u>.<br> | + | The dataset used for this model conversion demonstration is available for download here: <u>[https://downloads.tuflow.com/SWMM/XPSWMM_XPX_to_TUFLOW_Conversion.zip XPSWMM XPX to TUFLOW Conversion Dataset]</u>. <br> |
| | + | This dataset contains the XPSWMM model and the resulting TUFLOW model that is created. These can be found in the '''XPSWMM''' and '''Complete_Conversion''' folders respectively. <br> |
| | | | |
| − | '''If you are using this example conversion dataset, please rerun the XPSWMM model before beginning the conversion process.''' This will generate the XPSWMM TUFLOW files and establish the correct file paths within them, aligning with the location where you have saved the dataset on your computer. | + | '''If you are using this example conversion dataset, please rerun the XPSWMM model in the location where you save the dataset before beginning your own TUFLOW model conversion.''' Rerunning the model is necessary because XPSWMM will write TUFLOW files during its preprocessing, subsequently defining the correct file path information (for the location where you saved your files) in the newly written TUFLOW files. We also recommend creating your own TUFLOW model in a different folder from the provided TUFLOW dataset so you can easily compare your model against it.<br> |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | <br> | |
| | | | |
| − | == Two Dimensional (2D) Model Elements ==
| + | If you do not have access to a XPSWMM license and the XPSWMM Application, please refer to the <u>[[XPSWMM_to_TUFLOW-SWMM_Troubleshooting#Model_Conversion_Without_a_XPSWMM_License |XPSWMM to TUFLOW SWMM Troubleshooting]]</u> page. <br> |
| − | XPSWMM writes TUFLOW model files when it pre-processes the model inputs defined in its GUI (prior to the hydraulic calculations). Using default settings, XPSWMM typically writes the TUFLOW files to the '''2D\Data''' folder.<br> | |
| − | | |
| − | The following sections explain how 2D data can be exported from XPSWMM and/or reconfigured into a format that is more standard of a TUFLOW model. The conversion has been summarized into three steps:
| |
| − | <ol>
| |
| − | <li> Obtain Digital Terrain Model (DTM) dataset for TUFLOW model.
| |
| − | <li> Use TUFLOW's Processing Tool to configure the XPSWMM written TUFLOW files into a standard TUFLOW folder structure and GIS database format.
| |
| − | <li> Manual optional changes to the TUFLOW control files. | |
| − | </ol> | |
| | | | |
| − | === Digital Terrain Model (DTM) Data === | + | = XPSWMM to TUFLOW Model Conversion = |
| | + | == Export Data From XPSWMM Model == |
| | + | '''Digital Terrain Model (DTM) Data'''<br> |
| | XPSWMM reads its 2D DTM data in one of two ways: | | XPSWMM reads its 2D DTM data in one of two ways: |
| | * The DTM data can be directly specified in the '2D Model Settings', or | | * The DTM data can be directly specified in the '2D Model Settings', or |
| | * The DTM data can be internally processed by XPSWMM using its terrain tools and DTM builder. | | * The DTM data can be internally processed by XPSWMM using its terrain tools and DTM builder. |
| − | Depending which method is applied to your XPSWMM model, the steps required to convert the model to TUFLOW will vary. | + | Depending on which method is applied to your XPSWMM model, the steps required to will vary. Review which method is used: |
| − | | |
| − | Let's review what method is used:
| |
| | <ol> | | <ol> |
| | <li> Open your existing model in XPSWMM. | | <li> Open your existing model in XPSWMM. |
| − | <li> In the top dropdown menu options, navigate to Configuration > Job control > 2D Model Settings. This will open a dialog. | + | <li> In the top dropdown menu options, go to Configuration > Job Control > 2D Model Settings. This will open a dialog. |
| | <li> Under '2D Hydraulics Job Control', select 'Surface & Sampling'. | | <li> Under '2D Hydraulics Job Control', select 'Surface & Sampling'. |
| | <li> Review the options in the 'Surface' section: | | <li> Review the options in the 'Surface' section: |
| − | :* If 'Use DTM' is selected: Continue to the section below (<u>[[#XPSWMM_DTM_Preprocessing | XPSWMM DTM Preprocessing]]</u>) and complete the steps. | + | :* If 'Use DTM' is selected: Continue to the section below (<u>[[XPSWMM_to_TUFLOW-SWMM#Export_DTM_Data_from_XPSWMM |Export DTM Data from XPSWMM]]</u>) and complete the steps. |
| − | :* If 'Use Grid File for Topography' is selected and a 'Grid file' is specified: Go to the <u>[[#Convert_XPSWMM_Model_to_Recommended_TUFLOW_Structure | Convert XPSWMM Model to Recommended TUFLOW Structure]]</u> section. The steps outlined in the 'XPSWMM DTM Preprocessing' section can be skipped. | + | :* If 'Use Grid File for Topography' is selected and a 'Grid file' is specified, the steps outlined in the 'Export DTM Data From XPSWMM' section can be skipped. Go to the <u>[[XPSWMM_to_TUFLOW-SWMM#Export_XPX_Data_From_XPSWMM|Export XPX Data From XPSWMM]]</u> section. |
| − | <br> | + | '''Note:''' If you have a .tif elevation file, you can continue to the <u>[[XPSWMM_to_TUFLOW-SWMM#Export_XPX_Data_From_XPSWMM|Export XPX Data From XPSWMM]]</u> section. The conversion process will be identical however, once converted, you will have to create the '''TUFLOW\model\grid''' folder manually and copy the .tif file into it. |
| − | {{Video|name=Animation_XPtoTUFLOW_2D_model_01a.mp4|width=1350}}
| + | <br><br> |
| − | <br>
| + | {{Video|name=Animation_XPtoTUFLOW_Export_Data_01b.mp4|width=1350}} |
| − | </ol> | |
| − | | |
| − | ====XPSWMM DTM Preprocessing====
| |
| − | If 'Use DTM' was selected, XPSWMM pre-processes its Digital Terrain Model (DTM) into a binary XPTIN elevation dataset for inclusion in the TUFLOW model. XPTIN is a propriety format that can't readily be used in GIS software. For this reason, the following section outlines how to obtain a DTM dataset in a GIS friendly form. <br>
| |
| − | | |
| − | :'''Note:''' If 'Use DTM' was selected, follow the steps below. Otherwise, <u>do not</u> complete these steps; continue to the <u>[[#Convert_XPSWMM_Model_to_Recommended_TUFLOW_Structure | Convert XPSWMM Model to Recommended TUFLOW Structure]]</u> section.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | XPSWMM provides two options for preprocessing the DTM to be used in the TUFLOW model, both options are outlined below. As 'Option 1' is straightforward and 'Option 2' is more involved, 'Option 2' is demonstrated in the video below.
| |
| | <br> | | <br> |
| − | :'''Option 1 (recommended)''' - Use Original Source Elevation Data Imported to XPSWMM:
| |
| − | <ol>
| |
| − | <li> Locate the original 'Grid' file (.asc or .flt/.hdr format). Save it to the folder where XPSWMM writes the .tcf during its simulation preprocessing. By default, this is the '''2D\Data''' folder. <br>
| |
| − | If this folder does not exist, either:
| |
| − | :* The XPSWMM model has not run, so the TUFLOW control files have not been created by XPSWMM. Run the XPSWMM model (go to Analyze > Solve... in top dropdown menu options).
| |
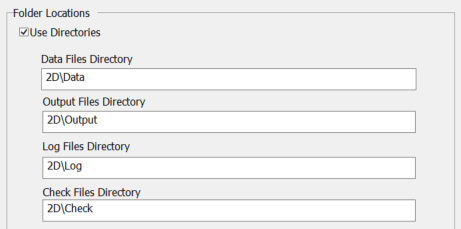
| − | :* Non-default output settings have been specified in XPSWMM. To determine the output location, in the top dropdown menu options, go to Configuration > Job Control > 2D Model Settings > Folder Options. Ensure the following 'Folder Locations' are selected:
| |
| − | ::[[File: XPSWMM_to_TUFLOW_2DJobControl_FolderOptions_Dialog_01c.png]]<br>
| |
| − |
| |
| − | <li> In the top dropdown menu options, navigate to Configuration > Job Control > 2D Model Settings. This will open a dialog, under '2D Hydraulics Job Control', select 'Surface & Sampling'.
| |
| − | <li> Tick on 'Use grid file for topography' and select '...' to navigate to the Grid file saved in the '''2D\Data''' folder. This file will be read directly into TUFLOW.
| |
| − | <li> Click 'OK' to save the settings.
| |
| − | <li> If these steps worked as expected, skip 'Option 2' and continue to the next section. Otherwise, proceed to 'Option 2'.
| |
| | </ol> | | </ol> |
| − | <br>
| |
| | | | |
| − | :'''Option 2''' - Export DTM Data from XPSWMM:
| + | === Export DTM Data From XPSWMM === |
| | + | If 'Use DTM' was selected, XPSWMM preprocesses its Digital Terrain Model (DTM) into a binary XPTIN elevation dataset for inclusion in the TUFLOW model. XPTIN is a binary format that can't readily be used in GIS software. For this reason, the following steps outline how to obtain a DTM dataset in a GIS friendly form. |
| | <ol> | | <ol> |
| | <li> In the XPSWMM Layers panel, under 'Topography', right click on '''DTM''' and select 'Export DTM Data'. | | <li> In the XPSWMM Layers panel, under 'Topography', right click on '''DTM''' and select 'Export DTM Data'. |
| | :* Input TIN File: Select the relevant XPSWMM Input TIN file. | | :* Input TIN File: Select the relevant XPSWMM Input TIN file. |
| | :* Output File Format: 'ASCII Grid File Format'. | | :* Output File Format: 'ASCII Grid File Format'. |
| − | :* Cell Size Value: Choose a suitable DTM resolution. This resolution should be finer than the hydraulic model resolution. Typically, a DTM resolution is 1/10th (or smaller) of the hydraulic model 2D cell size. | + | :* Cell Size Value: Choose a suitable DTM resolution. This resolution should be finer than the hydraulic model resolution. Typically, a DTM resolution is 1/5th to 1/10th of the hydraulic model 2D cell size is common (1 in the example dataset). |
| | + | ''Note: XPSWMM requires an integer cell size value for this export step. For example, Cell Size Values of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ... are suitable. The XPSWMM export will not function if you specify a decimal cell size value (eg. 0.5, 2.5, etc.).'' |
| | <li> Click 'Export'. | | <li> Click 'Export'. |
| − | <li> Save the file to the folder where XPSWMM writes the .tcf during its simulation preprocessing. By default, this is the '''2D\Data''' folder. <br> | + | <li> Save the file under an appropriate name (e.g. '''1D2D_Urban_Grid.asc''') to the folder where XPSWMM writes the .tcf during its simulation preprocessing. By default, this is the '''2D\Data''' folder. <br> |
| | If this folder does not exist, either: | | If this folder does not exist, either: |
| | :* The XPSWMM model has not run, so the TUFLOW control files have not been created by XPSWMM. Run the XPSWMM model (go to Analyze > Solve... in top dropdown menu options). | | :* The XPSWMM model has not run, so the TUFLOW control files have not been created by XPSWMM. Run the XPSWMM model (go to Analyze > Solve... in top dropdown menu options). |
| − | :* Non-default output settings have been specified in XPSWMM. To determine the output location, in the top dropdown menu options, go to Configuration > Job Control > 2D Model Settings > Folder Options. Ensure the 'Folder Locations' shown in the image above are selected. | + | :* Non-default output settings have been specified in XPSWMM. To determine the output location, in the top dropdown menu options, go to Configuration > Job Control > 2D Model Settings > Folder Options. Ensure the following 'Folder Locations' are selected. |
| | + | ::[[File: XPSWMM_to_TUFLOW_2DJobControl_FolderOptions_Dialog_01e.png]]<br><br> |
| | + | |
| | <li> In the top dropdown menu options, navigate to Configuration > Job Control > 2D Model Settings. This will open a dialog, under '2D Hydraulics Job Control', select 'Surface & Sampling'. | | <li> In the top dropdown menu options, navigate to Configuration > Job Control > 2D Model Settings. This will open a dialog, under '2D Hydraulics Job Control', select 'Surface & Sampling'. |
| | <li> Tick on 'Use grid file for topography' and select '...' to navigate to the Grid file saved in the '''2D\Data''' folder. This file will be read directly into TUFLOW. | | <li> Tick on 'Use grid file for topography' and select '...' to navigate to the Grid file saved in the '''2D\Data''' folder. This file will be read directly into TUFLOW. |
| | <li> Click 'OK' to save the settings. | | <li> Click 'OK' to save the settings. |
| − | <li> In the top dropdown menu options, go to Analyze > Solve. This will rerun the XPSWMM model and ensure that the Grid file is recorded. | + | <li> Run the XPSWMM model to rewrite the TUFLOW files (including the new linkage to the DTM dataset) to the Data folder (go to Analyze > Solve... in top dropdown menu options). |
| | <br><br> | | <br><br> |
| − | {{Video|name=Animation_XPtoTUFLOW_2D_model_02a.mp4|width=1350}} | + | {{Video|name=Animation_XPtoTUFLOW_Export_Data_02b.mp4|width=1350}} |
| | <br> | | <br> |
| | </ol> | | </ol> |
| | | | |
| − | === Convert XPSWMM Model to Recommended TUFLOW Structure === | + | === Export XPX Data From XPSWMM === |
| − | When XPSWMM writes its TUFLOW files, it consolidates all the information into a single folder (typically the '''2D\Data''' folder). This is not a standard TUFLOW structure. The standard structure used by the majority of TUFLOW modelers globally includes the following subfolders:
| + | A XPX file is a simple command line file that contains the information needed to create link and node objects. To export this data from the XPSWMM model: |
| | + | <ol> |
| | + | <li> In XPSWMM, in the top dropdown menu options, navigate to File > Import/Export Data > Export XPX Data. This will open a dialog. Leave all options as default and click 'Export'. |
| | + | <li> When prompted, save the file under an appropriate name (eg '''1D2D_Urban_001.xpx''') to the folder where the XPSWMM model is located. |
| | + | <br><br> |
| | + | {{Video|name=Animation_XPtoTUFLOW_Export_Data_03b.mp4|width=1350}} |
| | + | <br> |
| | + | </ol> |
| | | | |
| − | {| class="wikitable" width="80%" style="text-align:center"
| + | == Convert XPSWMM Model to TUFLOW SWMM == |
| − | !style="background-color:#005581; font-weight:bold; color:white;"| Folder
| + | Ensure you have QGIS and have the QGIS TUFLOW Plugin installed: |
| − | !style="background-color:#005581; font-weight:bold; color:white;"| Folder
| + | *Install QGIS 3.34 or later: <u>[https://www.qgis.org/en/site/forusers/download.html Latest 64-bit version of QGIS]</u>. |
| − | !style="background-color:#005581; font-weight:bold; color:white;"| Folder Purpose
| + | *Install the QGIS TUFLOW Plugin by following the instructions, <u>[[TUFLOW_QGIS_Plugin | QGIS TUFLOW Plugin Installation]]</u>. |
| | | | |
| − | |-
| + | The following steps outline the process of converting a XPSWMM model to TUFLOW SWMM using the '<u>[[QGIS_SWMM_Convert_XPSWMM_Model_From_XPX|Convert - XPSWMM model from XPX]]</u>' processing tool. |
| − | |rowspan="10"|[[File:TUFLOW_Folder_Structure.JPG | 150px]]
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |colspan="2"|'''Folders typically saved to the network within a folder titled TUFLOW'''
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | runs || TUFLOW Control File(s) (.tcf), the primary file(s) used to run TUFLOW simulations, are saved here.
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | runs\log || TUFLOW simulation log and error/warning message files are written here during a model simulation.
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | bc_dbase || Input boundary condition database(s) and time-series data for 1D and 2D domains are saved here.
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | model || TUFLOW's second level control files (.tgc, .tbc, .tscf, .ecf) are saved here.
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | model\gis <br> model\grid <br> model\mi <br> model\swmm || GIS layers defining the input spatial datasets are saved here.
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | |colspan="2"|'''Folders typically saved to a computers local drive in a Project folder'''
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | results || TUFLOW simulation results are written here during a model simulation.
| |
| − | |-
| |
| − | | check || TUFLOW simulation check files are written here during a model simulation.
| |
| − | |}
| |
| − | | |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | To simplify the process of converting the XPSWMM model to the recommended TUFLOW SWMM folder structure, we have created a processing tool. This tool converts the GIS format of the XPSWMM model, creates the recommended TUFLOW folder structure and saves the converted model files to their correct locations. For more information on the processing tool, see <u>[[Convert_TUFLOW_Model_GIS_Format | Convert TUFLOW Model GIS Format]]</u>.
| |
| | | | |
| | <ol> | | <ol> |
| − | <li> Open QGIS. If you do not have QGIS installed: | + | <li> Open QGIS and go to Processing > Toolbox from the top dropdown menu options to open the Processing Toolbox. |
| − | :*Install QGIS 3.34 or later: <u>[https://www.qgis.org/en/site/forusers/download.html Latest 64-bit version of QGIS]</u>.
| + | <li> Go to TUFLOW >> SWMM in the processing tool list and select '<u>[[QGIS_SWMM_Convert_XPSWMM_Model_From_XPX|Convert - XPSWMM model from XPX]]</u>'. This opens the dialog shown below. |
| − | :*Install the QGIS TUFLOW Plugin by following the instructions, <u>[[TUFLOW_QGIS_Plugin | QGIS TUFLOW Plugin Installation]]</u>.
| + | :* XPSWMM Exported XPX File: Click '...' and navigate to the exported XPX data (e.g. '''1D2D_Urban_001.xpx'''). This should be located in the same folder as the XPSWMM model. |
| − | <li> In QGIS, go to Processing > Toolbox from the top dropdown menu options to open the Processing Toolbox.
| + | :* TUFLOW TCF Filename: Click '...' and navigate to the XPSWMM .tcf. This should be located in the '''2D\Data''' folder (e.g. '''2D\Data >> 1D2D_Urban_001.tcf'''). |
| − | <li> Go to 'TUFLOW' in the processing tool list and select '<u>[[Convert_TUFLOW_Model_GIS_Format |Convert TUFLOW Model GIS Format]]</u>'. This opens the dialog shown below. | + | :* SWMM File Prefix: Choose an appropriate prefix for the SWMM files (e.g. '''1D2D_Urban_swmm'''). |
| − | :* TCF: Click '...' and navigate to the XPSWMM .tcf. This should be located in the '''2D\Data''' folder. | + | :* Output Solution Scheme: 'HPC' |
| | + | :* Output Hardware Specification: 'GPU' (if GPU is not available, select 'CPU') |
| | :* Output Vector Format: 'GPKG' | | :* Output Vector Format: 'GPKG' |
| | :* Output Raster Format: 'GTIFF' | | :* Output Raster Format: 'GTIFF' |
| − | :* Output Profile: Any option can be used. 'ALL IN ONE' is used in this example for model design consistency with the <u>[[Tutorial_Introduction | TUFLOW SWMM Tutorials]]</u>. | + | :* Output Profile: Any option can be used. 'ALL IN ONE' is used in this example for model design consistency with the <u>[[Tutorial_Introduction | TUFLOW SWMM Tutorials]]</u>. |
| − | :* Output Folder: Click '...' and navigate to an appropriate location to save your TUFLOW model. In this location, create a new folder called '''TUFLOW''' and select it. | + | :* Event name if no global storms: Choose an appropriate event name if applicable (100yr in the example dataset). |
| − | :* Advanced Parameters:
| + | :* BC width for created 1D/2D connections (HX/SX): This value should be approximately 2 times the width of the hydraulic model 2D cell size (10 in the example dataset). |
| − | ::* Tick on 'Write empty files'.
| + | :* BC offset distance for created 1D/2D connections (HX/SX): Distance from the channel endpoint to the midpoint of the BC line (2 in the example dataset). |
| − | ::* Output CRS: Select an appropriate Coordinate Reference System (CRS) for the model.
| + | :* Output Folder: Click '...' and navigate to an appropriate location to save your TUFLOW model. In this location, create a new folder called '''TUFLOW''' and select it. |
| − | ::* Tick on 'Force TUFLOW Directory Structure'.
| + | :* Output CRS: Select an appropriate Coordinate Reference System (CRS) for the model. For the demonstration model, the CRS is 'EPSG:32760 - WGS 84 / UTM zone 60S'. |
| − | ::* TUFLOW Directory Structure Settings: Click '...'. Under 'Folder Structure', click the plus button to add a folder. Set 'Key' to '''swmm''', and 'Path' to '''./model/swmm'''.
| + | <li> Click 'Run'. Once the tool is finished, click 'Close'. |
| − | <li> Click 'Run'. | |
| | <br><br> | | <br><br> |
| − | {{Video|name=Animation_XPtoTUFLOW_2D_model_03a.mp4|width=1350}} | + | {{Video|name=Animation_XPtoTUFLOW_Convert_01c.mp4|width=1350}} |
| | <br> | | <br> |
| | </ol> | | </ol> |
| − | <br>
| |
| | | | |
| − | === Load TUFLOW Model in QGIS ===
| + | Inspect the output of the '<u>[[QGIS_SWMM_Convert_XPSWMM_Model_From_XPX|Convert - XPSWMM model from XPX]]</u>' processing tool and load the TUFLOW model into QGIS: |
| − | Load and style the TUFLOW model in QGIS:
| |
| | <ol> | | <ol> |
| − | <li> Click on the ‘Load TUFLOW Layers from TCF’ symbol from the TUFLOW Plugin toolbar. | + | <li> In Windows File Explorer, inspect the files output by the processing tool. In particular: |
| | + | * The '''TUFLOW\bc_dbase''' folder contains the BC Database which will contain any curves used in BC conditions, for easy extending to other events. |
| | + | * The '''TUFLOW\model''' folder contains the TUFLOW SWMM Control File (TSCF) which holds all commands specific to SWMM, including links to the converted SWMM INP file. |
| | + | * The '''TUFLOW\model\swmm''' folder contains a GeoPackage database ('''*_convert_messages.gpkg'''). This GeoPackage contains locations and descriptions of any errors or warnings that occurred during the conversion process. |
| | + | : '''Note:''' Conversion messages are addressed in further detail here <u>[[XPSWMM_to_TUFLOW-SWMM_Troubleshooting#Common_Conversion_Issues |XPSWMM to TUFLOW SWMM Troubleshooting]]</u>. |
| | + | * The '''TUFLOW\runs''' folder contains the TCF. If event(s) are specified, the TCF filename with have event placeholder(s), i.e. '_~e1~_~e2~_' (e.g. '''1D2D_Urban_001_~e1~.tcf'''). Again, if event(s) are used, this folder also contains the TUFLOW Event File (TEF) with the event(s) specified. <br> |
| | + | {{Video|name=Animation_XPtoTUFLOW_Convert_02b.mp4|width=800}} |
| | + | <br> |
| | + | <li> Open QGIS, and click on the ‘Load TUFLOW Layers from TCF’ symbol from the QGIS TUFLOW Plugin toolbar. |
| | <br> | | <br> |
| | [[File: Tuflow_plugin_load_tcf_layers.png]]<br> | | [[File: Tuflow_plugin_load_tcf_layers.png]]<br> |
| | <br> | | <br> |
| − | <li> Go to the location of the TUFLOW model and navigate to the '''TUFLOW\runs''' folder. Select the TCF. | + | <li> Navigate to the location of the TUFLOW model and go to the '''TUFLOW\runs''' folder. Select the TCF. |
| | <li> In the Load Layers window, select: | | <li> In the Load Layers window, select: |
| | * Ordering Options: Alphabetical | | * Ordering Options: Alphabetical |
| Line 168: |
Line 121: |
| | * Raster Load Options: Load Normally | | * Raster Load Options: Load Normally |
| | <li> Click ‘Open’ and ‘OK’. | | <li> Click ‘Open’ and ‘OK’. |
| | + | <li> Change the symbology of the DTM dataset: |
| | + | * In the QGIS Layers panel, right click on the DTM Grid file and select 'Properties'. |
| | + | * In the Symbology tab, under 'Band Rendering', set the 'Render type' to 'Hillshade' and the 'Z Factor' to 3. |
| | + | <li> Inspect the output GIS layers. |
| | <br><br> | | <br><br> |
| − | {{Video|name=Animation_XPtoTUFLOW_2D_model_04a.mp4|width=1350}} | + | {{Video|name=Animation_XPtoTUFLOW_Convert_03b.mp4|width=1350}} |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | </ol>
| |
| − | | |
| − | Style the layers however you desire. Common steps to do this are:
| |
| − | <ol>
| |
| − | <li>Click on the ‘Apply TUFLOW Styles to Open Layers’ symbol from the TUFLOW Plugin toolbar.
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | [[File:tuflow_plugin_styles_open_layers.png]]<br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | <li>Change the symbology of the DEM:
| |
| − | *In the QGIS Layers panel, move the Grid file to the bottom of the list. This ensures that all the other layers are visible in the QGIS workspace.
| |
| − | *In the QGIS Layers panel, right click the Grid file and select 'Properties'.
| |
| − | *From the Symbology tab, under 'Band Rendering' select the following options:
| |
| − | :*Render type: Singleband pseudocolor
| |
| − | :*Color ramp: Spectral
| |
| − | :*Color ramp: Invert Color Ramp
| |
| − | :*Mode: Equal Interval
| |
| − | *From the Transparency tab, set the Global Opacity to 75%.
| |
| − | *Click 'Apply' and 'OK'.
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | {{Video|name=Animation_XPtoTUFLOW_2D_model_05a.mp4|width=1350}}
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | <li>Create a hillshade of the DEM:
| |
| − | *In the QGIS Layers panel, right click on the Grid file and select 'Duplicate Layer'.
| |
| − | *Right click on the copy and select 'Rename Layer'. Rename the layer to include 'Hillshade' in the filename. For example, '''1D2D_Urban_Grid_copy''' > '''1D2D_Urban_Grid_Hillshade'''.
| |
| − | *Right click on the Hillshade and select 'Properties'.
| |
| − | *From the Symbology tab, under 'Band Rendering' select the following options:
| |
| − | :*Render type: Hillshade
| |
| − | :*Z Factor: 3
| |
| − | *Click 'Apply' and 'OK'.
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | {{Video|name=Animation_XPtoTUFLOW_2D_model_06a.mp4|width=1350}}
| |
| | <br> | | <br> |
| | </ol> | | </ol> |
| | | | |
| − | Save the QGIS Workspace:
| + | == Recommended Additional Conversion Steps == |
| − | <ol> | + | While the bulk of the XPSWMM to TUFLOW SWMM model conversion is automated by the '<u>[[QGIS_SWMM_Convert_XPSWMM_Model_From_XPX|Convert - XPSWMM model from XPX]]</u>' processing tool, some required or recommended conventions must be implemented/updated manually. Therefore, it is highly recommended to complete the additional conversion steps: <u>[[XPSWMM_to_TUFLOW-SWMM_Recommended_Additional_Conversion_Steps|Recommended Additional Conversion Steps]]</u>. <br> |
| − | <li>From the top dropdown menu options, go to Project > Save As. | + | These steps can help improve model stability and they may also be helpful to address any messages that occurred when using the conversion tool. |
| − | <li>Navigate to the file location containing the '''TUFLOW''' folder and save the workspace with the extension, .qgz. | |
| − | </ol>
| |
| | <br> | | <br> |
| | | | |
| − | == One Dimensional (1D) SWMM Model Elements == | + | == TUFLOW Simulation Execution == |
| − | | + | Set up a simple batch file (.bat) to run TUFLOW. This approach calls the TUFLOW executable file (.exe) and runs the TCF file. |
| − | === Export 1D EPA SWMM Pipe Network Data from XPSWMM ===
| |
| − | Convert 1D XPSWMM hydraulics features into a EPA SWMM 5 INP file format for TUFLOW:
| |
| | <ol> | | <ol> |
| − | <li> In XPSWMM, select 'Hydraulics Mode' from the toolbar. | + | <li>Create a new text file in the '''TUFLOW\runs''' folder and save as '''_run_HPC.bat'''. |
| − | <br><br>
| + | <li>Open the '''_run_HPC.bat''' in a text editor and include a file path to the TUFLOW executable and the TCF name: <br> |
| − | [[File: XPSWMM_to_TUFLOW_toolbar_hydraulics_mode_01a.png|700px]]
| + | <font color="blue"><tt>set </font>exe<font color="red">=</font>"..\..\exe\2023-03-AD\TUFLOW_iSP_w64.exe"<br> |
| − | <br>
| + | <font color="blue"><tt>set </font>run<font color="red">=</font>start "TUFLOW" /wait <font color="orange">%exe%</font> -b<br> |
| − | <li> From the XPSWMM top dropmenu, select File > Import/Export Data > Export to EPASWMM5. The exported INP file will be saved under the same name and in the same folder location as the .xp project file.
| + | <font color="orange">%run%</font> -e1 100yr 1D2D_Urban_001_~e1~.tcf</tt></font></tt> <br> |
| − | <li> When prompted to save changes, select 'Yes'.
| |
| − | <li> In Windows File Explorer, navigate to the folder containing the .xp project file and rename the exported INP file by adding 'HDR' to the file name. For example, '''1D2D_Urban_001.inp''' > '''1D2D_Urban_HDR_001.inp'''.
| |
| − | <li> Copy the renamed INP file into the '''TUFLOW\model\swmm''' folder. From this folder, drag and drop the .inp file into QGIS. This will open the '<u>[[QGIS_SWMM_GeoPackage_Create_from_SWMM_inp |GeoPackage - Create from SWMM inp ]]</u>' tool from the QGIS Processing Toolbox. | |
| − | :* SWMM Input File (inp): Pre-populated
| |
| − | :* CRS for GeoPackage: Select and appropriate Coordinate Reference System (CRS) for the model.
| |
| − | :* GeoPackage output filename: Prepopulated to save the output GeoPackage file under the same name and in the same folder location as the SWMM input file.
| |
| − | <li> Click 'Run'. Once the tool is finished, click 'Close'. | |
| − | <li> A dialog will appear. Select 'Add Layers' to open all vectors within the newly created SWMM GeoPackage file. By default, all items in the available list should have been selected. | |
| − | <li> In the QGIS Layers panel, move the SWMM GeoPackage file to the top of the list. This will ensure the data within this database file is displayed above all other layers in the project. | |
| − | <li> Inspect the attributes associated with the various objects in the GeoPackage to familiarize yourself with the data. | |
| − | <br><br> | |
| − | {{Video|name=Animation_XPtoTUFLOW_1D_model_01a.mp4|width=1350}}
| |
| | <br> | | <br> |
| | + | '''Note:''' A relative path is used for the executable and the TCF, full file path can also be used. |
| | + | <li>Save the batch file and double click it in Windows File Explorer to run the simulation. This will open the TUFLOW DOS Console Window and the simulation should be executed. |
| | </ol> | | </ol> |
| | | | |
| − | ===Correct SWMM Nodes--Junction/Outfall Model Design===
| + | TUFLOW simulations can be executed via numerous ways. A comprehensive summary of the most commonly used approaches is documented in the <u>[[Running_TUFLOW | Running TUFLOW]]</u> Wiki page. |
| − | XPSWMM used a modified version of the EPA SWMM engine. Unlike traditional EPA SWMM networks that require '''Nodes--Junctions''' at the upstream end of culverts and '''Nodes--Outfalls''' at the outlets, XPSWMM uses '''Nodes--Junctions''' in all locations. TUFLOW's implementation of SWMM has retained the traditional EPA SWMM structure. Due to this fundamental difference in approach, some manipulation of the XPSWMM '''Nodes--Junctions''' information is necessary.
| |
| − | | |
| − | <ol>
| |
| − | <li> In the QGIS Layers panel, select (left click) '''Nodes--Junctions''' to make it the active dataset.
| |
| − | <li> Go to Processing > Toolbox from the top dropdown menu options to open the Processing Toolbox.
| |
| − | <li> Go to TUFLOW >> SWMM in the processing tool list and select '<u>[[QGIS_SWMM_Junctions_Downstream_Junctions_to_Outfalls |Junctions - Downstream junctions to outfalls]]</u>'. This opens the dialog shown below.
| |
| − | :* Input Junctions: '''Nodes--Junctions''' (this is prepopulated as '''Nodes--Junctions''' is the active dataset).
| |
| − | :* Input Conduits: Click '...' and tick on '''Links--Conduits'''
| |
| − | :* Modified Junctions Layer: Leave this field blank so the tool writes the data to a temporary file. It will not be used.
| |
| − | :* Modified Outfalls Layer:
| |
| − | <ol>
| |
| − | ::<li> Click '...', select 'Save to GeoPackage...'.
| |
| − | ::<li> Navigate to the '''TUFLOW\model\swmm''' folder and select the HDR GeoPackage file created in the <u>[[#Convert_XPSWMM_Model_to_Recommended_TUFLOW_Structure | Convert XPSWMM Model to Recommended TUFLOW Structure]]</u> section. Click 'Save'.
| |
| − | ::<li> A dialog will open. In the 'Layer Name' field, write '''Nodes--Outfalls'''. It is important that this layer is named correctly so it is recognized by the other TUFLOW SWMM processing tools.
| |
| − | ::<li> Click 'OK'.
| |
| − | </ol>
| |
| − | <li> Click 'Run'. Once the tool is finished, click 'Close'.
| |
| − | <li> The temporary junctions layer, '''Modified junctions layer''', and the new outfalls layer, '''Nodes--Outfalls''', will appear in the QGIS Layers panel.
| |
| − | <li> In the QGIS Layers panel, right click '''Modified junctions layer''', and select 'Remove Layer..'.
| |
| − | <li> In the QGIS Layers panel, select (left click) '''Nodes--Outfalls''' and toggle off editing.
| |
| − | <br><br>
| |
| − | {{Video|name=Animation_XPtoTUFLOW_1D_model_02a.mp4|width=1350}}
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | </ol>
| |
| | | | |
| − | To complete the update process, it is necessary to remove the junction nodes from '''Nodes--Junctions''' that coincide with the nodes created in '''Nodes-Outfalls'''. While this can be done manually, the steps below illustrate an automated process using a processing tool.
| + | === Troubleshooting === |
| − | <ol>
| + | Did your TUFLOW SWMM model fail to run successfully? If so, here is a link to a troubleshooting guide: <u>[[TUFLOW_SWMM_Troubleshooting | TUFLOW SWMM Troubleshooting]]</u>.<br> |
| − | <li> In the QGIS Layers panel, select (left click) '''Nodes--Junctions''' and toggle on editing.
| |
| − | <li> Use the 'Select Features' tool to select all nodes included in the '''Nodes--Junctions''' layer. This will change their color to bright yellow.
| |
| − | <li> In the Processing Toolbox, go to 'Vector Selection' and select 'Select within distance'. This opens the dialog shown below.
| |
| − | :* Select features from: '''Nodes--Junctions''' (this is prepopulated as '''Nodes--Junctions''' is the active dataset).
| |
| − | :* By comparing to the features from: Click the drop down menu and select '''Nodes--Outfalls'''.
| |
| − | :* Where the features are within: '0.1 meters'
| |
| − | :* Modify current selection by: 'selecting within current selection'
| |
| − | <li> Click 'Run'. Once the tool is finished, click 'Close'. | |
| − | <li> In the QGIS Layers panel, right click '''Nodes--Junctions''' and select 'Open Attribute Table'. | |
| − | <li> In the attributes table, only some of the junction nodes will be selected. Select 'Delete selected features' to delete these nodes. Close the attribute table.
| |
| − | <li> Toggle the editing off to save the edits.
| |
| − | <br><br>
| |
| − | {{Video|name=Animation_XPtoTUFLOW_1D_model_03a.mp4|width=1350}}
| |
| − | <br> | |
| − | </ol>
| |
| | | | |
| − | === 1D/2D Pipe Network Pit (Inlet Usage) Connections === | + | = TUFLOW SWMM Result Viewing = |
| − | Inlet usage connections establish the 1D/2D linkages between the ground surface, defined in 2D, and the 1D SWMM pipe network. Physically, these features come in various forms and dimensions; however they are commonly referred to as kerb inlets, with or without associated grates. An example is shown in the image below. <br>
| + | Are you familiar with loading and viewing TUFLOW results in QGIS? If not, we strongly recommend self-registering and completing our free eLearning: |
| − | <br> | + | <u>[https://www.tuflow.com/training/training-catalogue/tt001e-introduction-to-qgis-for-tuflow-elearning/ Introduction to QGIS for TUFLOW]</u>. <br> |
| − | [[File: XPSWMM_Kerb_Inlet.JPG | 300px ]] <br> | + | Our <u>[[TUFLOW_SWMM_Tutorial_Introduction | TUFLOW SWMM Tutorials]]</u> also demonstrate working with TUFLOW SWMM results. |
| − | <br> | |
| − | Transfer of inlet usage connection information from XPSWMM to TUFLOW involves a three step process:
| |
| − | <ol> | |
| − | <li> Export data from XPSWMM. | |
| − | <li> Convert the exported data into a TUFLOW SWMM compatible format.
| |
| − | <li> Make minor edits to correct for snapping deficiencies in the XPSWMM export tools.
| |
| − | </ol>
| |
| | | | |
| | + | = Recommended Further Reading = |
| | + | For users who wish to get a better understanding of either 2D TUFLOW or 1D EPA SWMM, the following resources may be of use:<br> |
| | + | '''TUFLOW''': <u>[https://www.tuflow.com www.tuflow.com]</u> |
| | + | *<u>[https://www.tuflow.com/downloads/#tuflow TUFLOW User Manual]</u> |
| | + | *<u>[https://docs.tuflow.com/classic-hpc/release/2023-03-AD/ TUFLOW 2023-03-AD release notes]</u> |
| | + | *<u>[[Tutorial_Introduction#Tutorial_Modules | TUFLOW Tutorial Models]]</u> |
| | | | |
| − | ==== Export Data from XPSWMM====
| |
| − | <ol>
| |
| − | <li> In XPSWMM, select 'Hydraulics Mode' from the toolbar.
| |
| − | <br><br>
| |
| − | [[File: XPSWMM_to_TUFLOW_toolbar_hydraulics_mode_01a.png|700px]]
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | <li> In the XPSWMM Layers panel, right click '''Nodes''' and select 'Export To GIS File...'. This will open a dialog.
| |
| − | <li> Select the GIS File: Click the '...' and navigate to the '''TUFLOW\model\swmm''' folder. Enter an appropriate filename and set the file type to ESRI (*.shp). For example, '''1D2D_Urban_Node_Export_001.shp'''
| |
| − | <li> Click 'Node Data and Results' to expand the folder tree. Go to Node Data and Results > Hydraulics Node > HDR Node Data. Double click to select the following items:
| |
| − | :* Node 2D Inflow Capture Flag
| |
| − | :* Ground Elevation (Spill Crest)
| |
| − | :* 2D Inflow Capture Coefficient
| |
| − | :* 2D Inflow Capture Exponent
| |
| − | <li> In the right-hand table, the items above, along with 'Node Name', 'Node X' and 'Node Y', should be selected.
| |
| − | <li> In the 'Custom Name' column, select each entry and shorten the text to less than 10 characters. For example, 'Node 2D Inflow Capture Flag' > 'NodeIn' and 'Ground Elevation (Spill Crest)' > 'Ground'.
| |
| − | <li> Click 'Export'. A message will appear reporting how many nodes were exported.
| |
| − | <br><br>
| |
| − | {{Video|name=Animation_XPtoTUFLOW_1D_model_04a.mp4|width=1350}}
| |
| | <br> | | <br> |
| − | </ol> | + | '''EPA SWMM''': <u>[https://www.epa.gov/water-research/storm-water-management-model-swmm www.epa.gov]</u> |
| | + | *<u>[https://downloads.tuflow.com/SWMM/SWMM5_Reference_Manual_Volume1_Hydrology_P100NYRA.pdf SWMM5 Reference Manual - Volume 1 (Hydrology)]</u> |
| | + | *<u>[https://downloads.tuflow.com/SWMM/SWMM5_Reference_Manual_Volume2_Hydaulics_P100S9AS.pdf SWMM5 Reference Manual - Volume 2 (Hydraulics) ]</u> |
| | + | *<u>[https://downloads.tuflow.com/SWMM/SWMM5_Reference_Manual_Volume2_Hydraulics_Addendum-20220210mas2wr.pdf SWMM5 Reference Manual - Volume 2 (Hydraulics Addendum) ]</u> |
| | + | *<u>[https://downloads.tuflow.com/SWMM/SWMM5_Reference_Manual_Volume3_Water_Quality_P100P2NY.pdf SWMM5 Reference Manual - Volume 3 (Water Quality) ]</u> |
| | + | *<u>[https://downloads.tuflow.com/SWMM/SWMM5_User%27s_Manual.pdf EPA SWMM5 User's Manual]</u> |
| | | | |
| − | ==== Convert Exported Data into TUFLOW SWMM Format ==== | + | =Feedback / Suggestions= |
| − | <ol>
| + | We hope you have found this model conversion page helpful. If you have any feedback or suggestions, please email <u>[mailto::support@tuflow.com support@tuflow.com]</u>. |
| − | <li> In Windows File Explorer, navigate to the '''TUFLOW\model\swmm''' folder. Drag and drop the node export .shp file into QGIS.
| |
| − | <li> In the QGIS Layers panel, select (left click) the node export layer.
| |
| − | <li> In the Processing Toolbox, go to TUFLOW >> SWMM and select '<u>[[QGIS_SWMM_Convert_XPSWMM_GIS_Inlet_Layers_to_SWMM |Convert - XPSWMM GIS inlet layers to SWMM]]</u>'. This opens the dialog shown below.
| |
| − | :* GIS layer with inlet information: This is prepopulated as the node export layer is the active dataset.
| |
| − | :* Inlet name field: 'Node Name'
| |
| − | :* Inlet elevation field: 'Ground'
| |
| − | :* Inlet 2d capture flag field: 'NodeIn'
| |
| − | :* Inlet discharge equation coefficient field: 'Coeff'
| |
| − | :* Inlet discharge exponent field: 'Exponent'
| |
| − | :* Inlet connection width: This defines the number of 2D cells associated with the 1D/2D connections. Typically, this should match the 2D cell size of the model.
| |
| − | :* CRS: Select the models' Coordinate Reference System (CRS).
| |
| − | :* SWMM inp file (for inlet definition and curves):
| |
| − | <ol>
| |
| − | ::<li> Click '...', and select 'Save to File...'.
| |
| − | ::<li> Navigate to the '''TUFLOW\model\swmm''' folder. Choose an appropriate .inp file name. For example, '''swmm_inlet_curves_XP_001.inp'''. This tool will also create a .gpkg file with the same data and name; saved in the same file location, i.e. '''swmm_inlet_curves_XP_001.gpkg'''.
| |
| − | ::<li> Click 'Save'.
| |
| − | </ol>
| |
| − | :* GeoPackage file for inlet usage:
| |
| − | <ol>
| |
| − | ::<li> Click '...', and select 'Save to File...'.
| |
| − | ::<li> Navigate to the '''TUFLOW\model\swmm''' folder. Choose an appropriate .gpkg file name. For example, '''swmm_iu_XP_001.gpkg'''.
| |
| − | ::<li> Click 'Save'.
| |
| − | </ol>
| |
| − | <li> Click 'Run'. Once the tool is finished, click 'Close'.
| |
| − | <li> Remove the node export layer from the QGIS workspace.
| |
| − | <li> In Windows File Explorer, navigate to the '''TUFLOW\model\swmm''' folder. Drag and drop the two new GeoPackage databases (i.e. '''swmm_iu_XP_001.gpkg''' and '''swmm_inlet_curves_XP_001.gpkg''') into QGIS (hold Ctrl to select multiple). Inspect the attributes associated with the objects in both GeoPackages.
| |
| − | <br><br>
| |
| − | {{Video|name=Animation_XPtoTUFLOW_1D_model_05a.mp4|width=1350}}
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | </ol>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ====Edit TUFLOW SWMM Data====
| |
| − | Unfortunately, the snapping tolerance set by XPSWMM for its Node GIS Data Export function is larger than the underlying model information it is associated with. This can cause a slight offset in the data. To rectify this issue, we will use a processing tool designed to assist in this task.
| |
| − | <ol>
| |
| − | <li> In the QGIS Layers panel, select (left click) the inlet usage layer (i.e. '''swmm_iu_XP_001''') and toggle on editing.
| |
| − | <li> In the Processing Toolbox, select the 'Edit Features In-Place' tool [[File:edit_features_in_place_icon.png]]. This allows the editing of an existing layer, instead of the creation of a new layer.
| |
| − | <li> Go to 'Vector geometry' in the processing tool list and select 'Snap geometries to layer'. This opens the dialog shown below.
| |
| − | :* Reference Layer: '''Nodes--Junctions'''. This is the layer we want the inlet usage layer to snap to.
| |
| − | :* Tolerance: '0.1 meters'
| |
| − | :* Behavior: 'Prefer aligning nodes, insert extra vertices where required'
| |
| − | <li> Click 'Modify All Features'. Once the tool is finished, click 'Close'.
| |
| − | <li> Toggle off the editing for the inlet usage layer (i.e.'''swmm_iu_XP_001''') to save the edits.
| |
| − | <br><br>
| |
| − | {{Video|name=Animation_XPtoTUFLOW_1D_model_06a.mp4|width=1350}}
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | </ol>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Create 1D/2D Culvert Connections===
| |
| − | In addition to the pipe network inlet usage 1D/2D connections, we also need to connect the 1D culvert inlet/outlets to the 2D. These features are typically associated with culverts located under raised roads or rail embankments, outlets from pipe networks into creeks, streams, or rivers, or open pipe network inlets and outlets linked to major stormwater drainage infrastructure, which often involves the modification of historically above-ground streamflows to an underground stormwater network. An example is shown in the image below.<br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | [[File: XPSWMM_Culvert_Inlet.JPG | 500px]]<br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | In order to connect a 1D SWMM culvert to TUFLOW 2D, TUFLOW SWMM necessitates 1D/2D HX connection lines at the upstream (inlet) end of the culvert and 1D/2D SX connection lines at the downstream (outlet) end. This model schematization differs from that of the TUFLOW ESTRY and XPSWMM, which require 1D/2D SX connections both upstream and downstream, but aligns with the traditional requirements of EPA SWMM.
| |
| − | | |
| − | <ol>
| |
| − | <li> In the QGIS Layers panel, select (left click) '''Links--Conduits'''.
| |
| − | <li> Use the 'Select Features' tool to select the culvert and pipe objects that will have a clear opening in '''Links--Conduits''' (hold Shift to select multiple). Typically, these culvert and pipe objects are located under an embankment or connect to/from a waterway, such as a creek. In XPSWMM, this type of feature is typically represented by '''Links''' snapped to '''Nodes''' with 'Link invert to 2D' selected.
| |
| − | <li> In the Processing Toolbox, go to TUFLOW >> SWMM and select '<u>[[QGIS_SWMM_BC_Create_Channel_Endpoint_1D/2D_Connections |BC - Create channel endpoint 1D/2D connections]]</u>'. This opens the dialog shown below.
| |
| − | :* Input Conduits Layer: '''Links--Conduits''' (this is prepopulated as '''Links--Conduits''' is the active dataset).
| |
| − | :* Tick on 'Selected features only'.
| |
| − | :* Create connections at: 'Both ends'.
| |
| − | :* Offset Distance: This value is the distance from the channel endpoint to the midpoint of the BC line. The recommended value is 2.
| |
| − | :* Length of BC lines: This value should be similar the width of the channel.
| |
| − | :* Tick on 'Set 2D cell elevation to 1D culvert invert at 1D/2D connection cells if needed'.
| |
| − | :* Output Layer:
| |
| − | <ol>
| |
| − | ::<li> Click the ... and select 'Save to GeoPackage'.
| |
| − | ::<li> Navigate to the '''TUFLOW\model\gis''' folder and select the GPKG created from the XPSWMM model in the <u>[[#Convert_XPSWMM_Model_to_Recommended_TUFLOW_Structure | Convert XPSWMM Model to Recommended TUFLOW Structure]]</u> section. This GPKG will have the same name as the original XPSWMM model.
| |
| − | ::<li> Click 'Save'. A dialog will open. In the 'Layer Name' field, write an appropriate layer name. It is recommended to name the output layer with the prefix '2d_bc' so TUFLOW styles can be automatically applied. For example, '''2d_bc_Culvert_Connections_001_L'''.
| |
| − | ::<li> Click 'OK'.
| |
| − | </ol>
| |
| − | <li> Click 'Run'. Once the tool is finished, click 'Close'.
| |
| − | <li> The 2d_bc layer will appear in the QGIS Layers panel. Select (left click) the 2d_bc layer and click 'Apply TUFLOW Styles to Current Layer'. Toggle on editing.
| |
| − | <li> Review the '''2d_bc_SWMM_Culvert_Connections_001_L''' data. Make corrections by deleting objects located where a 1D/2D connection was required only at one end of the conduit, rather than at both ends.
| |
| − | <li> Toggle editing off for '''2d_bc_SWMM_Culvert_Connections_001_L''' to save the edits.
| |
| − | <br><br>
| |
| − | {{Video|name=Animation_XPtoTUFLOW_1D_model_07a.mp4|width=1350}}
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | </ol>
| |
| − | | |
| − | === SWMM Hydrology ===
| |
| − | If the XPSWMM model includes EPA SWMM hydrology, the hydrology components can be brought across into TUFLOW SWMM.
| |
| − | | |
| − | First, to confirm the SWMM Hydrology runoff method has been used in the XPSWMM model, review the model settings. In XPSWMM, from the top dropdown menu options, go to Configuration > Mode Properties. Under 'Solve Mode', select 'Methods' Confirm 'SWMM Methods (64 bit)' is selected. <br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | [[File:XPSWMM_to_TUFLOW_swmm_hydrology_runoff_method_01b.png]]
| |
| − | <br><br>
| |
| − | | |
| − | Convert 1D XPSWMM hydraulics features into a EPA SWMM 5 INP file format for TUFLOW:
| |
| − | <ol>
| |
| − | <li> In XPSWMM, select 'Runoff Mode' from the toolbar.
| |
| − | <br><br>
| |
| − | [[File: XPSWMM_to_TUFLOW_toolbar_runoff_mode_01a.png|700px]]
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | <li> From the XPSWMM top dropdown menu options, select File > Import/Export Data > Export to EPASWMM 5. The exported INP file will be saved under the same name and in the same folder location as the .xp project file.
| |
| − | <li> When prompted to save changes, select 'Yes'.
| |
| − | <li> In QGIS, go to TUFLOW >> SWMM in the processing tool list and select '<u>[[QGIS_SWMM_GeoPackage_Create_from_SWMM_inp |GeoPackage - Create from SWMM inp ]]</u>'. This open the dialog shown below.
| |
| − | :* SWMM Input File (inp): Navigate to the folder location of the .xp project file and select the recently exported INP file.
| |
| − | :* CRS for GeoPackage: Select an appropriate Coordinate Reference System (CRS) for the model.
| |
| − | :* GeoPackage output filename: Navigate to the '''TUFLOW\model\swmm''' folder. Save the file with the same name as the SWMM input file, but append 'RNF' to the filename. For example '''1D2D_Urban_001.inp''' > '''1D2D_Urban_RNF_001.gpkg'''.
| |
| − | <li> Click 'Run'. Once the tool is finished, click 'Close'.
| |
| − | <br><br>
| |
| − | {{Video|name=Animation_XPtoTUFLOW_1D_model_08a.mp4|width=1350}}
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | <li> This tool has generated a '''Nodes--Junctions''' layer which is a duplicate of the '''Nodes--Junctions''' layer in the HDR GeoPackage. Thus, we will remove the RNF '''Nodes--Junctions''' layer.
| |
| − | <li> In QGIS, from the top dropdown menu options, select View > Panels. Tick on 'Browser Panel'.
| |
| − | <li> In the QGIS Browser Panel, navigate to the '''TUFLOW\model\swmm''' folder and open the RNF GeoPackage layer tree.
| |
| − | :'''Note:''' Within the QGIS Browser Panel, there is a dropdown directory, 'Project Home'. This directory is a shortcut to the location where the QGIS workspace is saved.
| |
| − | <li> Right click '''Nodes--Junctions''' and select Manage > Delete Layer.
| |
| − | <li> In Windows File Explorer, navigate to the '''TUFLOW\model\swmm''' folder. Drag and drop the RNF GeoPackage into QGIS.
| |
| − | <li> In the QGIS Layers panel, move the RNF GeoPackage below the other GeoPackages in the list. This will ensure the data within this database file does not cover the other layers in the project. <br>
| |
| − | '''Note:''' For hydrology, TUFLOW has more advanced, workflow efficient 'Event Scenario Management' options than XPSMM. If your project requires the simulation of multiple hydrology events, please complete <u>[[TUFLOW_SWMM_Tutorial_M04 | TUFLOW SWMM Module 4 (1D SWMM Pipe Network / 1D SWMM Urban Hydrology: Executing multiple different event simulations from a single model control file)]]</u>. and use the model design concepts in it to upgrade the configuration of your TUFLOW model to accommodate for the simulation of multiple events from a single model.
| |
| − | <br><br>
| |
| − | {{Video|name=Animation_XPtoTUFLOW_1D_model_09a.mp4|width=1350}}
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | </ol>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Update SWMM Nodes--Junction Attributes===
| |
| − | The following GIS feature update to the '''Nodes--Junctions'' attributes will finalize the SWMM portion of the TUFLOW model. This is typically the final step in the model building process, as the recommended attributes for junction node vary depending on whether the node is associated with inlet usage connections, 1D/2D culvert connections and SWMM hydrology sub-catchments.
| |
| − | | |
| − | <ol>
| |
| − | <li> In the QGIS Layers panel, select (left click) '''Nodes--Junctions''' and toggle on editing.
| |
| − | <li> In the Processing Toolbox, select the 'Edit Features In-Place' tool. This allows the editing of an existing layer, instead of the creation of a new layer.
| |
| − | <li> Go to TUFLOW >> SWMM in the processing tool list and select the '<u>[[QGIS_SWMM_Junctions_Set_Attributes |Junctions - Set attributes ]]</u>' processing tool. This opens the dialog shown below.
| |
| − | :* Input Subcatchment layers: If available, select '''Hydrology--Subcatchments'''.
| |
| − | :* Input Inlet Usage Layers: If available, select the inlet usage layer (i.e. '''swmm_iu_XP_001''')
| |
| − | :* Input BC Connection Layers: If available, select the 2d_bc connection layer.
| |
| − | :* General Options:
| |
| − | :::* Maximum Depth Option (Ymax): 'Set to 0.0'.
| |
| − | :::* Nodes receiving subcatchment flows option (if connected to 2D): 'Set Apond = 0.0; Ksur = 0.0 (overwrites options below)'.
| |
| − | :* Nodes connected to 2D without Inlets:
| |
| − | :::* Ysur: 0
| |
| − | :::* Area of ponding: This value should match the 2D cell area associated with 1D/2D culvert connections.
| |
| − | :* Nodes connected to 2D with Inlets:
| |
| − | :::* Maximum depth (Ymax) option: 'Use global option'
| |
| − | :::* Ysur: 0
| |
| − | :::* Area of ponding: This value should match the 2D cell area associated with the Inlet Usage connections.
| |
| − | :* Nodes without 2D Connection:
| |
| − | :::* Surcharge Depth: This value should be a value higher than any expected water level in the model.
| |
| − | :::* Area of ponding: 1
| |
| − | <li>Select 'Modify All Features'. Once the tool has finished, click 'Close'.
| |
| − | <li>Turn off editing to save the edits.
| |
| − | <li>View the attributes within '''Nodes--Junctions''' to verify the data processing has been completed correctly. <br>
| |
| − | For a summary of the attributes associated with the '''Nodes--Junctions''' layer, refer to <u>[https://docs.tuflow.com/classic-hpc/release/2023-03-AD/SWMM-Input-Detailed-1.html#tab:tab-SWMM-Input-Junctions TUFLOW 2023-03-AD Release Notes (Table A.30)]</u> and the <u>[https://downloads.tuflow.com/SWMM/SWMM5_Reference_Manual_Volume2_Hydaulics_P100S9AS.pdf SWMM Reference Manual - Volume 2 (Hydraulics)]</u>.
| |
| − | <br><br>
| |
| − | {{Video|name=Animation_XPtoTUFLOW_1D_model_10a.mp4|width=1350}}
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | </ol>
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Export INP Files===
| |
| − | SWMM cannot directly read GeoPackage databases. Therefore, we need to convert all three GeoPackage files (HDR, RNF and inlet curves) into the SWMM INP file format. Both the HDR and RNF GeoPackages contain a '''Project--Options''' section, which are identical as they were extracted from the same XPSWMM model. These options are necessary for executing the SWMM simulation. Since '''Project--Options''' is already included in the HDR and RNF, it is not needed in the inlet curves INP file. <br>
| |
| − | '''Note:''' The inlet usage GeoPackage does not need to be converted to a SWMM inp file. Since it contains only one layer, it can be directly read into TUFLOW SWMM.
| |
| − | | |
| − | <ol>
| |
| − | <li> In QGIS, go to TUFLOW >> SWMM in the processing tool list and select '<u>[[QGIS_SWMM_GeoPackage_Write_to_SWMM_inp |GeoPackage - Write to SWMM inp]]</u>'.
| |
| − | <li> In the tool window, click the '...' and navigate to the '''TUFLOW\model\swmm''' folder. Select the HDR GeoPackage file.
| |
| − | <li> Click 'Run'.
| |
| − | <li> Once the tool has finished, click the 'Parameters' tab.
| |
| − | <li> Repeat steps 2 and 3 for the RNF and inlet curves GeoPackages.
| |
| − | <li> Once the tool has finished, click 'Close'.
| |
| − | <li> The three SWMM INP files will be located in the '''TUFLOW\model\swmm''' folder, with each file sharing the same filename as their respective GeoPackages. For example, '''1D2D_Urban_HDR_001.gpkg''' > '''1D2D_Urban_HDR_001.inp'''.
| |
| − | <br><br>
| |
| − | {{Video|name=Animation_XPtoTUFLOW_1D_model_11a.mp4|width=1350}}
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | </ol>
| |
| − | | |
| − | = Link 1D SWMM and 2D TUFLOW Model =
| |
| − | The linking between the 1D SWMM and the 2D TUFLOW model is established within the TUFLOW control files, which are essential for running TUFLOW-SWMM simulations. The following steps outline the basic commands needed to complete the linking process and execute the model. These commands may need to be modified depending on the modeling task.
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | == Simulation Control Files ==
| |
| − | The following steps will require use of a text editor. The tutorial demonstration uses Notepad++. For its configuration information refer to <u>[[NotepadPlusPlus_Tips | Notepad++ Tips]]</u>. For a clean and organized model, it is recommended to name all the TUFLOW control files similarly. For example, '''1D2D_Urban_001.tscf''', '''1D2D_Urban_001.tbc''', '''1D2D_Urban_001.tgc''' and '''1D2D_Urban_5m_001.tcf'''. <br>
| |
| − | | |
| − | '''Note:''' For this demonstration, all commands will reference the datasets in the provided conversion model. Please update these references with the filenames sued in your model.<br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | | |
| − | === Clean TUFLOW Control Files ===
| |
| − | In the process of converting a model, the <u>[[Convert_TUFLOW_Model_GIS_Format |Convert TUFLOW Model GIS Format]]</u> processing tool adds commands to the TUFLOW control files created by XPSWMM. While these control files contain essential commands, they typically lack sufficient information to enable the mode to run smoothly. Additionally, these files are often not neatly structured. To ensure a functional and easily readable mode, it is recommended to 'clean up' the TUFLOW control files. This can be done by:
| |
| − | :* Adding in commands required to execute the model. For example, <font color="blue"><tt>Solution Scheme </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt> HPC </tt></font> <font color="green"><tt> ! Heavily Parallelised Compute, uses adaptive timestepping</tt></font>.<br>
| |
| − | :* Removing unnecessary commands.
| |
| − | :* Using relative file paths to specify the location of various files and layers in the model.
| |
| − | :* Including a title at the beginning of each control file. For example, <font color="green"><tt>! TUFLOW CONTROL FILE (.TCF) defines the model simulation parameters and directs input from other data sources</tt></font>.
| |
| − | :* Adding headings to sections of the control file. For example, <font color="green"><tt>! MODEL INITIALIZATION</tt></font> could be used as a header for the commands required to initialize the TUFLOW SWMM model.
| |
| − | :* Using comments to explain the purpose of commands. For example, <font color="blue"><tt>Spatial Database </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt> ..\model\gis\1D2D_Urban_001.gpkg </tt></font> <font color="green"><tt> ! Specify the location of the GeoPackage Spatial Database</tt></font>.<br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | | |
| − | The process below demonstrates how to clean up a TCF, using the provided model conversion dataset.
| |
| − | <ol>
| |
| − | <li> In Windows File Explorer, navigate to the '''TUFLOW\runs''' folder and open the TCF into a Text Editor (Notepad++ is recommended).
| |
| − | <li> Add control file title and section headings: <br>
| |
| − | <font color="green"><tt>! TUFLOW CONTROL FILE (.TCF) defines the model simulation parameters and directs input from other data sources<br>
| |
| − | ! MODEL INITIALIZATION <br>
| |
| − | ! SOLUTION SCHEME <br>
| |
| − | ! MODEL INPUTS <br>
| |
| − | ! TIME CONTROL <br>
| |
| − | ! OUTPUT FOLDERS <br>
| |
| − | ! OUTPUT SETTINGS <br>
| |
| − | ! TIME SERIES PLOT OUTPUT</tt></font>
| |
| − | <li> Organize the commands into these section headings. <br>
| |
| − | <font color="green"><tt>! MODEL INITIALIZATION</tt></font><br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>Spatial Database </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt> ..\model\gis\1D2D_Urban_001.gpkg </tt></font> <br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>GPKG Projection </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt> ??? </tt></font> <br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>TIF Projection </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt> ..\model\grid\1D2D_Urban_Grid.tif </tt></font> <br>
| |
| − | <font color="green"><tt>! MODEL INPUTS</tt></font><br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>Geometry Control File </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt> ..\model\1D2D_Urban_001.tgc </tt></font> <br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>BC Control File </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt> ..\model\1D2D_Urban_001.tbc </tt></font> <br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>BC Database </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt> ..\bc_dbase\1D2D_Urban_001_2d_bc_db.csv </tt></font> <br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>Read Materials File </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt> ..\model\1D2D_Urban_001_Mat.csv </tt></font> <br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>Read Soils File </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt> ..\model\1D2D_Urban_001.tsoilf </tt></font> <br>
| |
| − | <font color="green"><tt>! TIME CONTROL</tt></font><br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>Timestep </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt> 1.000000 </tt></font> <br>
| |
| − | <font color="green"><tt>! OUTPUT SETTINGS</tt></font><br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>Map Output Data Types </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt> q V d h Z0 </tt></font> <br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>Map Output Interval (s) </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt> 60.000000 </tt></font> <br>
| |
| − | <font color="green"><tt>! TIME SERIES PLOT OUTPUT</tt></font><br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>Read GIS PO </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt> 1D2D_Urban_001_2d_po_P </tt></font> <br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>Read GIS PO </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt> 1D2D_Urban_001_2d_po_L </tt></font> <br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>Time Series Output Interval (s) </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt> 60.000000 </tt></font> <br>
| |
| − | <li> In the 'Model Initialization' and 'Solution Scheme' sections, add in the commands required to run the TUFLOW model: <br>
| |
| − | <font color="green"><tt>! MODEL INITIALIZATION</tt></font><br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>Tutorial Model </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt> ON </tt></font> <br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>GIS Format </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="blue"><tt> GPKG </tt></font> <br>
| |
| − | <font color="green"><tt>! SOLUTION SCHEME</tt></font><br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>Solution Scheme </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="blue"><tt> HPC </tt></font> <br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>Hardware </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="blue"><tt> GPU </tt></font> <br>
| |
| − | <li> Set the start and end time of the model:<br>
| |
| − | <font color="green"><tt>! TIME CONTROL</tt></font><br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>Start Time </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt> 0</tt></font> <br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>End Time </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt> 3 </tt></font> <br>
| |
| − | <li> Set the model output folders:<br>
| |
| − | <font color="green"><tt>! OUTPUT FOLDERS</tt></font><br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>Log Folder </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt> log </tt></font> <br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>Output Folder </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt> ..\results\ </tt></font> <br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>Write Check Files </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt> ..\check\ </tt></font> <br>
| |
| − | <li> Add the following commands to the 'Output Settings' section:<br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>Map Output Format </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="blue"><tt> XMDF TIF </tt></font> <br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>TIF Map Output Interval </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt> 0 </tt></font> <br>
| |
| − | <li> Add comments to explain the commands.
| |
| − | <li> Remove all commands not included in the headings above, they are unnecessary for a TUFLOW SWMM model.
| |
| − | <li> If using the provided model conversion dataset, the final TCF should look like this:
| |
| − | <br><br>
| |
| − | [[File:XPSWMM_to_TUFLOW_clean_up_TCF_01b.png]]
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | </ol>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | | |
| − | === TUFLOW Control File (TCF) ===
| |
| − | The TCF file references all the control files, specifies time and output controls.
| |
| − | <ol>
| |
| − | <li> In Windows File Explorer, navigate to the '''TUFLOW\runs''' folder and open the TCF into a Text Editor (Notepad++ is recommended).
| |
| − | <li> Add the following command to the 'Model Inputs' section:<br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>SWMM Control File </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt>..\model\1D2D_Urban_001.tscf </tt></font> <font color="green"><tt> ! Reference the SWMM (1D) Control File</tt></font><br><br>
| |
| − | <font color="red"><tt> Video? </tt></font>
| |
| − | </ol>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | | |
| − | === TUFLOW SWMM Control File (TSCF) ===
| |
| − | The TUFLOW SWMM Control File (TSCF) is used to control the SWMM input data flow. All 1D SWMM files and commands are referenced in the TUFLOW SWMM Control File.<br>
| |
| − | <ol>
| |
| − | <li> In Windows File Explorer, navigate to the '''TUFLOW\model''' folder and create a new blank text file with the extension .tscf.
| |
| − | <li> Open the TSCF into a Text Editor (Notepad++ is recommended) and add the following commands. These filenames are examples, reference your model SWMM INP files.<br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>Read SWMM </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt>..\swmm\1D2D_Urban_HDR_001.inp </tt></font> <font color="green"><tt> ! 1D SWMM Pipe Network input file</tt></font><br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>Read SWMM </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt>..\swmm\1D2D_Urban_RNF_001.inp </tt></font> <font color="green"><tt> ! 1D SWMM Hydrology input file</tt></font><br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>Read SWMM </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt>..\swmm\swmm_inlet_curves_XP_001.inp </tt></font> <font color="green"><tt> ! 1D SWMM Inlet Curves input file</tt></font><br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>Read SWMM Inlet Usage</tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt>..\swmm\swmm_iu_XP_001.gpkg </tt></font> <font color="green"><tt> ! 1D SWMM Pipe Network Inlet Usage layer</tt></font>
| |
| − | <br><br>
| |
| − | '''<<Video>>'''
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | </ol>
| |
| − | | |
| − | === TUFLOW Boundary Control File (TBC) ===
| |
| − | The TUFLOW Boundary Control File (TBC) contains information regarding the location of boundary conditions and internal links within the model.
| |
| − | <ol>
| |
| − | <li> In Windows File Explorer, navigate to the '''TUFLOW\model''' folder and open the TBC into a text editor (Notepad++ is recommended).
| |
| − | <li> Remove all commands from the TBC file.
| |
| − | <li> Add the following command to reference the external model boundary: <br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>Read GIS BC </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt>1D2D_Urban_001_2d_bc_L </tt></font><br>
| |
| − | <li> Add the following command to reference the link between the 1D SWMM culverts and the 2D TUFLOW domain.<br>
| |
| − | <font color="blue"><tt>Read GIS BC </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt>2d_bc_Culvert_Connections_001_L </tt></font><br>
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | '''<font color="red">Video</font>'''
| |
| − | </ol>
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | === TUFLOW Geometry Control File (TGC) ===
| |
| − | The TGC file is a series of commands that build the geometry model. At its minimum, the TGC contains:
| |
| − | :* Information on the size and orientation of the grid;
| |
| − | :* Grid cell codes (whether cells are active or inactive);
| |
| − | :* Bed / ground elevations; and
| |
| − | :* Bed material type or flow resistance value.
| |
| − | <ol>
| |
| − | <li> In Windows File Explorer, navigate to the '''TUFLOW\model''' folder and open the TGC into a text editor (Notepad++ is recommended).
| |
| − | <li> Replace all '#' with '!'.
| |
| − | <br>
| |
| − | '''<font color="red">Video</font>'''
| |
| − | </ol>
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | '''<font color="red"> Below is from Pavlina's edits - keeping as a reference for now</font>'''
| |
| − | <ol>
| |
| − | <li>Update main TUFLOW control file (TCF):
| |
| − | :* Add below commands if applicable:
| |
| − | <ol><font color="blue"><tt>Solution Scheme </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt>HPC </tt></font></ol>
| |
| − | <ol><font color="blue"><tt>Hardware </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt>GPU </tt></font></ol>
| |
| − | <ol><font color="blue"><tt>GIS Format </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt>GPKG </tt></font></ol>
| |
| − | :* Add TSCF command to read the 1D SWMM features:
| |
| − | <ol><font color="blue"><tt>SWMM Control File </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt>..\swmm\SWMM.tscf </tt></font></ol>
| |
| − | :* Add time control comands:
| |
| − | <ol><font color="blue"><tt>Start Time</tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt><<start_time>> </tt></font></ol>
| |
| − | <ol><font color="blue"><tt>End Time </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt><<end_time>> </tt></font></ol>
| |
| − | :* Rarely used options to consider removing from the TCF:
| |
| − | <ol><font color="blue"><tt>SX ZC Check </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt>OFF </tt></font></ol>
| |
| − | <ol><font color="blue"><tt>HX ZC Check </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt>OFF </tt></font></ol>
| |
| − | <ol><font color="blue"><tt>Mass Balance Corrector </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt>OFF </tt></font></ol>
| |
| − | :* Remove XPSWMM references:
| |
| − | <ol><font color="blue"><tt>Read GIS XP Nodes </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt></tt></font></ol>
| |
| − | <ol><font color="blue"><tt>Read GIS XP WLL </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt></tt></font></ol>
| |
| − | <ol><font color="blue"><tt>Read GIS XP NETWORK </tt></font> <font color="red"><tt>== </tt></font> <font color="black"><tt></tt></font></ol>
| |
| − | :* Add scenarios/events if applicable
| |
| − | '''<<Video>>'''<br>
| |
| − | </ol>
| |
| | <br> | | <br> |
| | | | |
| − | =Feedback / Suggestions=
| |
| − | If you have any suggestions to be included in these pages, please email <u>[mailto::support@tuflow.com support@tuflow.com]</u>.
| |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | {{Tips Navigation | | {{Tips Navigation |
| − | |uplink=[[Main_Page| Back to Main Page]] | + | |uplink=[[Main_Page| Back to Wiki Main Page]] |
| | }} | | }} |